Specifics of management accounting at the enterprise assumes that each organization itself establishes a list of material costs and fixes it in its own accounting policy. Accounting for material costs at the enterprise at the same time is unified on accounts 20-29 of the plan established by the Ministry of Finance. Therefore, there are certain methods for calculating material costs according to the balance sheet and on their basis to derive the main coefficients for evaluating the company's activities.
Material costs: formula for calculating the balance
Let's look at the regulated reporting forms and determine how to find material costs in the balance sheet.
Its asset looks like this:
As you can see, there is no line for material costs in the balance sheet, although there are several accounts for their calculation in accounting:
- 20 main production
- 21 accounting of semi-finished products
- 23 ancillary production
- 25 and 26 - overhead and business expenses
- 29 service farms
According to PBU 4/99, accounts 25 and 26 have no balances, and are closed at the end of each reporting period. It turns out that for material costs, the calculation formula is based on the balances of accounts 20-23, 29, and is reflected in the balance sheet in the line “Inventories” of the II section of the Asset. It is this position that is the main one in the construction of cost forecasts, costing and analysis of efficiency. It is generally accepted that material costs in the balance sheet are a line with code 1210, if you use regulated coding, or “Inventories” by its name in the form 0710001 according to OKUD.
Analysis of the efficiency of the enterprise by costs
To estimate the costs of the company, the following values are used:
- Profit per ruble of material costs
The amount of profit per 1 rub. MZ is the main indicator of the efficiency of material turnover in a particular production. It is calculated as the ratio of profit from the main activity to the amount of material costs incurred. For example, if you need to calculate this parameter for reporting for last year, you need to take the profit / loss from sales on line 2200 of the income statement
and correlate it with the amount of reserves in section 4 of the notes to the balance sheet:
Please note that in this section, stocks should be reported by groups or types, for example: raw materials, goods for resale, basic materials, finished products, "incomplete". Thus, it is possible to calculate the profit per 1 ruble of material costs in the context of any expense of the main industries.
- Product material consumption parameter
Material consumption is calculated as the ratio of material costs to output products in its cost estimate. The calculated value characterizes the volume of MZ per unit of manufactured product. When evaluating the dynamics of the indicator, its decrease is assessed positively, and its growth is negative.
- The value of material yield per unit of product
If material consumption is the ratio of material costs to the cost of output, then material productivity is determined as the result of dividing the cost of production of a batch of products by the materials spent on its creation and other material costs. This parameter characterizes how many products were obtained in the cost estimate from each ruble of the consumed resource.
- The share of material costs in the cost
The proportion of material costs to the total cost shows the dynamics of material consumption, and if for profit per 1 ruble of material costs the formula is Pr / MZ, then to calculate the specific weight, it is necessary to correlate MZ / Cst full, where Cst full is the total cost of production.
- Material cost factor
All the main indicators in dynamics can be expressed through coefficients that will clearly show the growth / growth or decline in output and / or costs, therefore, the calculation of material costs is carried out both in absolute and in relative terms. The correct setting of statistical research will allow you to understand how wisely the business is being conducted and whether there are resources for profit growth. An increase in material costs indicates not only an increase in output, but also an inefficient use of resources and an increase in the cost of a unit of product. For the coefficient of material costs, the calculation formula is usually used as follows: they relate the actual value of material costs to its planned parameter. The resulting value characterizes how economically resources are used, whether there is an overrun. The coefficients of total material costs can be greater than one, then economists will record overspending, but if the indicator is less than one, resources are used sparingly. Accounting for material and labor costs in dynamics is carried out precisely from the point of view of management efficiency.
- Profitability of material costs
If we talk about the profitability of the Ministry of Health, then this indicator shows how much real income is received from 1 invested ruble of material resources. As a rule, for its calculation, the value is correlated net profit and total material costs.
ROI based on financial statements
Accounting for material and labor costs involves monitoring the effectiveness of their use. Let's look at an example financial statements of the Passive company, what will be the profit per ruble of material costs, the formula for its calculation and how to operate with the obtained coefficients in practice. Here is form 0710002 from a pulp and wood pulp company.
Calculating Rcosts using the VP/Cst formula, we obtain a coefficient of 0.25 (200/800), which shows that for each ruble invested in pulp production, the company receives 25 kopecks of gross profit, and last year this value was similar with a gross profit of only 80 thousand roubles. It turns out that the cost recovery has not changed with the increase in production.
Assessing the effectiveness of sales by the formula:
Sales profit (line 2200)/(Cst(line 2120)+Comm.exp.(2210)+Exp.management(line2220))
We get: in 2014 and 2015, the coefficient is 0.14 - the efficiency is the same.
Accounting features imply that all firms have the right to independently determine the list of material costs and reflect it in their accounting policies. In accounting, accounts from 20 to 29 are provided for accounting for material costs. In the balance sheet, line 1210 is provided specifically for their reflection.
Since the list of material costs in accounting is determined by all firms themselves, character traits Accounting for such expenses will be directly dependent on the characteristics of the activities of a particular company.
The unity of the approach to their accounting lies only in the fact that material costs, being a component production costs, are taken into account on accounts from 20 to 29.
General calculation formula
The cost formula will be as follows:
Mz \u003d Zmdt + Zte + Zsip + Zstop + VATm.
- Zmat - the cost of materials that are required for the implementation production process;
- Zte - expenses for energy and fuel and lubricants;
- Zsip - costs for the acquisition and use of natural raw materials;
- Zstop - the cost of services performed by third parties;
- VATm - the amount of VAT paid by the supplier.
Material costs on the balance sheet
Consider unified forms reports and establish how to find material costs in the balance sheet.
To account for material costs in the balance sheet is not provided for special. lines. But, despite this, accounting provides several accounts for their accounting: 20, 21, 23, 25, 26 and 29.
Analysis of material costs
Material costs are one of the main cost items of any production process. In this regard, they are usually under the close supervision of employees of the economic planning department. After all, it is not enough to calculate material costs, it is also important to analyze the results obtained.
One of the main coefficients, which is calculated using the indicator of material costs, is the consumption of materials. To calculate it, it is necessary to divide the material costs by the total cost of manufacturing goods. This indicator reflects how much is the share of material costs in the total cost of goods.
Another approach to determining the material consumption is the calculation of the share of material costs in the production of products. In this case, material consumption is the ratio of material costs to the number of manufactured goods in value or physical terms.
Raise this indicator means that the amount of material costs per product has increased, and the profitability of goods has decreased. That is why the management of material intensity is the key to reducing costs and increasing the profitability of production.
Separately, you can determine the profit per 1 rub. material costs. This can be done using the formula:
- Pmz - profit that falls on one ruble of material costs;
- P - income from the sale of goods;
- MZ - the amount of material costs that were committed for the manufacture of goods.
Material cost ratio
The coefficient of material costs is calculated by the formula:
Kmz \u003d MZf / MZp.
- MZf - actual expenses of a material nature;
- MZp - planned indicators of material costs, which are calculated on the actual volume of production.
An enterprise with large volumes of production must carefully control its material costs, for which accounting uses special indicators. The efficiency of the use of material resources can be determined through several general indicators, including:
- material return,
- Material consumption,
- Coefficients of material costs,
- Profit per ruble of material costs,
- The share of material consumption in the cost of products.
Formula of material return on balance
The formula for the return of materials on the balance sheet involves finding the ratio of the cost of manufactured products (volume) to the amount of material costs incurred for its release.
Material return formula general view as follows:
Mo = SP / MZ
Here, Mo is the material yield index,
JV - manufactured products, revenue (in physical or value terms),
MZ - material costs of production.
The balance sheet material yield formula assumes information from financial statements. In this case, the value of material costs is taken from the application to balance sheet(form No. 5, first line), and the value of revenue from the income statement (form No. 2).
Practical use of material recovery
The material yield index is considered dimensionless, the higher the coefficient calculated by the formula, the less material is required to produce the same amount of products.
The balance sheet formula for material productivity has one feature - the cost of production is measured not in sales prices, but in the prices of materials spent on its production. Otherwise, the indicator of material efficiency will not be so informative, since it will depend on changes in the rate of return and product prices.
The balance sheet material yield formula is most often used when comparing the indicator with past periods or when comparing with the material yield value of similar companies.
The rate of return on assets is increased through the introduction of advanced technologies (technology), increased control of the careful use of materials.
The value of the material return index
If the enterprise is able to competently optimize the material efficiency index, it becomes possible to obtain greater profit for reporting period. The balance sheet material yield formula allows you to analyze and characterize the resources that the company has.
Material output has an inverse indicator, called material consumption. These indicators can be considered as general values of the efficiency of the use of resources that are used in accounting for the production of an enterprise's products.
In the case of an increase in material efficiency, they speak of positive dynamics, since the cost is minimized and more competitive products are produced.
Examples of problem solving
EXAMPLE 1
| Exercise | The company has the following indicators on work for 2 periods: Gross output value In the reporting year - 254,000 thousand rubles, The planned value is 272,000 thousand rubles, The amount of material costs Per reporting year- 139,000 thousand rubles, The value according to the plan is 135,000 thousand rubles. |
| Solution | The formula for material yield in terms of balance for solving this problem looks like this: Mo = SP / MZ Mo (reporting period) \u003d 254000 / 139000 \u003d 1.83 rubles (that is, for each ruble of material costs, the enterprise received a profit of 1.83 rubles) Mo (plan) \u003d 272000 / 135000 \u003d 2.015 rubles. for every ruble of production, the enterprise plans to receive Conclusion. We see that the management of the enterprise is planning to increase the yield of materials from 1.83 rubles to 2.15 rubles. |
| Answer | Mo (otch) \u003d 1.83 rubles, Mo (plan) \u003d 2.15 rubles. |
The composition of material costs includes the costs of raw materials and basic materials that are part of the manufactured product, forming its basis, or that are necessary in the manufacture.
Material costs are calculated by the formula
MZ \u003d C o.m. + C tr. - With exhaust, (1)
where MZ - material costs for one part, rub.;
With o.m. - the cost of basic materials;
Since t.r. - the cost of transport and procurement
expenses, thousand rub.;
From otkh. - cost of waste.
MZ \u003d 9.216 * 16.1 + 9.216 * 16.1 * 1.3-0.262 * 8.6 \u003d 192.88 thousand rubles.
1.2 Calculation of the cost of basic materials.
The main materials are those materials from which products are directly manufactured (metal grade).
Cost of basic materials calculated by the formula
Z o.m. = C h * m h *TO tr -C about * m about (2)
Where C s, C o - respectively, the price for 1 kg of workpiece and waste,
C s \u003d 9.216 thousand rubles, C o \u003d 0.262 thousand rubles,
m s, m o - respectively, the weight of the workpiece and the weight of the waste,
m s \u003d 16.1 kg, m o \u003d 8.6 kg.
K tr - coefficient of transport costs (K tr \u003d 1.3).
Z o.m. \u003d 9.216 * 16.1 * 1.3-0.262 * 8.6 \u003d 109.63 thousand rubles.
1.2 Calculation of the cost of auxiliary materials.
Auxiliary materials are used for the production and operational needs of the enterprise and do not form the material content of manufactured products.
Auxiliary materials include: coolants, lubricants and cleaning materials. The cost of auxiliary materials is taken on an aggregate basis in the amount of 25% for the main materials.
Z w.m. = W o.m .*0,25 (3)
Z w.m. \u003d 109.63 * 0.25 \u003d 47.67 thousand rubles
1.3 Calculation of costs for energy resources.
Electricity costs for production purposes are determined by the formula:
Z email = C email * W forces / AT 4)
where C el is the tariff for 1 kWh of electricity, C el = 0.1 thousand rubles;
W forces - the need for power energy, W forces \u003d 48000 kW / h;
B - release program, B = 8000 pcs.
Z email = 0.1*4800 /8000=0.6 thousand rubles
Compressed air costs are determined by the formula:
Z szh = C szh *R sJ / AT 5)
where Ts szh - the tariff of 1 m 3 of compressed air, Css = 0.5 thousand rubles;
P szh - the need for compressed air, P szh \u003d 51000 m 3;
B - release program, pcs.
Z szh = 0.5*51000 /8000=3.19 thousand rubles
Water costs for technological purposes are determined by the formula:
Z in = C in * Q in / AT 6)
Where C in is the tariff for 1 m 3 of water, C in \u003d 1.3 thousand rubles;
Q in - the need for water, Q in \u003d 22000 m 3.
Z in = 1.3*22000 /8000=35.75 thousand rubles
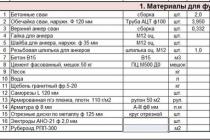
The results of the calculation of material costs are summarized in table 1.
Table 1
2 Calculation of wages of production workers, deductions and tax from it
Calculation wages production workers, deductions and tax from it is calculated analytically.
Salary - payments monetary form worker for his work.
The salary of the main workers consists of two parts:
basic salary;
additional salary.
Salary is calculated according to the formula
where ZP is the wages of production workers per
detail, rub.;
ZPO - the basic wages of production workers one part, rub.;
ZPd - additional wages of production workers one part, rub.
According to formulas (8) and (11)
The previous article discussed the structure production cost products, where the costs were grouped by costing items. Recall that all the costs that form the cost can be grouped in connection with their economic content on the following elements:
- material costs (minus the cost of returnable waste);
- labor costs;
- deductions for social needs;
- depreciation of fixed assets;
- other costs.
First of all, consider the most significant of the cost items - material. Their share in the total cost is 60-90% and therefore they should be addressed Special attention. First, let's break down what they include, and then talk a little about accounting for them.
The material costs of the enterprise include:
- the cost of raw materials and materials purchased on the side;
- the cost of purchased semi-finished products and components;
- the cost of works and services performed by a third-party organization;
- the cost of fuel of all types purchased from outside;
- the cost of energy resources of all kinds;
- commission fees, payment for brokerage and other intermediary services.
All of the above elements are included in the cost structure, minus the cost of waste sold. Waste should be understood as the remains of raw materials, materials, semi-finished products, heat carriers, etc., formed during the production process, which have completely or partially lost their consumer qualities. They can be sold at reduced or full price, depending on their further use. Material resources that, according to the established technology, are transferred to other workshops and used as a full-fledged material for the production of other products, do not belong to returnable waste.
The material costs of the enterprise should include all purchased materials used to ensure the technological process, including packaging of products and materials used for other production. household needs(maintenance and operation of equipment, buildings and structures, testing, control, etc.). This also includes fixtures, inventory, laboratory equipment and other means of labor not classified as fixed assets.
Big influence the cost of material resources is affected by the price of their acquisition (without VAT), margins (surcharges), commissions to supply and foreign economic organizations, the cost of brokerage services and commodity exchanges, customs duties, payment third parties for storage, transportation and delivery. In order to establish the optimal price of products, and increase profitability, enterprises should conduct a thorough analysis of the prices of materials and services offered by different suppliers. In addition, to improve the efficiency of the use of material resources, it is necessary to introduce low-waste, resource-saving technologies. An important point, affecting the cost, is the completeness of the collection and further use of waste, their reasonable assessment.
One of mandatory conditions rational use materials - rationing of material costs. The consumption rate is the maximum allowable amount of raw materials, materials, fuel spent on the manufacture of a unit of output of the established quality, the performance of technological operations. At present, the system of standards is a set of scientifically based labor, material and financial norms, the procedure and methods for their formation, updating and use in the development of long-term and current plans.
There are four methods for controlling the use of raw materials and materials:
- Documentation.
- Partition cutting.
- Party account.
- inventory method.
The documenting method is used at all enterprises, it is based on the registration of separate documents for all cases of deviations in the consumption of materials from the established standards.
The batch cutting method is widely used in the machine-building industry. Its essence lies in the preparation of cutting sheets (account cards) for each batch of material. They indicate the amount of materials, blanks and waste that should be received, and the actually received waste and blanks, then these values are compared with the normative ones, thereby saving or overspending is determined. AT account card indicate the reasons for deviations and the persons responsible for cutting.
With batch accounting, batches of raw materials and materials that are homogeneous in terms of technological parameters are formed. All batches are stored separately, and each is assigned its own number. These lot numbers should henceforth appear on all primary documents accounting of materials, which allows them to be attributed to specific types of products.
With the inventory method after the expiration certain period time (usually a month) an inventory of unused raw materials and materials is made. The inventory method can be characterized by the formula:
P \u003d He + P - Ok, where
R- the cost of the materials used;
He- the cost of the initial balance of materials;
P- receipt of materials per month;
OK- the cost of the final balance of materials.
Enterprises consume a huge amount of various material resources. Managers need to constantly monitor compliance with standards and the dynamics of actual material costs, since these costs have the greatest impact on the amount of profit received, and saving materials is the most important factor improve production efficiency.
That's all I wanted to say about material costs. In the following articles, we will consider other types of costs included in the cost of production.
If you have any questions you can ask them