Almost every adult citizen receives some kind of income: wages, pensions, benefits, rent or dividends. Otherwise, he simply will have nothing to live on. The state takes a tax from most of these payments, which is regulated by Chapter 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It is called: “Personal Income Tax” or personal income tax. The online calculator on our website will help you calculate the amount of tax you need to pay to the budget on your income. But in order to correctly enter the data necessary for calculation, for example, the personal income tax rate, you need to understand something.
Personal income tax rates, benefits and deductions
Income tax in most cases has a flat rate of 13%, which does not depend on the type of income received or its amount. However, for non-residents of the Russian Federation there is an increased tax rate of 30%. There are also two more increased rates: 15 and 35%. Taxpayers should know in what situations they apply, because without this knowledge the 2019 personal income tax calculator will be of little help. He himself cannot determine what kind of income was received by the payer, and, as a result, say what amount is due for payment and what deduction can be counted on. So, 35% personal income tax must be paid to the budget by those citizens who:
- participated in competitions and games held for advertising purposes and won prizes in an amount exceeding 4,000 rubles;
- received interest on ruble deposits placed in banks in the Russian Federation if they exceeded the amount of interest calculated based on the Bank of Russia refinancing rate increased by 5%;
- received interest (coupon) on ruble bonds of Russian organizations issued after 01/01/2017, which exceeded payments over interest calculated based on the nominal value of the bond and the refinancing rate of the Bank of Russia, increased by 5% (starting from 01/01/2018);
- received interest on deposits in banks in Russia in foreign currency, if the amount of interest exceeds 9% per annum;
- saved on interest on ruble loans (credits), but exceeded the amount of interest calculated based on 2/3 of the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of actual receipt of income.
A 15% rate is applied when an organization pays dividends to its participants or shareholders who are not residents of the Russian Federation (clause 3 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The Tax Code of the Russian Federation also provides for the possibility of applying deductions for this tax and a number of benefits. A personal income tax deduction calculator is sometimes necessary when you need to determine how much the state will return for a purchased apartment or expensive treatment.
How and who calculates personal income tax
In most cases, it is up to the employing organizations to calculate the amount of personal income tax that must be withheld from payments in favor of the taxpayer and transferred to the local budget. After all, they are the ones who act as tax agents for personal income tax in relation to all persons to whom payments are made. But taxpayers themselves must sometimes also be able to calculate how much they owe the state if they received income on their own: they sold an apartment or a car, or received money for services from other individuals. Someone plans to receive a tax deduction for the past year. Then citizen payers will have to fill out and submit a 3-NDFL declaration with the correctly indicated amounts of income received and calculated tax. Organizations, in turn, must submit 2-NDFL certificates for employees. An online personal income tax calculator can help them with this; However, this program will not cope with deductions for children; you will have to calculate them yourself.
How to use the calculator
Let's look at a specific example of how to calculate personal income tax (online calculator with deductions for children 2019). Let’s imagine that we need to calculate income tax on the employee’s accrued salary of 30,000 rubles per month of work. An employee of the organization has two minor children, for whom, by virtue of Art. 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides a deduction of 1,400 rubles per person. Before entering the income amount into the calculator, you must subtract the benefit amount from it:
30,000 - 1400 × 2 = 27,200 rubles.
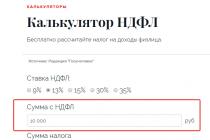
Thus, the 2-NDFL calculator with deductions online does not allow us to automatically subtract deductions, so we need to keep an eye on this. We see that the calculator has a choice of bets. Since we are calculating the salary tax, we choose a rate of 13%.
Below is a field in which you need to enter the taxpayer's estimated income so that the calculator can calculate the deduction from it. In our case, it is 27,200 rubles.

The calculator will instantly calculate the amount of income tax that needs to be withheld.

And finally, in the last field we see the total minus tax. This is exactly how much, in our case 23,664 rubles, needs to be handed over to the employee.

Obviously, using an online calculator is very simple. In this way, you can calculate deductions from any payments to employees or funds received by the taxpayer.
The online personal income tax calculator is quite easy to use. To calculate, you will need to select a bet and enter the required amount. The online personal income tax calculator from salary with deductions for children will do everything else automatically.
Step 2. In the “Amount” field, enter the data from which you want to calculate the tax (deductions are withheld in advance).

If you want to use a quick personal income tax calculation (online calculator) with deductions for children in 2019, you need to be careful, since the service does not take such a benefit into account. Thus, before calculating the required tax amount, the user needs to independently reduce the tax base by the standard deduction provided to him:
- 1,400 rubles each for the first and second child;
- 3,000 rubles each for the third and fourth;
- 12,000 rubles - for a disabled child.
Step 3. The calculation results in the calculator will be displayed automatically.

Using the service, you can also perform the reverse operation - calculate the taxable base from the amount received in hand. To do this, a known value is entered into the “Amount” line, the tax rate of 13 or 30% is determined, and then the tax base is calculated.

Finally, knowing the amount of deductions and the rate at which it was calculated, you can determine the original amount. To do this, indicate the desired percentage and enter the value in the “Tax Amount” field of the calculator.

What is personal income tax
- 251-FZ dated 07/03/2016;
- 281-FZ dated November 25, 2009;
- 229-FZ dated July 27, 2010;
- 279-FZ dated December 29, 2012.
Income tax is levied on income received by residents and non-residents of the Russian Federation from sources based in Russia and abroad (for residents only).
It is also used in the field of public procurement. Each contract that is concluded with an individual (with the exception of individual entrepreneurs and specialists engaged in private practice) necessarily contains the condition that from the amount that the customer must pay to the individual contractor, he deducts income and other tax payments. This is stated in Part 13 of Art. 34 44-FZ. In such a situation, remember that an online income tax calculator (with children) can do for you.
How much to pay
The following personal income tax rates have been established:
- 9% - rate for residents who received income in the form of dividends;
- 13% is the general tax rate for citizens of the Russian Federation (clauses 2-5 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- 15% is the rate for foreigners who received income in the form of dividends from Russian enterprises;
- 30% - rate for non-residents from sources - Russian organizations;
- 35% - from winnings and prizes from participation in various competitions and lotteries, as well as from income from bank deposits and on the basis of clause 2 of Art. 212 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Calculation of income tax using the formula
Personal income tax = tax base × tax rate.
The size of the tax base may change due to deductions: for children, property, social, etc.
For example, from a salary of 60,000.00 you need to pay 60,000.00 × 13% = 7800 rubles. If there is a child, then a deduction of 1,400 rubles is allowed. Then the deduction will be (60,000.00 - 1400.00) × 13% = 7618 rubles.
And if there were two children, and one of them is disabled, then the income tax will be: (60,000 - 1400 - 1400 - 12,000) × 13% = 5876 rubles.
Let us remind you that if you want to use the personal income tax calculator online with deductions for children, you must first subtract the deduction for each child from the full amount!
25.08.2019
Personal income tax is one of the taxes levied on the income of individuals. Payment can be made either by the employee himself or by his tax agent. The latter means an individual entrepreneur or organization that hires workers.
The agent's responsibilities include withholding taxes from wages and transferring them to the budget. Let's look at how the tax burden is calculated for residents of the Russian Federation from their income.
The current mechanism for calculating income tax on employee payments
The calculation occurs only in relation to those funds that the employer pays to his employee. He is not entitled to any other income that an individual receives outside of work.
In the Russian Federation, it is possible to assign several tax agents to an individual at once. For example, if he works in several places at once.
The taxpayer’s main point of payment to the budget of the Russian Federation is wages. Income tax is also imposed on sick leave benefits, bonuses, vacation pay, bonuses, etc.
An employee has the right to take advantage of preferential taxation by applying tax deductions.
When calculating personal income tax on an employee’s income, the tax agent is required to take into account the following benefits:
- , for example, if the employee has children (the amount of the benefit depends on the number of children);
- property, when received at the place of work (mortgage, purchase of apartments, construction of housing);
- social in relation to expenses for study and treatment.
You can use your right to deduct personal income tax only if the tax agent has received the necessary documents. First of all, this, as well as for property and social benefits, is a notice issued by the tax office and confirming these circumstances.
As soon as the employee brings a notification to the accounting department, the next salary will be subject to personal income tax, taking into account deductions.
If the employer did not take into account the benefits in the current year, then next year the employee can apply with documents to the Federal Tax Service for.
If the tax is not remitted on time, arrears arise. For each day of delay, you need to pay a penalty in the amount of 1/300 of the refinancing rate of the debt amount, from the 31st day of delay the share increases to 1/150. .
How to calculate from accrual - formula
In 2019, personal income tax on the accrued salary amount is calculated according to the following algorithm:
- all income related to the taxpayer’s remuneration in this organization is summed up. Income means salary, bonus and any other motivational payments;
- deductions to which the employee is entitled are calculated;
- from the amount received in the first paragraph, the value obtained when calculating deductible benefits is subtracted;
- The interest rate is determined depending on the status of the worker. A resident of the Russian Federation pays taxes at a rate of 13%, otherwise 30%;
- the due percentage is deducted from the amount taking into account deductions and sent to the federal budget;
- The employee receives his/her salary in hand minus the withheld income tax.
Formulas for calculating income tax from wages:
Personal income tax = (accrued wages – Deductions) * Rate.
Salary in hand = Salary accrued - personal income tax.
 Conditions:
Conditions:
A resident of the Russian Federation with three children must receive a salary. The accountant will have to calculate income taxes.
For a month of work, the taxpayer receives 70,000.
According to Article 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the first two children in a family can receive a benefit of 1,400 rubles. for each, and subsequent ones - 3 thousand rubles.
Calculation:
Total benefit for three children = 1400 + 1400 + 3000 = 5800.
Now we remove this amount from income: 70,000 – 5800 = 62,400.
The tax rate for residents of the Russian Federation is 13%.
Personal income tax = 62400 * 0.13 = 8346.
Salary on hand = 70000 – 8346 = 61654.
Important: if an employee’s salary for the current year exceeded 350 thousand rubles, then starting from the next month, deductions for children are canceled.
How to calculate the amount to be paid?
An ordinary employee employed at an enterprise or factory does not even think about how much money from his salary the accountant sends to the tax office.
To calculate, you need to know the rate, as well as the income that the employee receives in hand. Rates are regulated by Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, their full list:
- basic tax – 13%;
- for mortgage management founders – 9%;
- a person who is not a resident of the Russian Federation is obliged to pay 30% of any income from activities in the territory of the Russian Federation;
- in case of winning money, for example, in a lottery – 35%;
That is, an ordinary employee whose income comes from payments from the enterprise pays only 13%.
Formula for calculating personal income tax from the amount in hand without deductions:
Personal income tax = salary in hand / 0.87 – salary in hand
Formula for calculation with children's deductions:
Personal income tax = (salary in hand – Deductions * 0.13) / 0.87 – salary in hand.
Let's look at where such formulas come from using the examples below.
Example without deductions
 Conditions:
Conditions:
Dmitry got a job at the company in 2012. The employer promised him exactly 30 thousand rubles. in your arms.
Calculation:
100% in our calculations is the resident’s full salary.
With a bet of 13%, it turns out that he receives only 87%.
Thus:
- 30000/0.87 = 34482.75 – full salary.
- 34482.75 – 30000 = 4482.75 is paid by the tax agent from Dmitry’s salary.
You can check:
Personal income tax on accrued wages = 34482.75 * 13% = 4482.75.
Salary after tax = 34482.75 – 4482.75 = 30000 – this is exactly how much money the employee receives.
Example with deductions
Conditions:
Valeria got a job at the company in 1999. Her payable salary is 60 thousand rubles.
She is also the mother of two children who have not reached adulthood. That is, Valeria has the right to a tax benefit for children of 1,400 for each.
Calculation:
- Let's calculate the amount of deduction for children = 1400 * 2 = 2800.
- Let's calculate wages before tax = (60000 - 2800*0.13) / 0.87 = 68547.13.
- Personal income tax = 68547.13 – 60000 = 8547.13.
Let's check whether the calculation was carried out correctly:
- Personal income tax = (68547.13 – 2800) * 13% = 8547.13.
- Salary on hand = 68547.13 – 8547.13 = 60000.
Examples of calculations for 2019
Below are several examples of calculating income tax from various employee payments:
- wages with and without deductions;
- salaries to be paid.
How is it calculated from salary without taking into account deductions?
 Initial data:
Initial data:
Let's calculate the income tax of E. A. Akseeva. She earns 40 thousand a month, and in May 2019 she received a bonus of 10 thousand for good work.
Let's calculate how much she needs to send to the budget of the Russian Federation for the period January - May:
Calculation:
- 40000 * 4 + 10000 = 170000 earned by E. A. Akseeva for a given period of time, taking into account the bonus.
- 170000*0.13 = 22100 rubles – income tax that must be paid.
- 170000 – 22100 = 147900 – will be received in hand.
From the salaries of employees with children
It's fast and free!
The most lively interest is in income tax (NDFL). This is not surprising, since it is taxed on the income of any person. Let's talk about the methodology for calculating payroll tax, the amount of applied rates and benefits legally established for various categories of citizens.
As a mandatory federal tax, personal income tax is withheld from the salary of each employee, regardless of whether he is a full-time employee or temporarily works in a company on the basis of a concluded contract. To understand how to calculate income tax on wages, let’s get acquainted with the formula by which these calculations are made:
Personal income tax = NB * R ns / 100
where NB is the tax base,
R ns - % of the rate, separately determined for each payer.
The tax base is income - dividends or wages, consisting of charges:
- salary/tariff or amounts specified in the contract (on the provision of services or labor);
- bonus payments;
- allowances for length of service, qualifications, territorial location;
- temporary disability benefits.
All these charges are subject to personal income tax. But there are also exceptions. Amounts of payments not related to work activities are not subject to taxation: financial assistance (up to 4,000 rubles), alimony, scholarships, pensions, redundancy benefits, as well as business trip expenses.
The size of the tax base is affected by deductions that certain categories of payers are entitled to. In the article we consider only deductions related to the payment of wages, i.e. standard. The law establishes different amounts of deductions - 500, 1400 and 3000 rubles. A deduction of 500 rubles. provide:
- heroes of the USSR and the Russian Federation;
- studies of the Second World War and other wars;
- disabled people of the 1st and 2nd groups;
- victims of disasters at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant and Mayak Production Association.
A deduction of 1,400 rubles is issued by the parents of the first and second minor children. It is applicable until the annual income exceeds 280 thousand rubles. and is provided for a child under 18 years of age, or up to 24 years of age if he is a full-time student. For the third and subsequent children, the deduction is 3,000 rubles. To determine the amount of the deduction, the total number of children is taken into account, regardless of their age. The only parent (or adoptive parent) is given the right to a monthly double deduction for the child. The benefit is applied until the income reaches 280 thousand and ceases upon marriage the next month from the date of this event.
A deduction of 3000 rubles. relies:
- liquidators of the Chernobyl nuclear power plant and similar accidents;
- parents/guardians of a disabled child, as well as third, fourth and subsequent minor children;
- disabled people of the Second World War and other military operations;
- participants in nuclear weapons tests.
If the right to apply for several benefits arises, the highest value is taken into account. The number of deductions cannot be summed up; the only exceptions are deductions for children.
The tax rate applied today is 13% or 30%. The lower limit of 13% applies to the income of tax residents, i.e. citizens staying in the Russian Federation for at least 183 days over the previous 12 months. Almost all employees of Russian companies fall under this definition, although a similar status, depending on the length of stay in the country, can be assigned to any individual.

If this condition is not met, the payer cannot be a tax resident and pays personal income tax on income of 30%. Please note that the status is determined each time the salary is calculated and may change throughout the year.

Now that we have found out which payments are included in the taxable base, determined the rates and found out who is entitled to receive benefits, let’s consider the algorithm for calculating personal income tax. Necessary:
- calculate salaries taking into account all types of accruals;
- find out whether they are subject to taxation;
- determine the status of the payer - resident or not;
- establish his right to use the deduction;
- income is reduced by the amount on which tax is not withheld and deducted (if applicable);
- income tax is charged on the amount received, applying rates in accordance with the payer’s status.
For clarity, let's look at a few examples.
Example No. 1 - calculating income tax for an employee with three children
Dispatcher Ivanova I.I. got a job at the company, whose salary is 35,000 rubles, respectively, the income for the year will be 35,000 * 12 = 420,000 rubles. The employee has three children aged 26, 15 and 10 years. The deduction does not apply to the older child, but it is taken into account in calculating the tax. For the second - a deduction of 1,400 rubles, and for the third - 3,000 rubles. That is, Ivanova I.I. has the right to receive a monthly deduction in the amount of 4,400 rubles. (1,400 + 3,000 = 4,400 rubles) and pays personal income tax in the amount of 3,978 rubles. (35,000 - 4,400) * 13/100 = 3,978 rub. The deduction is valid until the annual salary exceeds 280 thousand rubles. In the example, this limit will occur after August, so from September the right to the benefit is lost, and the full amount of the salary will be taxed: 35,000 * 0.13 = 4,550 rubles.
Example No. 2 - tax calculation using double deduction
The company employs T.T. Rebrova, who has obtained guardianship for two children, 8 and 10 years old. As an unmarried woman, she exercises the right to double deduction. Rebrova’s salary is 30,000 rubles. per month, i.e. 360,000 rubles. in year. The threshold is 280,000 rubles. comes in September, which means that from October the salary is taxed in full.
The deduction is 1,400 * 2 * 2 = 5,600 rubles. for both children. The monthly tax amount will be 3,172 rubles ((30,000 - 5,600) * 0.13) from January to September, provided that the salary remains unchanged.
If Rebrova T.T. formalizes the marriage (for example, in May), then from June she loses the right to double deduction and the tax amount will be 3,536 rubles. ((30,000 - 2,800)* 0.13). In addition, the accountant needs to monitor that the benefit is applied until the threshold of 280 thousand rubles is reached. From October the tax will be withheld in full.
Example No. 3 - tax calculation for a person who is not a tax resident
Employee Petrov M.G., who arrived from abroad on January 20 after a 2-year absence, got a job at the company in May. Salary - 40,000 rubles. At the time of his appointment, he has non-resident status and his salary is taxed at a rate of 30%. The personal income tax amount will be 12,000 rubles. (40,000 * 0.3 = 12,000 rubles) Transition to resident status is possible after 183 days of stay in the country. This period will expire on July 22, therefore, from August the tax rate will be 13% and the tax amount will be 5,200 rubles. (40,000 * 0.13= 5,200 rub.)
On the issue of reporting and deadlines for its submission
In 2015, personal income tax is calculated and withheld when income is calculated, i.e., having calculated the salary, the accountant transfers the tax amount to the budget no later than the day the salary is issued. From 2016, it will be possible to transfer personal income tax the next day after the payment of salaries. At the end of the year, a certificate of form No. 2-NDFL is drawn up for each employee of the company. Entrepreneurs report on income tax by annually submitting a declaration of Form 3-NDFL. This information is submitted to the Federal Tax Service once a year before April 1 of the year following the reporting year. From 2016, it is planned to introduce a quarterly reporting system for the calculation and payment of income tax.
Failure to pay, late payment of tax or late reporting will, of course, result in penalties. A bill is under development that proposes impressive measures: the fine for failure to submit or late submission of tax calculations will be 5,000 rubles. for each month from the date established by law for submitting the report. It is possible to block all company accounts. Paying only part of the tax will entail a fine of 20% of the unpaid amount, and for a repeated similar violation the fine will be 40%.
Individuals who receive income from work or business activities are required to contribute a certain portion of their income to the state treasury. Transfers can be made both by the payers themselves and by their tax residents, which include entrepreneurs or organizations. The accountant of the enterprise is obliged to calculate payments on a monthly basis based on the salary of each employee, and the organization must promptly transfer them to the state fund that collects taxes. There are a lot of nuances in the question of how to calculate personal income tax from a salary, which we will talk about later.
Basic tax rate
The employer calculates tax payments based on wages and other income accrued to the employee in this organization based on the result of work activity. A citizen can be on the staff of several companies at once. At the same time, each tax agent calculates deductions and draws up a reporting form independently. Payment of personal income tax is mandatory for all employees, regardless of whether they work temporarily or are on staff. The salary specified in the employment contract with the employee is taken into account.
According to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, taxable:
- wage;
- allowances (qualification, territorial, for length of service);
- all types of bonus payments;
- benefits for temporary disability (sick leave);
- vacation pay.
Financial receipts that are not related to the work activity of an individual in a given organization are not subject to taxation . Such income includes:
- child support;
- pensions;
- student scholarships;
- severance pay paid to employees dismissed due to staff reduction;
- financial assistance (if its amount does not exceed 4 thousand rubles);
- travel expenses.
The tax base for personal income is calculated taking into account the tax benefits to which the employee is entitled. The legislation of the Russian Federation provides for preferential deductions of four types: standard, social, professional, for the acquisition of real estate. The first one is taken into account without fail when calculating personal income tax. The employee has the right to receive other payments only if he presents documentary evidence of the expenses incurred. After providing the necessary documents, the accountant will be able to determine the amount of the deduction and carry out the necessary calculations. The law provides for two ways to receive personal income tax payments. An employee can act through the accounting department of the enterprise where he works or submit an application to the tax authorities.
Tax deduction - basic concepts
The law provides tax benefits for certain categories of citizens. For example, standard deductions are available to employees with dependent children. In addition, the tax base may be reduced:
- heroes of the Soviet Union and Russia,
- participants of the Second World War and military operations,
- citizens with disabilities,
- victims of the Chernobyl explosion.
The maximum tax deduction for Russians is limited to 3,000 rubles. You can count on receiving it:
- parents, adoptive parents or guardians with three or more minor children or a disabled child;
- specialists and volunteers who took part in the liquidation of the Chernobyl accident and other similar events;
- disabled people of WWII or later military operations;
- participants in nuclear tests.
The amount of deductions is not cumulative, with the exception of benefits provided in the presence of children. If a citizen is entitled to several deductions, the calculation is made based on the larger number.
Formula for calculating income tax
Now, knowing which payments are subject to taxation, let’s create a general algorithm for calculating personal income tax. First, you need to calculate your salary, including all the necessary payments. After this, you need to exclude those amounts that are not subject to taxation. The remainder will be the taxable base. To determine the tax rate, you need to find out the payer’s status, that is, whether he is a resident or not. Then, from the base salary, deductions are made to which the employee is entitled. Based on the remaining funds, the tax payable is calculated.
The formula for calculating income tax on wages (taking into account the tax deduction) looks like this:
N=(D-V)×S
Here is the tax amount ( N ) is the difference between labor income ( D ), subject to personal income tax and tax deduction ( V ), multiplied by the base rate, ( S ) adopted in Russia.

Currently, the “income tax” on wages is levied at 13%. If we are talking about accounting for the income of foreigners (non-residents of the Russian Federation), it is 30%. This issue will be discussed in more detail a little later.
How to calculate income tax on salary if you have a child
The deduction for one or more children is determined by tax law, and its size depends on the number of dependents. Both parents, as well as guardians and adoptive parents can take advantage of the benefits. The calculation procedure and amounts of payments are reflected in Art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The size of the standard preferential deduction is: for the first and second child - 1400 rubles, for the third – 3000 rubles. Having a disabled person on their hands, parents have the right to claim a deduction in the amount 12 thousand rubles. Guardians, trustees and adoptive parents will receive only half, that is 6000 thousand rubles
It should be remembered that the money is not returned to the taxpayer; personal income tax is simply not withheld from this amount. Not only parents of minors can reduce their tax base. The tax deduction is also applicable for parents whose children have reached the age of 18, but are students, graduate students or cadets. The legal age limit in this case is 24 years. Both parents are entitled to a mandatory tax deduction and receive it at the same time.
To understand how personal income tax is calculated on wages for parents of one or more children, let’s give an example. With a salary of 30 thousand rubles. monthly, an employee who has two dependent children aged 5 and 12 years has a tax deduction in the amount of 2800 rubles. Using the following formula - N=(D-V)×S, Let's calculate the amount of basic tax as follows:
(30000 – 2x1400)×13% = 3536 rub.
Please note that the child tax credit is not permanent. After the amount of annual income reaches 280,000, a citizen is required to pay tax on all income. In this case, the right to deduction is valid from January to September; in the remaining months, the salary is taxed in full.

Example of income tax calculation
Let's consider another example, for cases where an employee has the right to double tax deduction. An unmarried employee of the company, who has taken custody of two young children, has a salary of 40,000 rubles. Since the citizen is not married, she receives tax benefits. Its amount will be:
(1,400×2)×2 = 5,600 rub.
The monthly tax will be calculated as (40000 – 5600) × 13% = 4,472 rubles. At the same time, the accountant needs to take into account that the threshold of 280 thousand will be reached in July. If the employee gets married in May, then she will lose the right to double the deduction in June.
Calculation of personal income tax for foreigners
Citizens of other states operating on the territory of the Russian Federation are also required to pay tax contributions. To understand how to calculate income tax on the salary of an employee who comes from countries far and near abroad, you need to determine their status. According to Art. 207 (clause 2) of the Tax Code, citizens who have been on the territory of the Russian Federation for a total of no more than 183 days within 12 (consecutive) months are recognized as non-residents. They are subject to a tax rate of 30%. The status is not permanent; it may change throughout the year; this must be taken into account when calculating salaries.
After amendments were made to the Tax Code, the concept of “special status” was introduced when calculating personal income tax for foreign citizens. It is assigned to the following categories:
- highly qualified specialists,
- residents of countries included in the EAEU,
- participants in the resettlement program for compatriots,
- citizens working under a patent,
- refugees.
Let us give an example of how the salary of an employee who arrived from abroad after a two-year absence is calculated. In this case, the calculation takes into account the employee's tax status. Until the expiration of the due period, that is, 183 days, the employee remains a non-resident of the Russian Federation and the tax rate for him is 30%. With a salary of 40 thousand rubles. Personal income tax is 12,000 rubles. After 26 full weeks the rate will decrease to 13%.
Transfer deadlines and penalties for violation
Tax collections from income from the labor activities of employees are transferred to the budget the next day after wages are issued. If the transfer is made to a personal bank account, issues with timing, as a rule, do not arise. But some organizations still practice payment through the cash register, that is, they hand out cash to the employee. In this case, the starting point is the day when the funds were withdrawn from the company’s account.

Government organizations pay wages to employees twice a month. And here questions may arise about how personal income tax is calculated. Tax is not deducted from the advance payment; it is levied on the total amount only upon final payment. In a situation where an employee quits before the advance payment has been worked out, it is not possible to recover the payment. The employer is obliged to inform the tax authorities about this. Next, the personal income tax debt is transferred to the former employee, and he pays it off on his own.
It also happens that an organization or entrepreneur misses the deadline for paying taxes to the budget. The legislation provides for administrative liability for such violations. The fine is 20% percent of non-payment, in addition, penalties will be accrued daily on this amount, the amount of which is calculated based on the refinancing rate and is equal to one three hundredth. If the deadlines are violated again, the penalties will double. We are talking specifically about transferring funds to a state fund. Even if the tax agent collected funds from the employee, but they were not received as intended, a fine will be charged to him.
When calculating personal income tax, it should be taken into account that there is a sequence of deductions established by law. If an employee has other financial obligations, for example, to pay alimony or fines, income tax is collected first from his earnings, and only then everything else.