Before considering the issues of ensuring the economic security of the industry national economy, apparently, it is necessary to analyze its features, which manifested themselves in the process of creation, and manifest themselves in the process of functioning.
First of all, this is a mixed administrative-market character, which is manifested in the fact that the industry operates mainly in the commodity markets, and management is carried out within a strict administrative framework - up to the intervention of the Russian Government.
As a feature, we note specialization within the specifics of the product range, which limits the possibility of strengthening market security through inter-industry diversification.
We also note that the fundamental feature of the industry is the absence of strategic financial goals, due to the macroeconomic model, that is, the mechanism of income redistribution is included in the tax system at the macro level. There is also a contradiction between the nature of operations and the impossibility of their execution, due to legislative restrictions on the performance of business operations by the administrative bodies exercising management.
It should be borne in mind that the industry is distinguished by the fundamental impossibility of monopoly use of budgetary resources; possible options for using budgetary funds are the provision of budgetary guarantees for servicing targeted loans.
The functioning of the industry is carried out in conditions of fierce competition with similar industries on a global scale, which increases the threat to economic security, and also increases the need to regulate the conditions for the functioning of industry entities at the macro level.
In addition, there is an urgent need for highly qualified specialists with real restrictions on their wages, which entails the use of the services of professional market participants and the provision of certain rights in return for the use of part of the allocated funds for their stimulation.
The listed features of the branch of the national economy significantly distinguish it both from the functioning of a company with a purely market orientation, and from an administratively oriented organization. Consequently, ensuring the economic security of the industry should be carried out on the basis of a synthesis of administrative and market management methods, and this, in turn, means the need for compromise solutions.
Let us now consider economic security as a separate concept, which is necessary both for the conceptual apparatus and for developing a concept for ensuring the economic security of a sector of the national economy. The category of economic security itself is quite new and little used in management theory and practice. The traditional understanding of security is most often reduced to national security, which is defined as the security guaranteed by constitutional, legislative and practical measures and ensuring the national interests of citizens and the country.
A significant number of definitions of the concept of "economic security" and the semantic meanings that the authors of the research put into it indicate that, firstly, there is a great interest in this problem, and secondly, about its relevance, and also that as yet there is no single categorical judgment. Apparently, this is precisely why the "State Strategy for the Economic Security of the Russian Federation" lacks a single definition of economic security.
This indicates that research in this area will be continued, and a final definition that satisfies everyone, on the basis of which a general concept will appear that reflects the goals, objectives, structure, functions, sets of tasks that ensure economic security in the country, its national economy and various institutions - a matter of the near, but the future. It is interesting that the concept of "economic security" entered the economic life of the country as market relations were established, and, in our opinion, is a consequence of the development of these relations. In any case, it seems that we also have the right to our own judgment on this issue, especially since the object of our research is significantly different from the objects of research of most authors.
Among the developments carried out at the state level, one should especially highlight the "State Strategy for the Economic Security of the Russian Federation", approved by Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of April 29, 1996 No.
State strategy develops and concretizes the provisions of the National Security Concept of Russia, taking into account national interests in the field of economy. Its goal is to ensure such development of the economy, which would create acceptable conditions for the life and development of the individual, the socio-economic and military-political stability of society and the preservation of the integrity of the state, successfully countering the influence of internal and external threats.
The state strategy includes:
- Characterization of external and internal threats to the economic security of the Russian Federation as a set of conditions and factors that create a danger to the vital economic interests of the individual, society and the state; identification and monitoring of factors that undermine the stability of the socio-economic system of the state.
- Determination of criteria and parameters that characterize national interests in the field of economy and meet the requirements of Russia's economic security.
- Formation economic policy, institutional changes and the necessary mechanisms to eliminate or mitigate the impact of factors that undermine the stability of the national economy.
The implementation of the mentioned State Strategy should be carried out through a system of specific measures implemented on the basis of qualitative indicators and quantitative indicators - macroeconomic, demographic, foreign economic, environmental, technological, etc.
The Government of the Russian Federation, in turn, adopted the Decree "On Priority Measures for the Implementation of the State Strategy for Economic Security of the Russian Federation." It contains a list of measures to prevent threats to economic security:
- reduction of property differentiation of the population in order to ensure a relative balance of social interests;
- prevention of further deformation of the structure of the Russian economy, including:
- 2.1 reducing the level of uneven socio-economic development of regions;
- 2.2 identification and elimination of the causes leading to the criminalization of society and economic activity.
A special place in the Strategy is given to the economic priorities of the country, among which are noted: the strategy of the economy, structural transformations, financial and monetary relations, budgetary priorities, scientific and technical policy, agricultural policy, the elimination of crime, regional policy, foreign economic activity, relations with the CIS countries , commodity policy.
Comparing these priorities with conceptual foundations economic security of a particular industry, one can be convinced of their almost complete compliance. This indicates that the industry itself is a comprehensive tool for ensuring the economic security of the country (in this case, the economy of the pipeline transport industry). In the vast majority of developments and publications devoted to the problem of economic security:
From the analysis of literary sources and developments devoted to the problem of economic security, one general conclusion of interest to us in the context of our study can be drawn. The authors choose the state, society, subject of the federation (region), firm, family, individual as the main objects in the developments, and measures to improve infrastructure systems, such as, for example, scientific and technical, economic, financial , political, social, informational, legal, military, environmental, cultural, criminological, etc.
It is noteworthy that in none of the developments on economic security known to the authors, none of the above infrastructure systems is chosen as an object, which is explained by the obvious insufficient elaboration of the problem of economic security, and at the same time determines the prospects for studying this problem. What has been said again and again convinces us of the relevance of the chosen topic of the study, devoted to the economic security of the sector of the national economy of Russia.
Using the above approaches to the definition of the concept of economic security, we will try to formulate one for the sector of the national economy. In our opinion, it may look like this: the economic security of a branch of the national economy is understood as the economic protection of the branch and the interests of its participants from external and internal threats, which makes it possible to reliably preserve and effectively use its economic potential to fulfill its mission.
The mission of the industry is to meet the needs of the market for the products of the industry by improving technological processes, based on reducing the volume of budget financing, as part of the state strategy for the development of the national economy. This means that if the industry is in a state of development, then the main criterion for the effectiveness of its activities are precisely the factors listed above.
It should be noted that the need to address the problem of economic security is determined by the presence of external (exogenous) and internal (endogenous) destructive factors (threats) in relation to the industry and, as a result, the entire national economy. External destructive factors, for example, include:
- economic and political instability;
- imperfection of the legislation;
- the well-known unwillingness of potential investors to interact with the industry;
- sabotage activities of various subjects;
- dynamic mobility of commodity markets;
- lack of reliable information for investors about the state of the market and issuers of securities, etc.
Among the internal factors that generate threats that are fraught with risks of failure situations, include:
- limited opportunities to insure business risks;
- lack of clear technologies for the interaction of professional participants in the commodity market in Russia;
- complex system of relationships between industries.
It should be said that the concept of "economic security" is closely related to such concepts as:
- Monitoring the state of the industry as a tool for predicting, if possible - preventing, as well as minimizing losses in the event of failure situations.
- Rational motivational schemes of economic incentives for enterprises in the industry, allowing to take into account and satisfy their economic interests in the field of core activity.
- Regulatory support for the activities of enterprises in the industry, which enables them to exist, operate and develop in relatively stable and predictable conditions within a foreseeable time interval, as well as in conditions of relative external economic stability.
Links
- Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of April 29, 1996 No. 608 "On the State Strategy for the Economic Security of the Russian Federation (Basic Provisions)".
- State strategy of economic security of the Russian Federation. // Safety. 1994. No. 3.
- Business and security. Explanatory terminological dictionary. - M.: "Beck", 1995., p. 336.
I . Purpose and objects of the State strategy of economic security of the Russian Federation
The Russian Federation is going through a difficult historical period in the formation of new socio-economic relations. The transition to new forms of public administration takes place in conditions of constant deficit and inconsistency legal framework regulating economic relations, the backlog of legislation from the processes actually taking place in society.
In international relations, Russia is faced with the desire of industrialized countries, large foreign corporations to use the situation in Russia and the member states of the Commonwealth of Independent States in their economic and political interests.
All this makes it especially relevant to purposeful activities to ensure the economic security of the country and its citizens on the basis of a unified state strategy.
I. Purpose and objects of the State Strategy for Economic Security of the Russian Federation
The State Strategy for the Economic Security of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the State Strategy) is an integral part of the national security of the Russian Federation as a whole and is focused on the implementation of the economic transformations being carried out in the Russian Federation in the next three to five years.
The State Strategy develops and specifies the relevant provisions of the developed concept of national security of the Russian Federation, taking into account national interests in the field of economy.
The purpose of the State Strategy is to ensure such development of the economy, which would create acceptable conditions for the life and development of the individual, the socio-economic and military-political stability of society and the preservation of the integrity of the state, successfully countering the influence of internal and external threats.
Without ensuring economic security, it is practically impossible to solve any of the tasks facing the country, both domestically and internationally.
The implementation of the State Strategy should create the necessary conditions for achieving the overall goals of national security. In particular, ensure:
protection of the civil rights of the population, raising the level and quality of its life, guaranteeing social peace in the country and tranquility in society;
effective solution of internal political, economic and social tasks based on national interests;
active influence on the processes in the world affecting the national interests of Russia.
The foreign economic orientation of the State Strategy lies in the effective implementation of the advantages of the international division of labor, the sustainability of the country's development in the context of its equal integration into world economic relations, and the prevention of Russia's critical dependence on foreign countries or their communities in vital issues of economic cooperation.
Despite the complexity of the experience transition period, Russia has ample opportunities to ensure its economic security, maintain the political and military status of a great power. The country has qualified personnel scientists, engineers, workers, the overwhelming majority of types of mineral resources, the created production potential is able to meet the needs of its further development.
The objects of economic security of the Russian Federation are the individual, society, the state and the main elements of the economic system, including the system of institutional relations in the state regulation of economic activity.
The state strategy includes:
1. Characteristics of external and internal threats to the economic security of the Russian Federation as a set of conditions and factors that create a danger to the vital economic interests of the individual, society and the state;
identification and monitoring of factors that undermine the stability of the socio-economic system of the state, for the short and medium term (three to five years) perspective.
2. Determination of criteria and parameters that characterize national interests in the field of economy and meet the requirements of the economic security of the Russian Federation.
3. Formation of economic policy, institutional reforms and the necessary mechanisms to eliminate or mitigate the impact of factors that undermine the stability of the national economy.
The implementation of the State Strategy should be carried out through a system of specific measures implemented on the basis of qualitative indicators and quantitative indicators - macroeconomic, demographic, foreign economic, environmental, technological and others.
II. Threats to the economic security of the Russian Federation
The identification of possible threats to economic security and the development of measures to prevent them are of paramount importance in the system of ensuring the economic security of the Russian Federation.
The most likely threats to the economic security of the Russian Federation, the localization of which should be directed by the activities of federal government bodies, are:
1. An increase in property differentiation of the population and an increase in the level of poverty, which leads to a violation of social peace and social harmony. The achieved relative balance of social interests may be disturbed as a result of the following factors:
the stratification of society into a narrow circle of the rich and the predominant mass of poor people who are uncertain about their future;
an increase in the proportion of the poor in the city compared to the countryside, which creates social and criminal tension and the ground for the widespread spread of negative phenomena that are relatively new to Russia - drug addiction, organized crime, prostitution, and the like;
rising unemployment, which can lead to social conflicts;
payment delay wages, stop businesses and so on.
2. The deformity of the structure of the Russian economy, due to factors such as:
strengthening the fuel and raw material orientation of the economy;
backlog of exploration of mineral reserves from their extraction;
low competitiveness of the products of most domestic enterprises;
curtailment of production in the vital branches of the manufacturing industry, primarily in mechanical engineering;
decrease in efficiency, destruction of the technological unity of scientific research and development, disintegration of established scientific teams and, on this basis, undermining the scientific and technical potential of Russia;
the conquest by foreign firms of the domestic market of Russia for many types of consumer goods;
the acquisition by foreign firms of Russian enterprises in order to oust domestic products both from the external and from the domestic market;
the growth of Russia's external debt and the associated increase in budget expenditures for its repayment.
3. Increasing uneven socio-economic development of the regions.
The most important factors of this threat are:
objectively existing differences in the level of socio-economic development of regions, the presence of depressive, crisis and economically backward regions against the background of structural shifts in industrial production, accompanied by a sharp decrease in the share of manufacturing industries;
violation of production and technological ties between enterprises of certain regions of Russia;
widening output gap national income per capita between individual subjects of the Russian Federation.
4. Criminalization of society and economic activity, caused mainly by such factors as:
an increase in unemployment, since a significant part of crimes is committed by persons who do not have a permanent source of income;
splicing part of the officials government agencies with organized crime, the possibility of access by criminal structures to the management of a certain part of production and their penetration into various power structures;
the weakening of the state control system, which led to the expansion of the activities of criminal structures in the domestic financial market, in the field of privatization, export-import operations and trade.
The main reasons for the emergence of these threats are the instability of the financial situation of enterprises, the unfavorable investment climate, the persistence of inflationary processes and other problems associated with financial destabilization in the economy.
Prevention or mitigation of the consequences of threats to the economic security of the Russian Federation requires the identification and monitoring of factors that undermine the stability of the socio-economic system of the state.
See the List of measures to prevent threats to the economic security of the Russian Federation and the federal executive bodies responsible for their development, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 27, 1996 N 1569
III. Criteria and parameters of the state of the economy that meet the requirements of the economic security of the Russian Federation
The list of criteria for the economic security of the Russian Federation and federal executive bodies responsible for the development of their quantitative (threshold) and qualitative parameters was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 27, 1996 N 1569
The state of the economy that meets the requirements of the economic security of the Russian Federation should be characterized by certain qualitative criteria and parameters (threshold values) that provide acceptable living conditions and personal development for the majority of the population, the stability of the socio-economic situation, the military-political stability of society, the integrity of the state, the ability to resist influence of internal and external threats. To determine the criteria and parameters that meet the requirements of the economic security of the Russian Federation, it is necessary to take into account:
1. The ability of the economy to function in the mode of expanded reproduction. This means that the country must have sufficiently developed industries and industries that are vital for the functioning of the state both in normal and extreme conditions, capable of ensuring the reproduction process regardless of external influences.
Russia should not allow the critical dependence of the economy on imports the most important types products, the production of which at the required level can be organized in the country. At the same time, it is necessary to develop our economy, taking into account foreign economic cooperation, international production cooperation.
The most important requirement for the economic security of the Russian Federation is the preservation of state control over strategic resources, the prevention of their export in amounts that could harm Russia's national interests.
2. An acceptable standard of living for the population and the possibility of maintaining it. It is impossible to allow the indicators of the level of poverty, property differentiation of the population and unemployment to go beyond the maximum allowable from the standpoint of the socio-political stability of society.
Qualified, conscientious work should ensure a decent standard of living.
Accessibility for the population of education, culture, medical care, heat, electricity and water supply, transport, communications, utilities is one of the necessary conditions for the economic security of Russia.
3. Sustainability financial system determined by the level of the budget deficit, price stability, normalization financial flows and settlement relations, stability banking system and national currency, the degree of protection of the interests of depositors, the gold and foreign exchange reserves, the development of the Russian financial market and the securities market, as well as the reduction of external and internal debt and the balance of payments deficit, and the provision of financial conditions for intensifying investment activities.
4. A rational structure of foreign trade, providing access for domestic goods of the processing industry to the foreign market, as much as possible allowable level meeting domestic needs through imports (taking into account regional characteristics), ensuring the priority of economic relations with neighboring countries. A balanced foreign economic policy that involves both meeting the needs of the domestic market and protecting domestic producers using protective measures adopted in international practice.
On the basics of state regulation of foreign trade activities, see Federal Law of December 8, 2003 N 164-FZ
5. Maintaining the scientific potential of the country and preserving the leading domestic scientific schools capable of ensuring Russia's independence in the strategically important areas of scientific and technological progress.
6. Preservation of a single economic space and broad interregional economic relations that ensure the observance of national interests, excluding the development of separatist tendencies, and the functioning of a single all-Russian market or an integrated system of regional markets, taking into account their production specialization.
7. Creation of economic and legal conditions excluding the criminalization of society and all spheres of economic and financial activity, the capture of industrial and financial institutions by criminal structures, their penetration into various power structures.
8. Determining and ensuring the necessary state regulation of economic processes, capable of guaranteeing the normal functioning of a market economy, both in normal and extreme conditions.
IV. Measures and mechanisms of economic policy aimed at ensuring economic security
Economic policy measures and mechanisms developed and implemented at the federal and regional levels should be aimed at preventing internal and external threats to the economic security of the Russian Federation.
1. Monitoring of factors that determine threats to the economic security of the Russian Federation
The most important elements of the mechanism for ensuring the economic security of the Russian Federation are monitoring and forecasting the factors that determine threats to economic security.
Monitoring as an operational information and analytical system for observing the dynamics of economic security indicators is of great importance for the transitional state of the economy in the presence of serious intersectoral imbalances and acute insufficiency of resources (primarily financial), strong mobility and instability of socio-economic indicators.
This determines the increase in requirements for state statistics in terms of complexity, depth and forms of coverage of objects of statistical observation, quality and timeliness of information.
Objective and comprehensive monitoring of the economy and society from the point of view of the economic security of the Russian Federation should be carried out on the basis of an analysis of specific quantitative values of indicators of economic security.
To monitor the factors that determine internal and external threats to the economic interests of the individual, society and the state, the first task is to create an organizational and information base.
2. Development of criteria and parameters (threshold values) for the economic security of the Russian Federation
In order to implement the State Strategy, quantitative and qualitative parameters (threshold values) of the state of the economy should be developed, beyond which the economic security of the country is threatened, characterizing:
the dynamics and structure of the gross domestic product, indicators of volumes and rates of industrial production, the sectoral and regional structure of the economy and the dynamics of individual industries, capital investments, and the like;
the state of the natural resource, production and scientific and technical potential of the country;
the ability of the economic mechanism to adapt to changing internal and external factors (inflation rates, the state budget deficit, the impact of external economic factors, the stability of the national currency, internal and external debt, etc.);
the state of the financial-budgetary and credit systems;
the quality of life of the population (gross domestic product per capita), the level of unemployment and income differentiation, the provision of the main groups of the population with material goods and services, the state of the environment, and the like.
Quantitative parameters should be developed not only for the country as a whole, but also for each of its regions. At the same time, the composition of criteria and indicators of the economic security of the Russian Federation by region should correspond with the corresponding composition of criteria and parameters in terms of the economy and national interests of Russia as a whole.
On the basis of the national interests in the field of economy, criteria and parameters of the economic security of the Russian Federation formulated in the State Strategy, measures are determined and mechanisms for the implementation of economic policy aimed at ensuring the economic security of the country are developed.
3. Activities of the state to ensure the economic security of the Russian Federation
The activities of the state to ensure the economic security of the Russian Federation are carried out in the following main areas:
1. Identification of cases when the actual or predicted parameters of economic development deviate from the threshold values of economic security, and the development of comprehensive government measures to exit the country from the danger zone.
Measures and mechanisms that ensure the economic security of the Russian Federation are developed simultaneously with state forecasts for its socio-economic development, and are implemented in the program for the socio-economic development of the Russian Federation.
2. Organization of work in order to implement a set of measures to overcome or prevent the emergence of threats to the economic security of the Russian Federation. During this work:
The Security Council of the Russian Federation considers the concept of the federal budget from the point of view of ensuring the economic security of the state;
The Government of the Russian Federation coordinates the work of federal executive authorities, executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation in order to implement a set of measures to overcome or prevent threats to the economic security of the country, including in the preparation of legislative and other regulatory legal acts.
3. Examination of decisions made on financial and economic issues from the standpoint of the economic security of the Russian Federation. Legislative and other normative legal acts, when they are prepared, must undergo an expert examination for the economic security of the Russian Federation. The procedure for conducting this examination is determined by the President of the Russian Federation.
The implementation of measures to eliminate threats to the economic security of the Russian Federation requires a system of control over their implementation. The control system should take into account the rights and responsibilities of the owner.
Well-being in the sphere of economy is the main condition for the functioning of the state. The existence of a stable system in the Russian Federation will make it possible to maintain a competitive position in the world market. Economic security plays a crucial role in the Russian national security system, so I propose to consider this issue in detail. Let's start with the basic concept.
The concept of economic security
National economic security is understood as the protection of the country's economy from external and internal factors that adversely affect economic functioning and undermine the standard of living of the population. This is the main element of national security.
There are 3 main principles:
- independence: the level of the economy is being formed, which allows the least possible dependence on other states and the world market;
- stability: stability, exclusion of crises, social upheavals, crime;
- sustainable growth of the national economy: improving the system, creating conditions for the work of citizens, reducing unemployment, developing unique products, developing industry.
Concept
The concept of Russia's economic security is a set of provisions aimed at maintaining the stability and growth of economic indicators necessary to ensure the normal life of citizens and maintain a reliable status of the state in the international market. Maintaining economic resilience directly affects overall national security. That is why, when political conflicts arise, the first blow always falls on the economy.
Russia's Economic Security Strategy until 2030 is a document ordered to be approved by Russian President Vladimir Putin in 2017. It contains the main goals and objectives of economic policy aimed at maintaining financial security. The implementation of the strategy should completely improve the situation in the country and on the world market, despite the difficult international relations with some states.
Types of security
Economic security cannot be perceived as something abstract. Maintaining a safe level implies the adoption of specific measures in certain areas. From here, the main types of economic security of Russia are distinguished.
- Financial. The state when the state is able to guarantee the conditions for the functioning of the state. institutions, create favorable conditions for the development of a market economy, create favorable conditions for citizens, and reduce unemployment. It is necessary to control the budgets (state, consolidated), the level public debt, financial markets, balance of payments and other structural elements.
- Energy. The state of the fuel and energy industries is implied. It is necessary to ensure a reliable energy supply for the successful development of all regions of the country.
- Defense. Reflects the readiness of the army to contain external threats and counter them.
- Defensively-industrial. Maintenance of military security, readiness for the most unfavorable outcome of international relations.
- Informational. A set of measures aimed at maintaining the protection of information, the correct presentation of data. Any leak or false data leads to an aggravation of the situation. Also, information security involves counteracting fraudulent activities.
Main characteristics
There is a system of indicators that can visually characterize the security in the country. It is distinguished by its versatility, the interconnection of elements. Indicators display one process from different angles. In total, about 150 indicators can be counted, which are combined into 4 groups:
- production and economic(GDP, GDP deflator, net national product, income (net and used), the economic growth;
- financial and economic(balance of payments, state budget, deficit, investment, monetary indicators);
- socio-economic(employment, unemployment, cost of living, poverty + its upper and lower thresholds, inflation, price index, etc.);
- political(legitimate power).
Russia's economic security indicators are not stable. The task of experienced analysts is to search for relationships, which helps to identify patterns and provide new ideas for implementation at the legislative level.
Main tasks
The problems of ensuring the economic security of Russia are solved as follows:
- competent analytics and identification of weaknesses in the country's economy, a multifaceted study of the issue based on the experience of past years (including in other states);
- forecasting: involves an analysis of the risk of security threats, a detailed forecast of possible outcomes is given;
- development of a long-term strategy and specific threat reduction activities;
- creation of independent sources, including the scientific and technological sphere;
- normalization and support of favorable international relations;
- development and improvement of the legislative framework in the field of economics;
- formation of financial independence: reducing debt to other countries, refusal of loans.
This is not the whole list of tasks, but here is the most necessary.
Threats to economic security
There are internal and external threats to Russia's economic security. These are phenomena and processes that have a negative impact on the economy in the state, limit the interests of society and the individual citizen, and destroy national values and social foundations.
Internal
Internal threats include:
- intensive stratification of society - the excess of the income level of well-to-do citizens over the level of less well-off;
- criminalization - the shadow economy as a threat to the economic security of Russia is becoming an increasingly dangerous problem, corruption among officials and various structures, mostly state-owned, is also at a high level;
- destruction of potential in the field of science and technology - in other countries, the costs in this area are much higher.
Corruption as a threat to the economic security of Russia is the most serious domestic problem. Due to corrupt representatives of state and some private structures, there is a huge budget drain, which has an extremely negative impact on the economy of our country. Corruption affects almost all areas of life, from healthcare to the defense industry.
External
Modern threats to the economic security of Russia from the outside look like this:
- leakage of intellectual potential - scientists and highly qualified specialists actively go abroad, where they have better conditions for development than in Russia;
- capital flight - funds illegally flow abroad;
- import dependence - regarding food and consumer goods Russia is highly dependent on Western countries, citizens are accustomed to using imported products, problems with import substitution are extremely relevant.
Foreign policy is a special factor, because it is extremely difficult to control, everything depends on the colleagues of the state, especially Western ones. The aggravation of the situation in Syria and Ukraine, the annexation of Crimea - all this caused a violent reaction in the world, the Russian Federation falls under sanctions. Economic relations between countries are the first thing that is threatened, so it is necessary to think about import substitution and the adoption of new measures aimed at normalizing the foreign policy situation. The necessary measures to neutralize threats to Russia's economic security must be taken resolutely and quickly, but the main thing is the development of strategies in the economy.
Prospects for development and improvement of the security level
The Ministry of Economic Development has developed a concept, one of the main guidelines of which was the restoration of the status of a world economic power. Russia should become one of the main states, reach the level of highly industrialized countries. In terms of GDP, it is necessary to enter the top six of the world top, as well as significantly increase the level of well-being among the population. An integral part. This plan becomes dominance in scientific, technological and financial sector.
The current state of Russia's economic security leaves much to be desired, so the solution to the problem is the transition from raw materials export to innovative development. Advantages in science, education and technology are becoming a decisive factor in promoting economic development. It is important to make a breakthrough in the industries that are the main specialization of the Russian Federation in the world market. 4 main strategies:
- competition in energy, transport, agricultural sector;
- formation of a powerful scientific and technological complex;
- diversification of national farms;
- development of the market, entrepreneurship, provision at the legislative level.
Development trends also create certain risks. Prospects depend on the objective conditions for the development of the world economy and subjective - the processes taking place on the world stage and in individual regions of the Russian Federation. The economic security of Russia in 2018 still leaves much to be desired, so new partners are being sought, the economy is gradually developing. The 2030 strategy should help to solve many problems.
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Hosted at http://www.allbest.ru/
- Introduction
- 1. Regulatory - legal basis for the economic security of Russia
- 1.1 State strategy of economic security.
- 1.2 Main provisions of the state strategy of economic security.7
- 2. The concept and structure of the economic security of the state
- 2.1 Critical elements of economic security
- 2.2 Classification of threats to economic security
- 3. Mechanism for ensuring economic security
- 3.1 Monitoring, development of criteria and parameters of economic security.
- 3.2 Activities of the state to ensure economic security and quality of life of the population.
- 4. Necessary measures to improve the economic security of Russia
- Conclusion
- Bibliography
Introduction
The need for protection from unwanted external influences and radical internal changes, in other words, the need for security, is a basic, fundamental need for both the life of an individual, a family, and various associations of people, including society and the state. In the conditions of the formation of a market economy, the sphere of safe existence has narrowed so much that the constant and massive dissatisfaction of this need has a negative impact on the development and functioning of individual citizens, families, organizations, the state and society as a whole, exacerbating the crisis in all spheres of its life.
Today, the most pressing issues are those related to threats to the national security of the Russian Federation. Economic security is one of the most important components of the country's national security.
The economic security of the state is a complex and multifaceted structure. Being part of the national security system, it simultaneously forms the basis for the formation of all the elements included in its structure:
military,
technological,
food,
environmental safety, etc.
At present, the object of security is the economy at all levels with its tasks of stability, invulnerability, a balance of obvious benefits and certain damage brought about by the process of "drawing" into international market relations and economic ties. The crisis state of the economy is manifested through a significant reduction in production, a decrease investment activity, the destruction of scientific and technical potential, the stagnation of the agricultural sector, a decrease in the revenue side of the federal budget, etc.
The expansion of business cooperation with economic entities in the country and abroad actualizes the tasks of overcoming negative circumstances that impede the normal functioning of the economy and its sustainable development.
The state of the economy, the assessment of the negative consequences of the political and economic decisions taken, including those on reform and restructuring, the identification of cause-and-effect relationships of crisis phenomena led to the consideration of economic security factors within the framework of state economic policy.
In its most general form, economic security depends on a combination of factors. optimal ratio on the scale of state structures, the state of the economy of society, the content of the institution of power and the culture of public life. It is understood as a multilevel phenomenon: the economic security of the individual; economic security of a business entity; economic security of the region or sphere of economic activity; economic security of the country as a whole.
Due to the lack of a coherent system for ensuring economic security, the forecast and models for the further socio-economic development of the country were largely based on international programs developed by international bank reconstruction and development (IBRD) and the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
The implementation of a reform policy inadequate to the economic conditions further exacerbated the situation. The openness of the economy allowed foreign manufacturers to capture the Russian market, as a result of which the Russian economy began a sharp decline in production, which is still ongoing. Russia's national security is under threat. A sharp drop in the level of income and living standards of the population poses a threat to the statehood of Russia. All this is due to the state of the economy. How to assess it, how to make decisions to bring it out of the protracted crisis? The problem of economic security in foreign literature has been considered, apparently, for a long time, since F. Roosevelt laid the foundation for this in 1934 when he started using the term economic security.
In our country, the term "economic security" began to sound in the 90s in the articles of economists and in the media. The first articles on the problems of Russia's economic security appeared at the end of 1994. The theoretical side of the issue was considered most fully in the journal Questions of Economics No. 12 for 1994 by L. Abalkin, A. Arkhipov and others. Later, other major Russian economists also entered into polemics on this issue.
The problems of ensuring the economic security of Russia as an indispensable condition for its revival are attracting more and more close attention of politicians, scientists, and the widest sections of the population. Such attention is by no means accidental. The scale of the threats and even the real damage inflicted on the economic security of the country bring these problems to the forefront of public life.
1. Regulatory framework for the economic security of Russia
1.1 . State strategy of economic security.
The most important element of Russia's state security is economic security. In accordance with the Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of April 29, 1996 No. 608 "On the State Strategy for the Economic Security of the Russian Federation (Basic Provisions)", the economic security of Russia is the state of protection of the economic interests of the individual, society and the state from internal and external threats, based on independence , efficiency and competitiveness of the country's economy. The objects of economic security of the Russian Federation, in accordance with the Decree, are the individual, society, the state and the main elements of the economic system, including the system of institutional relations.
Without ensuring economic security, it is impossible to solve the tasks facing the state, both at the national and international levels. Thus, the state strategy of economic security, being an integral part of the national security of Russia, pursues the goal of ensuring the protection of the population by improving the level and quality of life, effectively solving internal economic and social problems, as well as influencing world processes, taking into account national state interests.
The current situation in the Russian economy requires the definition of an economic security strategy. However, all ongoing economic measures are mostly impulsive, fragmented.
Despite the complexity of the transition period, Russia has a huge potential to ensure its economic security not only within the country, but also abroad. The foreign economic orientation of the state strategy lies in the effective realization of the advantages of the international division of labor, in the participation of the country in its equal integration into world economic relations, in the elimination of its dependence on foreign countries in matters of economic and technical cooperation. The objects of economic security, in addition to the individual and the state, are the main elements of the economic system and economic activity.
1 .2 Main provisions of the state strategy of economic security
The main provisions of the state strategy in the field of economic security define concepts, objects, indicators, threats and the main mechanisms for their prevention or repayment within the framework of real resource constraints.
There are three blocks of provisions of the strategy:
1. Determination of national state interests in the field of economy that meet the requirements of economic security and ensure the protection of important conditions for the life of the country.
2. Identification of dangers and threats to economic security as a set of conditions and factors that harm the vital economic interests of the individual, society and the state, identification and monitoring of factors that undermine the stability of the socio-economic system and the state in the short and medium term (3-5 years) .
3. Formation of proposals for the adjustment of economic policy, institutional reforms and the necessary mechanisms to eliminate or mitigate the impact that undermines the stability of the economy.
The implementation of the economic state strategy should be carried out through a system of specific measures implemented on the basis of qualitative indicators and quantitative indicators - macroeconomic, demographic, foreign economic, economic, technological, etc.
2. The concept and structure of the economic security of the state
2.1 Critical elements of economic security
In order to understand and realize the meaning of the category "economic security" it is necessary to characterize the term "security" and determine what its essence is. Security is such a state of the subject, in which the probability of a change in the qualities inherent in this subject and the parameters of its external environment is small, less than a certain interval. The "desirable" state of the subject is determined by a specific combination of parameters of vital activity. Depending on the change in this combination, the concept of a "desirable" change will also change. Thus, the correct assessment of the level of security is no less important for the subject. The subject's assessment of security may not coincide with its actual level. The depth of this discrepancy depends on the completeness and depth of information about the current situation, on the degree of influence of its changes on the state of security, etc.
In general, the category of economic security is interpreted differently in the scientific literature. So, for example, according to V. Tambovtsev, "... under the economic security of a particular system, one should understand the totality of the properties of the state of its production subsystem, which ensures the ability to achieve the goals of the entire system."
V.A.Savin believes that "economic security is a system for protecting the vital interests of Russia. The objects of protection can be: National economy countries as a whole, certain regions of the country, certain spheres and sectors of the economy, legal entities and individuals as business entities. "According to L.I. Abalkin," economic security is the state of the economic system, which allows it to develop dynamically, efficiently and solve social problems and in which the state is able to formulate and implement an independent economic policy."
So in general sense In other words, economic security should be understood as the most important qualitative characteristic of the economic system, which determines its ability to maintain normal living conditions for the population, sustainable provision of resources for the development of the national economy.
Economic security itself has a rather complex internal structure. Three of its most important elements can be distinguished:
Economic independence, which in the conditions of the modern world economy is by no means absolute. The international division of labor makes national economies interdependent on each other. Under these conditions, economic independence means the possibility of state control over national resources, the achievement of such a level of production, efficiency and product quality that ensures its competitiveness and allows it to participate on an equal footing in world trade, the exchange of scientific and technological achievements;
Stability and stability of the national economy, which implies the protection of property in all its forms, the creation of reliable conditions and guarantees for entrepreneurial activity, the fight against criminal structures in the economy, the prevention of serious gaps in the distribution of income that threaten to cause social upheavals, etc.;
The ability to self-development and progress, which is especially important in today's dynamically developing world. Creation of a favorable climate for investments and innovations, constant modernization of production, raising the professional, educational and general cultural level of workers become necessary and mandatory conditions for the stability and self-preservation of the national economy.
Thus, economic security is a set of conditions and factors that ensure the independence of the national economy, its stability and sustainability, the ability to constantly update and improve itself.
2.2 Classification of threats to economic security
The most likely threats to the economic security of the Russian Federation, the localization of which should be directed by the activities of federal government bodies, are:
1. Weakening of the scientific, technical and technological potential of the country.
The scientific and technical potential, despite the well-known weaknesses (in particular, the unilateral orientation towards military goals), was generally comparable to that of North America and Western Europe. The collapse in production, especially in the military-industrial complex, paralyzed the demand for R&D. At the same time, budget allocations for science were sharply reduced.
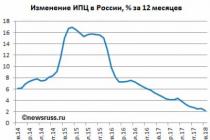
The share of appropriations for science in industrialized countries is at least 2% of GDP (this, according to the Security Council, is the threshold value). In Russia, this share is 0.3-0.5%. It is believed that if within 5-7 years the cost of research and development does not exceed 1% of GDP, then irreversible processes begin in the country in the destruction of scientific and technical potential.
Science and scientific services have turned from the most prestigious and financially secure sphere of activity into one of the lowest paid. At the end of 1996, the average salary here was lower than in the gas industry, electric power industry and industry as a whole by 5 times, 2.5 and 1.4 times, respectively. Purchases of instruments, equipment and materials, subscriptions to foreign literature and periodicals have almost completely stopped. Left to their own devices, scientific institutions and institutes are fighting for survival, they are preoccupied with finding money to pay utility bills.
Reducing R&D funding by more than 10 times over the past 7 years and the associated outflow of the best minds abroad (emigration of more than 100 thousand scientists in these years is equivalent to an economic loss of 80 billion dollars), the degradation of scientific schools, the collapse of research teams and world-class design bureaus, the destruction of the connection between science and production dooms the country to the deprivation of the main factor of modern economic development - scientific and technological progress.
However, despite the catastrophic destruction of the domestic scientific potential, the Government does not increase appropriations for R&D even up to the legally prescribed 4 percent of the level of the expenditure side of the budget, refuses to include R&D expenditures in the cost of production, to provide tax incentives to stimulate innovative activity.
2. Disintegration of the economy and decline in production.
As a result of the macroeconomic policy pursued by the government of the Russian Federation in different years, the country's economic space has split into two spheres that are weakly connected with each other. The sphere of capital circulation (operations in the securities market, the foreign exchange market, as well as in trade) is characterized by high (and even ultra-high) profits and the speed of money circulation. The production sector (“real sector of the economy”, covering material production, domestic services, medical service, education, transportation and other areas related to the production of material and spiritual wealth) low profitability and velocity of money circulation, as well as significant risks (all this is due to the chaotic rupture of economic ties, the uncertainty of property relations, the instability of demand, unfair competition and general unfavorable market conditions market).
In a balanced economic system in a state of equilibrium, the sphere of circulation of capital and the production sphere perform complementary functions from a reproductive point of view. Through the sphere of circulation, there is a constant exchange of goods and the redistribution of capital from less efficient to more efficient areas of investment, which ensures the continuity of the social reproduction process, the basis of which is the sphere of production. These areas are connected by banks, marketing organizations, the state budget into a single whole and function in an inseparable unity.
In the non-equilibrium and unbalanced state of the current Russian economy, the sphere of circulation of capital and the production sphere turned out to be disintegrated. A sharp gap between them in terms of profitability and attractiveness of operations led to a massive flow of capital from the production sphere to the circulation sphere (with the subsequent transfer of a significant part of it abroad)
Disintegration is also progressing in the manufacturing sector of the economy. In this regard, it is significant that enterprises that are forced to maintain their own reproduction in the conditions of a constant outflow of cash resources and depreciation of working capital are divided into three groups depending on the stability of effective demand and the internal rate of return.
The first group is distinguished by stable solvent demand and a rate of return sufficient to retain its own working capital and mobilize external loans to replenish them. These are, as a rule, enterprises of the oil and gas, chemical and metallurgical industries, supplying a significant part of their products for export. The latter allows them to maintain a relatively high rate of return, ensure a timely return of funds and attract relatively cheap credit resources from abroad to finance working capital. Under favorable circumstances, they are able to use credit and accumulated own funds in the amounts necessary to finance investments.
The second group of enterprises is characterized by a rate of profit sufficient to maintain simple reproduction and by the presence, to some extent, of effective demand for their products, which makes it possible to carry out (albeit belatedly) the circulation of capital. They are focused mainly on the demand of the enterprises of the first group. This includes a few enterprises that produce competitive consumer products, as well as those belonging to the sphere of natural monopolies.
The third group includes solvent enterprises characterized by low or negative profitability, non-competitiveness of their products or the absence of solvent consumers. This is the largest group, covering enterprises in agriculture, light industry, construction and related industries of mechanical engineering, as well as production with long production cycles (which are especially difficult to survive in a liquidity crisis).
3. Loss of economic independence.
At present, the degree of the country's economic dependence on the outside world is unacceptably high. Up to 70% of the food consumed by the population of large cities comes from abroad. The state is not able to stop the illegal massive export of capital. The amount of payments on external debts exceeds the capacity of the Russian economy. The country is forced to adjust its economic policy to the universalist demands of international economic organizations, which often do not adequately take into account Russian specifics, and sometimes act directly to the detriment of the Russian economy.
The economy turned out to be structurally even more distorted - the share of extractive industries increased and the share of the processing industry, especially those producing end products with a high degree of processing, decreased. From the point of view of our country's specialization in the world market, and from the point of view of the structure of capital investments, which determines the future structure of the economy, Russia has acquired the typical features of a raw material colony.
The share of the main types of fuel and energy resources in the total volume of exports in recent years has amounted to more than half, of all raw materials - 3/4, and machinery and equipment - only 8--9%. independence, the share in the export of the manufacturing industry should be at least 40%, including at least 10% should account for high-tech and science-intensive products. These figures in Russia are about 12% and 1%, respectively. . In exchange for natural resource rent, Russia purchases consumer goods, machinery and equipment, financing scientific and technological progress and creating jobs abroad.
However, such a deformed economy (in particular, the backwardness of the manufacturing industry and curtailment of the development of new deposits), as well as the instability of world prices, have predetermined the fact that the efficiency of Russian exports is steadily declining, depriving the Russian government of the main source of replenishment of the country's budget.
In the National Security Concept of January 10, 2000, the low level of investment is among the most serious threats to Russia's economic security. Indeed, attracting foreign investment to the Russian economy (especially its oil and gas industry) can slow down the backlog of replenishment of mineral reserves from their production, curtailment in vital manufacturing industries, and, in the future, may be able to influence the solution of such acute problems of the Russian economy. security, such as low competitiveness of domestic products or delays in salary payments.
However, it is possible that under the influence of the influx of foreign investment, the accelerated development of the oil and gas complex will lead to a further increase in the share of the fuel and raw materials sector in the country's economy and strengthening its fuel and raw materials orientation. Another important guideline can be considered the position that foreign companies should not be allowed to establish control over strategically important sectors of the economy.
There is a real threat of losing national control over non-ferrous metallurgy, instrument making, the chemical industry, and the electric power industry. In the context of an acute budget crisis, the administrations of the subjects of the federation, seeking to close the gaping budget holes, are ready to transfer to foreign companies the last thing - subsoil plots with deposits of valuable natural resources.
It is necessary to dwell on another way of losing Russia's national security. The fact is that low economic activity not only makes it impossible to maintain at least simple reproduction, defense capability and the achieved parameters of well-being. It excludes the provision of the minimum necessary level of economic development of the country's territory and the maintenance of the existing infrastructure. This is expressed in the mass exodus of the population from the regions of the North and the Far East in a sharp increase in catastrophes and accidents in basic industries: transport, energy, and the chemical industry. If the prevailing trends continue, the “rarefied” economic space of Russia will inevitably be filled with foreign capital. This is already clearly felt in the growing pressure on the authorities of various forces lobbying the interests of foreign companies. The latter are striving to seize the most valuable and mineral-rich tracts of land, to strengthen their control over the information space and transport communications in Russia.
Russia's loss of food independence deserves special consideration. Agricultural production is always more conservative than industrial production. The dependence of the former on soil and climatic conditions, technical and technological backwardness, lower capital-labor ratio of production and labor, as well as weak power supply slowed down the pace of development in the agrarian sphere of economic activity.
Of all the troubles that have fallen on the Russian economy, the most burdensome is the decline in agricultural production and the deterioration in the nutrition of the country's population. Back in the years of Soviet power, a steady lag of agriculture behind industry and the level of its development in the industrialized countries developed. The implementation of reforms aggravated the situation in the agrarian sector of the economy. Agriculture during natural and social cataclysms suffers more than other branches of production.
The undermining of agriculture has basically caused a deterioration in the nutrition of the population of Russia.
Earlier, during the years of socialism, the country in terms of food per capita ranked 6th in the world. Now it's the 40s.
The deterioration in nutrition is caused not only by a decrease in the production of basic food products, the curtailment of the food industry, but also by a drop in the purchasing power of the population, an increase in the number of people living below the poverty line, especially in rural areas. Today, the average monthly wage in the countryside is 42% of the national average.
4. The impoverishment of the population.
On September 22, 2004, the World Bank presented its Poverty Assessment Report in Russia. According to his estimates, during the period from 1997 to 1999, poverty in Russia increased from 24.1% of the population (35.3 million people) to 41.5% (60.5 million). Then, from 1999 to 2002, Russia more than halved poverty to 19.6%. Unemployment during this time fell from 13.2% to 8.2% of the working population, and average salary increased by 15%.
The poor in Russia are most often able-bodied residents of villages and small towns with children. There is a very high proportion of people living below the official poverty line among workers in education, culture and healthcare.
At the same time, experts World Bank and Russian statisticians use different methods for determining the level of poverty. Russian experts estimate the share of the poor in terms of monthly income. For example, in the II quarter of 2004 the official subsistence minimum amounted to 2363 rubles. per month per person, and incomes below this level had 29.8 million people - 20.8% of the population.
The World Bank considers this methodology not entirely correct and proposes to measure poverty not by the level of income (about which people do not always tell the truth), but by the level of consumption. Therefore, in 2002, according to the World Bank, 19.6% of the Russian population suffered from poverty, and according to the Russian government, 25%.
According to the World Bank, only 8% of transport subsidies go to the poorest 20% of the country's citizens, while the richest 20% receive 30% of such subsidies. And the amount of housing benefits received by the richest is 2.1 times the amount of assistance received by the poor.
The world community, represented by the relevant UN organizations, has long recognized that an hourly wage below three dollars is the limit. It pushes the worker beyond the threshold of his life, beyond which the labor potential of the economy is destroyed. Our average salary is three times below this threshold.
The decline in real incomes of the population led to a decrease in consumption.
The problem of impoverishment of the population is recognized, but completely ignored in the conduct of socio-economic policy. Although it was officially declared "unacceptable excessive social price reforms”, the inadmissibility of an even greater decline in the living standards of the population. However, the government repeatedly refused to comply with social guarantees, arbitrarily sequestered social spending established by law, allowed a sharp deterioration in the quality of education and health care, and abandoned the disabled population, including millions of children from poor families, to the mercy of fate.
In these socio-economic conditions, the natural reaction of the population was to reduce the birth rate. Over 40% of families with two or more children live in poverty, and the likelihood of large family fall into poverty is 50%. Not surprisingly, almost 6 million fewer children were born in the last 10 years than in the previous decade.
Of all federal budget expenditure items, steady and rapid growth is observed in only one - public debt service expenditures, which have reached a quarter of the entire federal budget.
As you can see, the preservation of the super-profits of the oligarchic clans that control part of the banks and raw material monopolies, the income of the alcohol mafia is more important for the government than ensuring national security, minimum social guarantees, saving children from hunger and degradation, protecting the health of the population and educating young people.
5. Property differentiation of the population and mass unemployment
The rapid split of the country into a narrow circle of rich people and a huge mass of the poor, unsure of their future, creates two polarized classes of society with different ideas of social justice. The distance between them is increasing, and the social base of reforms is being strengthened. Obviously, this leads to the fact that the threat of social conflicts is constantly reproduced. Also, the preconditions for social tension are created by the growing unemployment rate. The threshold level is considered to be up to 10% of the number of able-bodied. According to official data, Russia is approaching this threshold, but taking into account hidden unemployment (vacation without pay, part-time work, etc.), its real level is 13-15%.
Unemployment is a new phenomenon for Russia, so one should keep in mind its moral impact on the population and its actions. According to American scientists, a 1% increase in unemployment increases prison occupancy by 5-7%.
6. Criminalization.
As a threat to the economic security of Russia, it is necessary to single out the criminalization of economic activity caused by rising unemployment, the merging of some government officials with organized crime, the possibility of criminal structures gaining access to managing a certain part of production, and the weakening of the state control system.
Crime has affected almost all spheres of economic life: property relations; production and distribution of the produced product; financial and banking activities, public administration and foreign economic activity. Already the first year of the so-called "liberalization" of the economy has become a year of freedom for the criminal community. The annual turnover of the shadow economy in 1992 increased by 25 times compared to 1991 and exceeded a trillion milestone. However, then the share of the shadow sector of the economy was comparable to that of most countries with developed market economies. And by 1996 it was already 45%.
By now, the last romantic hopes of the liberals for a possible ennoblement of the "black" market have collapsed.
The problem of criminalization of the country's economy remains the number one problem today.
The processes of criminalization of economic life in the country are based on the shadow economy, that is, the system of economic relations outside the legal field of the state. Shadow financial capital is the economic basis (basis) of organized crime.
The shadow economy, like any social phenomenon, has two sides. On the one hand, this is the creation of additional jobs, the production of products, the provision of various services and, ultimately, the improvement of the welfare of society. On the other hand, tax evasion, capital laundering, transfer of capital abroad, withdrawal of unrecorded income and currency from circulation. In addition, by competing with the official economy, the shadow economy, having a higher profit, turns out to be more efficient and hinders the development of the official economy.
In Russia, the centralized management system has created a set of conditions for the emergence and development of the shadow economy and shadow capital. A wide range of people, resources, as well as officials of various ranks were involved in the shadow economy system.
A decisive role throughout the world is played by the active assistance to the shadow economy of representatives of power structures at all levels. Studies show that from the first days, shadow companies, in parallel with racketeers, and sometimes exclusively, entered into an alliance with representatives of law enforcement agencies and local executive authorities. Over time, law enforcement agencies began to actively oust crime from the shadow economy, and at present, representatives of these structures, together with tax services, are “making a roof” for almost all large and medium-sized businesses. Super-big business has become the domain of government officials and deputies of the highest rank. The spheres of influence are distributed quite clearly, and, as a rule, there are no disruptions.
The result of the criminalization of the economic system was the subordination of the economic policy of the state to the specific economic interests of criminal structures. The shadow economy is the core on which the modern criminal structure has been formed.
The most important factor that led to the criminalization of the economic life of society is the destruction of the mechanisms of state power, as well as the ongoing socio-economic policy.
The potential danger of the criminalization of the economy was objectively amplified by the very focus of the reforms on the development of market relations. The stage of initial accumulation of capital is inevitably accompanied by the aggravation of criminal phenomena in the economic life of society.
Despite the increased activity of the state in the fight against crime, the results do not provide a basis for a satisfactory assessment. The most dangerous is not the rate of growth of various kinds of economic crimes (no matter how impressive the specific figures and examples may look), but the transition of economic crime to a new quality, expressed in an increasingly real threat to the economic security of the Russian Federation.
Speaking about economic security in terms of the impact of the criminal economy on it, it is necessary to pay attention to the fact that economic crime has acquired qualitatively new properties. The leaders and authorities of the criminal world create criminal communities that actively influence enterprises and organizations that have federal significance. These communities are increasingly characterized by rigid centralization and clear discipline. Of particular concern is the existence in these communities of such attributes as intelligence and counterintelligence, technical support and the presence of militant groups, while previously these attributes could only be characteristic of the state. This leads to the idea that criminal communities are trying to replace the state, taking over its functions and, along with them, powers. This trend is extremely dangerous, as it threatens the existence of the state itself. In other words, the problem of the criminalization of the economy should also be considered as a problem of national security.
7. Aggravation of differentiation of economic and social development of regions. Separatism of a number of subjects of the Federation.
One of the most acute problems of economic security is the aggravation of the differentiation of economic and social development of its constituent territories. Russian regions, which previously were far from identical in terms of their socio-economic characteristics, are rapidly stratifying into rich and poor in the face of a decline in production.
Without a doubt, this generates not only economic, but also political consequences: the growth of separatism in certain regions (Tatarstan, Bashkortostan, Yakutia, etc.), the popularity of the idea of secession from Russia (the North Caucasus, the "Ural Republic"), etc. Extrapolation of these trends shows that they lead to the final collapse of the single economic space of Russia (given the level of integration of the Russian economy and the lack of competitiveness of most of its industries in the world market, this will inevitably lead to complete economic degradation and finally give the economy a "colonial" structure), and then to disintegration of Russia into many separate states.
Prevention or mitigation of the consequences of threats to the economic security of the Russian Federation requires the identification and monitoring of factors that undermine the stability of the socio-economic system of the state.
3. Mechanism for ensuring economic security
economic state security
3.1 Monitoring, development of criteria and parameters of economic security
Economic policy measures and mechanisms developed and implemented at the federal and regional levels should be aimed at preventing internal and external threats to the economic security of the Russian Federation.
Monitoring of factors that determine threats to the economic security of the Russian Federation
The most important elements of the mechanism for ensuring the economic security of the Russian Federation are monitoring and forecasting the factors that determine threats to economic security.
Monitoring as an operational information and analytical system for monitoring the dynamics of economic security indicators is of great importance for the transitional state of the economy in the presence of serious intersectoral proportions and an acute shortage of resources (primarily financial).
Development of criteria and parameters (threshold values) for the economic security of the Russian Federation
In order to implement the State Strategy, quantitative and qualitative parameters (threshold values) of the state of the economy should be developed, beyond which the economic security of the country is threatened, characterizing:
the dynamics and structure of the gross domestic product, indicators of volumes and rates of industrial production, the sectoral and regional structure of the economy and the dynamics of individual industries, capital investments, and the like;
the state of the natural resource, production and scientific and technical potential of the country;
the ability of the economic mechanism to adapt to changing internal and external factors;
the state of the financial-budgetary and credit systems.
3.2 Activities of the state to ensure economic security and quality of life of the population
The activities of the state to ensure the economic security of the Russian Federation are carried out in the following main areas:
1. Identification of cases when the actual or predicted parameters of economic development deviate from the threshold values of economic security, and the development of comprehensive government measures to exit the country from the danger zone.
2. Organization of work in order to implement a set of measures to overcome or prevent the emergence of threats to the economic security of the Russian Federation.
Examination of decisions made on financial and economic issues from the standpoint of the economic security of the Russian Federation.
4. Necessary measures to improve the economic security of Russia
The difference in the size of foreign direct investment in the economy of China and Russia indicates the difference in the attitude of foreigners towards Russia and China. The confrontation between China and the United States does not prevent the latter from investing dozens of times more in the Chinese economy. Would you develop the economy of a future competitor and military adversary? No. This means that the West perceives Russia differently than China, although China follows Russia in terms of economic transparency. This is also evidenced by the investment activity (more precisely, the absence of such activity) of the largest TNCs in Russia. Their main task is to capture one or another share of the Russian market in order to expand the sales of their own products. The total of actual and declared investments of the largest TNCs in the Russian economy is slightly more than 1% of the total foreign assets. E.A. Gryaznov, KTNK in Russia. Positions of the world's largest transnational corporations in the Russian economy. Moscow, 2000. This means that the largest investors have not invested in Russia, and are not going to invest (of course, if there are no completely free offers, but for cheap acquisitions a lot of money is not required). This means that Russia is viewed as a very strong potential rival, in the development of whose economy it is better not to invest - it will be more expensive for yourself. So the big investments that are about to pour in from abroad in a wide stream following the opening and liberalization of the market is a myth that needs to be eliminated as soon as possible. The G7 countries will not invest in the Russian economy (unless they buy Gazprom at a low price and the most cost-effective generating power plants, or something else). Well, in principle, we are not the first, we are the last. After all, there is an active pulling away of the electric power industry and the gas industry in Eastern Europe and in the Baltic countries at bargain prices, they just haven’t reached us yet.
Why cheap? Because in Russia today there is practically zero capitalization. During the years of reforms, the state “lowered” its fellow citizens and its own industry for money several times. As a result, RAO UES, which at the time of its formation was worth $425 billion, was worth $102 billion during Gaidar's collapse of the ruble, and is now worth $4-6 billion. Lukoil is worth $10-12 billion, while a similar company, Chevron, is worth $70-80 billion. Gazprom, whose value should range from 150 to 300 billion dollars, costs 8 billion. A. Godzinsky, On liquid debts and conscientious borrowers, Expert No. 21, 2001 Russian companies, more precisely, with all companies of the countries participating in the Warsaw Pact. The enemy of NATO died in the late 80s, now there is an active eating of the fallen.
We must honestly admit that economic course was imposed from outside. After all, as practice has shown, almost all large developing countries, using the advice and assistance of the IMF and other international organizations created and expressing the interests of the United States and its allies, failed to develop to the level of the "big seven". Moreover, the external debt of such countries as Mexico, Argentina and Brazil is now comparable to the Russian debt. Although they have been trying to pull their economy out of debt through exports for much longer than Russia.
So, you can only rely on your own strength. And there are hidden reserves, because according to various estimates, only monetary form from 150 to 350 billion dollars.
Listed below are some of the measures that contribute to strengthening economic security.
The state should take control of the development of the economy, because the United States, while preaching liberalization in other countries at home, is pursuing a very tough policy on import tariffs, protecting its own market, and supporting agricultural producers. And it was the state that, with its state order and a number of other measures, pulled the US economy out of the depression of the 1930s and is trying to do the same at the moment.
Under no circumstances should we now join the WTO, stronger foreign competitors will simply crush Russian producers. Another reform of customs tariffs is needed, with the aim of protecting domestic producers, and not opening the market for foreign companies to enter.
An important task is to restore ties with the Warsaw Pact countries and the CIS countries, it is necessary to return sales markets for the Russian economy, it is desirable to create trade unions such as NAFTA.
Strict measures are needed to prevent the illegal export of capital abroad.
The stock market, in its current form, is highly dependent on the speculative game of non-residents. This is a kind of casino. It is necessary to make the Russian market more competitive, its architecture less distorted, finally introduce tax incentives for investments in securities and start creating “ financial platform"Russia"". Emphasis should be placed on the development of the corporate bond market with a long maturity.
In the near future, a recession in the global economy is expected, so it is necessary to develop the domestic Russian market and increase the solvency of the population.
Property management needs to be improved, both in the private and public sectors. Do not privatize profitable state-owned enterprises for a penny, as is happening now. And fire those managers who advise it.
It is necessary to carry out a full investigation into the privatization of the largest Russian enterprises in order to nationalize the enterprises privatized with major violations and inefficiently managed by the real owners, and for efficient enterprises with a transparent financial structure, to resolve all small violations of the law and close cases. Thus, the owners will be firmly convinced that this is their property and the state will no longer make claims for old offenses.
Reduce the current bias of the national economy in favor of the export-oriented sector of the economy by placing large-scale state orders in the military-industrial complex, nuclear, engineering, aviation and aerospace, chemical and pharmaceutical, electronic industries, and a number of other areas that ensure the creation of goods with high added value. It is necessary to ensure maximum transparency of the entire investment process, for constant monitoring and control.
Create tax incentives for enterprises cooperating in their activities with enterprises from other regions. Moreover, doing this is smarter than the created benefit for small businesses in the form of the abolition of VAT for enterprises with a quarterly turnover of less than one million rubles. After that, other enterprises simply refused to work with beneficiaries, due to the non-reimbursement of VAT by the state.
Reconsider the restructuring plan for RAO UES, which in its present form only leads to a multiple increase in electricity prices, a rupture of the single energy space and the separation of the most economically profitable power plants into the ownership of management and large foreign energy companies.
By all means to increase the well-being of the population, through an increase in wages for state employees, the recognition by the state of a debt to citizens and enterprises, an amnesty for the debts of the latter.
Building a state policy in the field of interaction with national TNCs, by acquiring a blocking stake in them for the provision by the state of equipment, land plots and certain infrastructure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, I would like to emphasize once again that economic security is a characteristic, the essence of which is:
normal functioning of the economic system as a whole;
the possibility of painless inclusion and normal operation of the internal economic system in the world.
In my work, I analyzed the main threats and considered the mechanism for ensuring economic security. Also, general directions for maintaining the economic security of Russia at the proper level were given - these are:
Conducting an effective industrial and structural policy;
Recovery of investment activity;
Rescue of the main array of manufacturing industry and agriculture, scientific and technical potential of the country;
Gradual transition to structural and technological restructuring of production.
From all of the above, we can conclude that in order to create a national structure of its economy that is adequate to market requirements, Russia must go through the painful path of determining its priorities in all areas and at all levels of society and economy. It is necessary to improve the regulatory framework for all types of economic relations. The national interests of Russia in the field of economy are key. A comprehensive solution to the problems associated with the realization of Russia's interests is possible only on the basis of the stable functioning of a diversified high-tech production capable of providing the leading sectors of the economy with high-quality raw materials and equipment, the army with weapons, the population and the social sphere with consumer goods and services, and foreign trade with - competitive export goods. Russia should not just join the modern world economy, but predict its role and place in the global division of labor. One cannot ignore the fact that no one is going to solve Russian problems to the detriment of their national interests. Therefore, when making decisions to ensure economic security, one should be wary of advice from other countries that, in pursuing their foreign policy, take care, first of all, of their own interests. Of course, foreign experience should be used, but taking into account the Russian specifics of the economic situation.
Bibliography
Arsentiev M. Economic security. / M. Arsentiev // Observer. 1998. No. 5. S.10-11.
Bogdanov I.A. Economic security of Russia: theory and practice. / I.A. Bogdanov. M.: ISPIRAN, 2005. 263 p.
Ippolitov K.Kh. Economic security: Strategy for the revival of Russia. / K.Kh. Ippolitov. M.: INFRA-M, 1996. 503 p.
Kononov D.A. Formation of scenario spaces and analysis of the dynamics of the behavior of socio-economic systems. / YES. Kononov, V.V. Kulba, S.S. Kovalevsky, S.A. Kosyachenko. M.: Preprint IPU RAN, 1999. 184 p.
Nekipelov A.D. Consequences of globalization in the financial sector. Macroeconomic and financial policy in crisis situations: world experience and Russian reality. Materials of the situational analysis. / A.D. Nekipelov. M.: IMEPI RAN "EPIKON", 2004. 674 p.
Fundamentals of economic security (state, region, enterprise, personality): textbook / ed. E.A. Oleinikov. M: Business School “Intel-Synthesis”, 1997. 317 p.
Potrubach N.N. Priorities of the state economic policy at the present stage. / N.N. Potrubach // Rossiyskaya Gazeta. 2005. No. 6. S. 7-8.
Senchagov V. How to ensure the economic security of Russia // RF today. 2007. No. 6. S. 5-7.
Similar Documents
Economic security as a basis for ensuring the national security of the Russian Federation. Research of the state strategy of economic security. Description of the main problems of the development of the Russian economy in the context of globalization.
abstract, added 10/17/2015
Economic security as a set of conditions and factors that ensure the independence of the national economy, tasks: curbing inflation and unemployment, reducing the budget deficit. Analysis of the problems of the raw material orientation of Russian exports.
thesis, added 12/18/2012
The concept of economic security. The concept of national security of the Russian Federation, its brief description. Criteria and indicators of economic security of the national economy. Analysis of Russia's economic security indicators.
article, added 03/03/2013
Security is a social phenomenon and a category of national security theory. The concept of national security of the Russian Federation. Threats to national security, the tasks of its provision. The role of economic security in stabilizing the economy.
term paper, added 04/08/2012
The economic potential of the country and the system of national security. Quantitative and qualitative parameters (threshold values) of the state of the economy. The main measures and activities of the state to ensure the economic security of Russia.
abstract, added 08/14/2015
The main threats to the economic security of the Russian Federation, their classification and characteristics. Ensuring the stability and sustainability of the state economy. Psychological reasons for creating dangerous situations in the production team.
test, added 05/09/2014
Economic security as a component of the country's national security structures. The relationship of the country's economic security with the state of the economy. Digital indicators to determine the state of the economy. Economic security of Russia.
presentation, added 09/07/2011
Essence and subjects of economic security. Macroeconomic indicators of the economic security of the national economy. The main trends, factors and conditions of the socio-economic development of the Russian Federation. Ways of Russia's integration into the world economy.
term paper, added 05/20/2014
National economic security, determination of its level and provision. State strategy of economic security of the Russian Federation. The spectrum of threats to the economic security of the country, the main prerequisites and consequences of their occurrence.
test, added 03/29/2013
The concept, essence and concept of economic security. Description of the main criteria and indicators of the economic security of the national economy. Existing and potential threats to the economic security of the Russian Federation at the present stage of development.
Keywords
STATE STRATEGY / ECONOMIC SECURITY / THE FEDERAL LAW/ ECONOMY / STATE STRATEGY / ECONOMIC SECURITY / FEDERAL LAW / ECONOMYannotation scientific article on economics and business, author of scientific work - Burmistrova Alevtina Anatolyevna, Kondrashova Inna Sergeevna, Rodionova Natalia Konstantinovna
The Russian Federation is experiencing a difficult historical period in the formation of the latest socio-economic relations. The transition to new forms of state administration is taking place in the conditions of a constant lack and duality of the legal framework that regulates economic relations, the backlog of legislation from the actions actually taking place in the world. In international relations, the Russian Federation meets with the desire to industrially developed countries, large foreign corporations to use the situation in the Russian Federation and countries of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) in their financial and political interests. All this, without exception, creates a particularly significant purposeful activity to ensure the financial security of the state and its citizens on the basis of a common state strategy. State strategy economic security The Russian Federation is a complex component of the state security of the Russian Federation as a whole. It aims to implement economic transformations in the next three to five years. State strategy forms and concretizes the relevant statements of the developed concept of national security of Russia, taking into account state interests in the field of economy. Strategy economic security and state economic policy categories and instruments of state regulation of the economy should be interdependent and interact with each other. On the one hand, the strategy economic security part of the economic policy reflects its strategic targets, the desired quality of the regulated macroeconomic system. On the other hand, estimates of quantitative parameters that characterize the desired state of the economy determine restrictions on the use of those methods of conducting economic policy, the possible results of which can reduce the level of economic security. This article discusses the main goals and objectives of the development state strategy economic security RF. The principles are presented in accordance with which the state strategy.
Related Topics scientific papers on economics and business, author of scientific work - Burmistrova Alevtina Anatolyevna, Kondrashova Inna Sergeevna, Rodionova Natalia Konstantinovna
-
Formation of a national payment system as one of the directions for ensuring the economic security of the state
-
Shadow economy as a threat to the economic security of the state
2016 / Burmistrova Alevtina Anatolyevna, Kondrashova Inna Sergeevna, Rodionova Natalia Konstantinovna -
Fictitious and criminal economic activity as a threat to the economic security of Russia
2017 / Burmistrova Alevtina Anatolyevna, Rodionova Natalia Konstantinovna, Moiseev Pavel Sergeevich -
Substantiation of new measures to protect the national interests of Russia in the modern world economy
2015 / Klimova Dina Nikolaevna, Kondrashova Inna Sergeevna -
Economic Security in the Context of Globalization: Threats and Opportunities
2014 / Klimonova Anastasia Nikolaevna, Yurina Elena Alexandrovna -
Key areas of fertilizer production in the Tambov region
2014 / Sviridova Anna Ivanovna, Rodionova Natalia Konstantinovna, Burmistrova Alevtina Anatolyevna -
The main approaches to the study of the concepts of "Economic security" and "Economic security of the state"
2014 / Klimonova Anastasia Nikolaevna -
Modernization of the regional infrastructure for the development of agriculture
2012 / Rodionova Natalia Kondrashova, Kondrashova Inna Sergeevna, Burmistrova Alevtina Anatolyevna -
On the strategy of economic security
2016 / Sergey Kazantsev
The Russian Federation tests the difficult historical period of formation of the latest social and economic relationship. Transition to new forms of public administration realizes in the conditions of a constant lack and duality of the legal basis governing the economic relations, lags of the legislation from the actions which are really happening in the world. In the international relations the Russian Federation meets the aspiration of industrially developed states, big foreign corporations to use a situation in the Russian Federation and the countries participants of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) in the financial and political interests. All this without exception creates especially considerable purposeful activities for ensuring financial security of the state and its citizens on the basis of the general state strategy. The state strategy of economic security of the Russian Federation is the difficult making state security of the Russian Federation in general. It aims at realizing of economic reorganizations in the next three-five years. The state strategy forms and specifies the corresponding approvals of the developed concept of national security of Russia taking into account the state interest in the field of economy. Strategy of economic security and the state economic policy categories and instruments of state regulation of the economy have to be in interdependence and interaction with each other. On the one hand, strategy of economic security part of economic policy reflects its strategic target reference points, desirable quality of adjustable macroeconomic system. On the other hand, the estimates of quantitative parameters characterizing a desirable state of the economy define restrictions for the use of those methods of carrying out economic policy, possible results which applications are capable of reducing the level of economic security. In this article, the authors considered the main objectives and problems of development of the state strategy of economic security of the Russian Federation and presented the principles according to which the state strategy is developed.
The text of the scientific work on the topic "State strategy of economic security of the Russian Federation: goals, objectives, principles"
UDC 330.101 doi: 10.20310/1819-8813-2016-11-3-48-52
STATE STRATEGY FOR ECONOMIC SECURITY OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION: GOALS, OBJECTIVES, PRINCIPLES
BURMISTROVA ALEFTINA ANATOLYEVNA Tambov State University named after G. R. Derzhavin, Tambov, Russian Federation, e-mail: [email protected]
INNA KONDRASHOVA Tambov State University named after G. R. Derzhavin, Tambov, Russian Federation, e-mail: [email protected]
RODIONOVA NATALIA KONSTANTINOVNA Tambov State University named after G. R. Derzhavin, Tambov, Russian Federation, e-mail: [email protected]
The Russian Federation is experiencing a difficult historical period in the formation of the latest socio-economic relations. The transition to new forms of state administration is taking place in the conditions of a constant lack and duality of the legal framework that regulates economic relations, the backlog of legislation from the actions actually taking place in the world. In international relations, the Russian Federation meets with the desire of industrialized states, large foreign corporations to use the situation in the Russian Federation and the countries - members of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) in their financial and political interests. All this, without exception, creates a particularly significant purposeful activity to ensure the financial security of the state and its citizens on the basis of a general state strategy. The state strategy for the economic security of the Russian Federation is a complex component of the state security of the Russian Federation as a whole. It aims to implement economic transformations in the next three to five years. The state strategy forms and concretizes the relevant statements of the developed concept of Russia's national security, taking into account state interests in the field of economy. The strategy of economic security and state economic policy - categories and instruments of state regulation of the economy - should be interdependent and interact with each other. On the one hand, the strategy of economic security - a part of economic policy - reflects its strategic targets, the desired quality of the regulated macroeconomic system. On the other hand, estimates of quantitative parameters that characterize the desired state of the economy determine restrictions on the use of those methods of conducting economic policy, the possible results of which can reduce the level of economic security. This article discusses the main goals and objectives of developing a state strategy for the economic security of the Russian Federation. The principles in accordance with which the state strategy has been developed are presented.
Keywords: state strategy, economic security, federal law, economics
The state strategy of economic security of the Russian Federation consists in restoring economic growth in Russia on a new basis and with the help of new institutions of a market economy, ensuring guaranteed protection of national interests, social policy orientation, sufficient defense potential even under adverse conditions for the development of internal and external processes.
The economic security strategy of the Russian Federation is determined by the fact that
even today it has a highly developed production potential, but its development depends on the path it takes.
The first course is the most difficult, leading to progress. It implies political foresight, administrative freedom, will require the use of absolutely all internal resources (this means an inevitable increase in social tension). This course is associated with a difficult restructuring of the elements of financial
control, bringing them into line with the structure of civil society.
The second course involves the use of resources coming from outside. The inevitable consequence (and condition) is the weakening of control, the neglect of the interests of the country's economic security. Such specification is facilitated by the classification of threats to the economic security of the Russian Federation, which is presented in the section on the state strategy of economic security of the Law of the Russian Federation "On Security", which refers to the absence of illusions about the general nature of these threats among the subjects of state-political management.
The difficulties associated with the growth of social deviations (deviations) and socio-political phenomena are put in the foreground. In situations of decline, long-standing contradictions giving rise to social deviations were supplemented by a large number of new ones.
The modern Russian Federation is an impeccable combination of absolutely all conditions: the state of the economy, sharp social differentiation and polarization, economic decline, social disorganization, “change of milestones” in ideology, etc.
The goal of the State Strategy for the Economic Security of Russia is to provide such an economy formation that would organize an acceptable requirement for the existence and formation of the individual, the socio-economic and military-political stability of the community and the preservation of the country's unity, effective opposition to the impact of internal and external threats. Almost none of the issues facing the state, both within the state and internationally, can not be resolved without ensuring economic security.
The implementation of the State Strategy is obliged to create the required conditions in order to achieve the common goals of state security. In particular, ensure:
1) protecting the civil rights of residents, increasing the level and quality of life of the population, guaranteeing social society in the state and peace in the world;
2) effective resolution of internal political, financial and social issues, based on state interests;
3) active influence on movements in society, including those relating to the state interests of the Russian Federation.
The objects of economic security of the Russian Federation are: personality, society,
the government and key components of the economic concept, including the concept of institutional relationships in the municipal regulation of financial activities.
The state economic security strategy includes:
1. Characteristics of external and internal threats to the economic security of the Russian Federation as a combination of factors and conditions that form a threat to the vital economic interests of the individual, community and country.
2. Establishment of criteria and parameters that determine the range of interests of the state in the sphere of economy and corresponding to the conditions of economic security of the Russian Federation.
3. Development of economic policy, institutional restructuring and the required elements that eliminate or mitigate the impact of conditions that undermine the stability of the state economy.
4. Establishment and monitoring of conditions that undermine the stability of the socio-economic concept of the country in the short and medium term (three to five years) perspective.
In order to counteract threats to economic security, public authorities and local governments, in cooperation with civil society institutions, implement the state socio-economic policy, which provides for:
ensuring the stability of the macroeconomic situation, stimulating economic growth rates that exceed those of developed countries, supporting the real sector of the economy;
Improving the efficiency and quality of state management of the economy, reducing costs and inefficient budget expenditures, combating the misuse and theft of public funds, corruption, and increasing the efficiency of managing state-owned assets;
Strengthening the financial system, ensuring its sovereignty, stability of the ruble exchange rate, optimization of currency regulation and control, reduction of inflation, development of the national infrastructure of financial markets, reduction of bank rates, increase in the level of direct investment, availability of lending through long-term money, attraction of domestic savings, deoffshorization of the economy, the return of Russian capital and the reduction of its export abroad;
A. A. BURMISTROVA, I. S. KONDRASHOVA, N. J. RODÜNOVA
ensuring a balanced budget system and improving interbudgetary relations in the Russian Federation;
Increasing the attractiveness of the Russian jurisdiction, improving the conditions for entrepreneurial activity, developing competition, developing new approaches to the activities of state control (supervision) bodies, ensuring the stability of the tax and legal systems, guaranteed protection of the right to private property and the implementation of contracts;
Implementation of rational import substitution, reduction of critical dependence on foreign technologies and industrial products, the accelerated development of the agro-industrial complex and the pharmaceutical industry;
development of new high-tech industries, strengthening of positions in the field of space exploration, nuclear energy, the return of leadership in traditional industrial sectors (heavy engineering, aircraft and instrumentation), restoration of electronic and light industries, shipbuilding and machine tool building, as well as systems for statistical assessment of the level of technological state branches of the economy;
Development of the country's military-industrial complex as an engine for the modernization of industrial production, renewal of the production base of organizations of the military-industrial complex on a new technological basis, improvement of their human resources and production of civilian products in demand;
creation of strategic reserves of mineral resources sufficient to guarantee the mobilization needs of the Russian Federation and the needs of the country's economy in the long term;
Formation of a single transport space based on a balanced outstripping development of an efficient transport infrastructure and an increase in the level of transport connectivity of the Russian Federation, the creation of transport corridors and multimodal transport and logistics hubs, an increase in the volume and improvement in the quality of road construction;
Expansion of the use of public-private partnership tools for solving strategic problems of economic development, completion of the formation of basic transport, energy, information, military infrastructures, especially in the Arctic, Eastern Siberia and the Far East, development of the Northern Sea
way, the Baikal-Amur and Trans-Siberian railways;
Stimulating the development of small and medium-sized businesses in the manufacturing sector by reducing the costs associated with starting a business, supporting it at the stage of formation by reducing the tax burden, creating business incubators, industrial parks and technology parks, creating demand for the products of small and medium-sized enterprises, expanding access to procurement by state-owned companies, participation in the implementation of large projects;
Reducing informal employment and legalizing labor relations, increasing investment in the development of human capital;
Ensuring a balance of interests of the indigenous population and labor migrants, including foreign citizens, taking into account their ethnic, linguistic, cultural and confessional differences, improving migration accounting, reasonable territorial distribution of labor migrants based on the needs of regions in workforce;
Development of international business contacts, attraction of foreign investments and technologies, implementation of joint projects, expansion of sales markets for Russian products, counteraction to attempts by foreign states to regulate world markets based on their political and economic interests.
The state strategy for the economic security of Russia should be developed, adopted and implemented in accordance with the principles of structuring the elements of economic security based on the method of a systematic approach; consolidation; the effectiveness of state regulation in the field of ensuring economic security; long-term; internal consistency of the elements of the economic security system.
The state strategy for the economic security of the Russian Federation should establish (or assume) a system of strategic priorities, goals and measures in the field of domestic and foreign policy aimed at ensuring economic security.
Economic security is the state of the economy in which reliable economic growth is maintained, the needs of the population are met, and there is effective leadership. Ensuring the economic security of the state must have the nature of state policy and involve the totality, the concept of the facets of the socio-political, economic,
administrative-regime, propaganda and special nature, connected by a cunning plan, common targets and problems.
Literature
1. Agaev I. A. Features of the concept of national security in modern conditions // Russian entrepreneurship. 2014. No. 13 (259).
2. Balynin I. V. Comprehensive analysis of debt policy within the rating score subjects of the Russian Federation according to the level of risk of imbalance in regional budgets // Economics and Entrepreneurship. 2014. No. 5.
3. Radyukova Ya. Yu., Pakhomov N. N. Formation of the competitive advantages of the national economy based on the modernization of industrial policy // Scientific notes of the Tambov regional branch of the Free Economic Society of Russia: collection: Tambov, 2015. P. 126-135.
4. Radyukova Ya. Yu. Natural monopolies in the system of economic relations of the national economy // Socio-economic phenomena and processes. Tambov, 2013. No. 2 (48). pp. 96-101.
5. The State Strategy for the Economic Security of the Russian Federation (Basic Provisions) was approved by Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of April 29, 1996 No. 608 URL: http://www.scrf.gov.ru-/docu-ments/23.html
6. Strategy and problems of Russia's sustainable development in the 21st century. / ed. A. G. Granberga [et al.] M., 2014.
1. Agaev I. A. Osobennosti kontseptsii natsional "noj bezopasnosti v sovremennykh usloviyakh // Ros-sijskoye predprinimatel" stvo. 2014. No. 13 (259).
2. Balynin I. V. Kompleksnyj analiz dolgovoj politi-ki v ramkakh rejtingovoj otsenki sub "yektov Rossijskoj Federatsii po urovnyu riska nesbalansirovannosti region-al" nykh byudzhetov // Ekonomika i predprinimatel "stvo. 2014. No. 5.
3. Radiukova Ya. Yu., Pakhomov N. N. Formirova-niye konkurentnykh preimushchestv natsional "noj ekono-miki na osnove modernizatsii promyshlennoj politiki // V sbornike: UCHENYE ZAPISKI Tambovs-kogo regional" nogo otdeleniya Vol "nogo ekonomicheskogo obshchestva Rossii Tambov, 2015. S. 126. 126. S. 126 .
4. Radyukova Ya. Yu. Estestvennye monopolii v sisteme ekonomicheskikh otnoshenij natsional "nogo kho-zyajstva // Sotsial" no-ekono-micheskiye yavleniya i protsessy. 2013. No. 2 (48). S. 96-101.
5. Gosudarstvennaya strategiya ekonomicheskoj bezopasnosti Rossijskoj Federatsii (Osnovnye polozheniya) odobrena Ukazom Prezidenta RF dated April 29, 1996. No. 608 . URL: http://www.scrf.gov.ru-/documents/23.html
6. Strategy i problemy ustojchivogo razvitiya Rossii v XXI century / pod red. A. G. Granberga i dr. M., 2014.
STATE STRATEGY OF ECONOMIC SECURITY OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION: PURPOSES, TASKS, PRINCIPLES
BURMISTROVA ALEVTINA ANATOLYEVNA Tambov State University named after G. R. Derzhavin, Tambov, the Russian Federation, e-mail: [email protected]
KONDRASHOVA INNA SERGEEVNA Tambov State University named after G. R. Derzhavin, Tambov, the Russian Federation, e-mail: [email protected]
RODIONOVA NATALIYA KONSTANTINOVNA Tambov State University named after G. R. Derzhavin, Tambov, the Russian Federation, e-mail: [email protected]
The Russian Federation tests the difficult historical period of formation of the latest social and economic relationship. Transition to new forms of public administration realizes in the conditions of a constant lack and duality of the legal basis governing the economic relations, lags of the legislation from the actions which are really
A. A. BURMISTROVA, I. S. KONDRASHOVA, N. K. RODIONOVA
happening in the world. In the international relations the Russian Federation meets the aspiration of industrially developed states, big foreign corporations to use a situation in the Russian Federation and the countries - participants of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) in the financial and political interests. All this without exception creates especially considerable purposeful activities for ensuring financial security of the state and its citizens on the basis of the general state strategy. The state strategy of economic security of the Russian Federation is the difficult making state security of the Russian Federation in general. It aims at realizing of economic reorganizations in the next three-five years. The state strategy forms and specifies the corresponding approvals of the developed concept of national security of Russia taking into account the state interest in the field of economy. Strategy of economic security and the state economic policy - categories and instruments of state regulation of the economy - have to be in interdependence and interaction with each other. On the one hand, strategy of economic security - part of economic policy - reflects its strategic target reference points, desirable quality of adjustable macroeconomic system. On the other hand, the estimates of quantitative parameters characterizing a desirable state of the economy define restrictions for the use of those methods of carrying out economic policy, possible results which applications are capable of reducing the level of economic security. In this article, the authors considered the main objectives and problems of development of the state strategy of economic security of the Russian Federation and presented the principles according to which the state strategy is developed.
Key words: state strategy, economic security, Federal law, economy