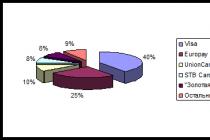
In Western Europe, there are 58 different stock exchanges in 17 countries. In the leading capitalist countries, the stock market is of great, though far from equal, importance. This concerns, first of all, the UK, Switzerland, Holland and also France, Germany, Belgium and the brightly specific market of Luxembourg. In countries such as Austria, Italy, Spain and also in the Scandinavian countries, the role of stock markets is small. In Greece, Ireland, Portugal, they practically do not matter.
Obviously, the largest Western European stock market is English, much smaller than the American one, but at the same time much larger than other Western European ones - Swiss, German and French. With regard to the importance of the stock market and the reproduction of capital, the leading role, on an equal footing with the United States, is played by the stock markets of Great Britain and Switzerland, but here one should take into account the large share of foreign shares. The Dutch stock market plays a much smaller role, and the French, Belgian, and German markets play an even smaller role. Of the bond markets, the largest is in Germany, the second largest in the UK, and their lagging behind the US is less significant. The bond market is most important in the economy of Great Britain, Belgium and Germany.
But the difference lies not only in the volume and significance of stock exchanges. A number of differences are shown by a brief description of the leading Western European stock markets.
UK stock market
The UK stock market is traditionally, due to the significant capitalization of British monopolies ($324 billion in 1992), an important part of the country's credit and financial mechanism. Wide re-privatization public sector gave a significant impetus to the growth of stock capitalization. In 1967, all the country's stock exchanges were merged into regional stock exchanges in Manchester, Birmingham, Glasgow and Belfast. The clear leader is the London Stock Exchange. She is joint stock company and is not subject to direct state control. Its leadership is carried out by the Board of the exchange, consisting of 45 members, including one representative Central Bank without the right to vote. The council is elected by a meeting of 4482 members and "self-regulates" in cooperation with Central Bank stock exchange activity.
Shares and bonds are issued mainly in nominal form. Bearer securities are allowed, but are not common among English issuers. Foreign shares must be kept in special depots of authorized credit institutions. Transactions are made, basically, on time. Bonds are realized by cash transactions. The current course is set. Exchange trading covers a very large share of the total turnover of stock values. Trading in unlisted securities conducted on the exchange with the permission of the board of the exchange. Since 1980, the so-called mini-exchange has been operating at the exchange with reduced admission conditions for the exchange circulation of shares of medium and small firms.
The very large share of foreign securities confirmed the great importance of London as an international financial center and in the field of stock markets, for example, as largest center Eurobond loans. In recent years, the London Stock Exchange has been the scene of significant change as part of the reform carried out from 1983 to 1986, which, in turn, had a significant impact on the reforms of other Western European stock markets. The reform is aimed mainly at increasing its international competitiveness and, thereby, at strengthening the position of British capital.
So, as part of this reform, the traditional, purely English division of brokers into brokers and jobbers was removed. Their functions are now performed by the same brokers. The reduction in commissions associated with this simplification was supplemented by a reduction in the taxation of stock turnover. Computer technology was widely introduced into the work of the exchange. British brokerage firms (about 200) lost their monopoly in stock transactions. First, 29.9% participation was allowed, and then 100% takeover of these firms by industrial and banking monopolies. This was taken advantage of by the British monopoly banks, which actively invaded the area of stock transactions previously closed to them.
Swiss stock market
The Swiss stock market is characterized primarily by its international functions. In the Swiss economy, it plays, on the one hand, the role of a source of financing for the reproduction of national capital and, on the other hand, is an important component of the credit and financial system, which, due to its international significance, is an extremely important "branch" of the Swiss economy. There are 7 stock exchanges in the country, among which Zurich, Geneva and Basel stand out. Monopoly position in the stock market big banks that determine the course of events there. There are no special brokers on the stock exchanges. All operations are carried out by representatives of banks. Along with banks, about 120 brokerage firms operate on the over-the-counter market alone, most of which are foreign. The over-the-counter market is significant. Along with the cash market, there is a developed market for term transactions. A single course is established. State regulation subtle, but there is a fairly strict banking "self-regulation", for example, in terms of the sequence of emissions.
The importance of Switzerland as an international financial center is clearly reflected in the stock market, where about half of the shares and almost 1/3 of the bonds are foreign. Here the Swiss monopoly banks, using the stock market subordinate to them, act as intermediaries between foreign borrowers and creditors. The Swiss stock market is something of a spinning disc for international capital inflows. But thanks to the presence of such a developed stock market adapted to the needs of international financial capital, it has also become an important element in the reproduction of Swiss capital. Thus, the significant capitalization of Swiss corporations - $59 billion in 1992 - testifies to this. This is what distinguishes the Swiss stock market from the Luxembourg stock market. The latter is almost exclusively bonded and has almost no effect on the country's economy.
Holland stock market
The stock market in Holland is notable for, although less bright than, for example, in Switzerland, the international focus, but it has, nevertheless, intensified in recent years. The main stock exchange of the country is the Amsterdam Stock Exchange founded in 1602. The Stock Exchange is a private institution that is subordinate to the "Union for stock trading", uniting banks and brokerage firms. All its 255 members are allowed to exchange trading - both representatives of banks and brokers.
Implemented cash transactions, there is a very developed market for term transactions, which are traditionally of great importance here. For the shares of Dutch and foreign TNCs, the current rate is set, for all the rest - a single rate twice a day. There is no over-the-counter market. Trading in non-quoted securities is carried out on the stock exchange before or after the regular exchange session. In 1982, a mini-exchange was created for the shares of smaller companies. The importance for the reproduction of both international and Dutch capital is significant. Foreign shares make up approximately 55% of the exchange capitalization. But the capitalization of Dutch corporations - $ 48 billion in 1992 - important factor their reproduction, although half are the shares of two corporations: Royal Dutch and Philips.
French stock market
The French stock market is an important part of the tools of state-monopoly regulation. Among the seven French stock exchanges, the Parisian stock exchange is the clear leader. stock exchanges local importance are located in Bordeaux, in Lyle, in Lyon, in Marseille, in Nancy and in Nantes. The state regulation of the stock exchange dates back to the reign of Napoleon and was introduced by his order after the speculative excesses that shook the French credit and financial system. Today, the stock exchange is subordinate to the Ministry of Economy and Finance, which appoints brokers (about 80 in Paris) who have a monopoly on stock transactions inside and outside the exchange. State supervision, as well as admission to exchange trading, is carried out by the exchange commission.
A single course is established. Commission averages. There is both a cash register and futures market, but each share is allowed only one type of transactions. Until 1986, all shares in France were registered, but now there is an active transition to non-cash shares, which now account for 35% of the total number of all shares. The capitalization of French corporations is substantial. A factor in its further growth is the privatization program for a large share of the public sector. As part of the exchange reform, a mini-exchange was created and a certain "deregulation" of stock circulation was carried out. Various measures have been taken to provide tax incentives for investments in securities.
For the purposes of international competitiveness, further lifting of various restrictions is planned. Even undermining the monopoly of brokers in favor of expanding the range of activities is being discussed. financial institutions and attracting foreign intermediaries. But so far, the international functions of the French stock market, due to its relatively strict state-monopoly regulation and also the low level of liberalization of international capital flows limited.
German stock market
There are 7 stock exchanges in Germany located in Frankfurt-Main, Düsseldorf, Bremen, Hamburg, Hannover, Munich, Stuttgart and Berlin, among which the Frankfurt and Düsseldorf stock exchanges stand out, realizing 51% and 39% of the total exchange turnover. Stock exchanges are public institutions and are subject to, according to federal structure countries, lands. The council managing the activity of the exchange is elected by its members - brokers, among whom representatives of banks predominate. The market is predominantly cash market. Forward transactions are only allowed in the form of options. For the majority of shares, a single rate is set; for the shares of large monopolies, the current rate is determined. Commission averages.
A distinctive feature of the German stock market is the enormous influence exerted by monopoly banks throughout their development. The stock market is relatively small, the capitalization of corporations is about 580 billion marks. The bond market is more developed, but first of all, government and bank bonds are circulated there. The traditionally close ties between banking and industrial capital explains the preference for using medium- and long-term bank loans over the use of securities. German banks "prefer to issue loans than mediate access to the stock exchange." Monopoly banks almost completely monopolize the stock market. They are engaged in the issue and placement of securities, actively participate in the secondary market and own large blocks of securities themselves. Influence based on own, direct ownership of shares (about 9% of all shares) is multiplied by shares held in trust departments. Thus, the share of German banks in the disposal of capital is very significant.
Germany's financial capital is highly organized and relatively stable structures. About 48% of all shares are permanently owned and circulated only formally. The secondary market is therefore not very active, although the turnover on the exchange is only a part of the stock turnover, since many transactions are carried out directly between banks, bypassing the exchange. government intervention weak.
The Federation, the Länder and their bodies are actively using the bond market to refinance public debt. In recent years, the state has been more actively trying, through tax rebates and reprivatization of the public sector, to encourage both the issuance and acquisition of shares, and their exchange circulation.
Belgian stock market
The Belgian stock market, although not very large, is essential in financing the reproduction of national capital. The Brussels Stock Exchange is central. The stock exchanges in Antwerp, Ghent, Liege have a provincial character. The exchange is an independent institution, which is under the supervision of the Ministry of Finance. Brokers have the monopoly right to conduct transactions with securities. Trade in unlisted is carried out, as necessary, on the stock exchange. Deals for the term have become widespread. Commissions are relatively low.
The exchange capitalization is significant, although about 1/3 is accounted for by the shares of the Petrofina concern. In 1992, it amounted to 859 billion bp. fr. There are quite a few foreign securities in circulation, but the nomination of Brussels as the "Western European capital" had little effect on the stock market.
Italian stock market
Although Italy is among the economically developed countries, the country's stock market is extremely underdeveloped. It is purely national, aimed mainly at securing the financing of the public debt. The country's main stock exchange is located in Milan, along with which there are 7 more local exchanges. As a reflection of the relatively low concentration in many industries, the capitalization of Italian corporations is low - $ 43 billion in 1993.
The main subject of exchange trading are Italian government bonds. This is facilitated by strict state control of the exchange itself and the corresponding tax policy. The exchange itself is a public legal institution and is subordinate to the Ministry of Finance. Others characteristic features of the Italian stock market are: a high share of the OTC market, weak legislative support for the circulation itself, the absence of a formal ban on insider trading. Shares are issued registered, bearer bonds. Transactions for a period of time are not permitted. The course is set uniform. The international significance is reduced in fact, due to an undeveloped market and a lack of capital, to zero.
Making money abroad has always attracted the attention of domestic freelancers. In popular blogs, the authors highlight the achievements of foreign colleagues and advise to learn from their experience. Masters of various industries cooperate with customers in Europe and America, succeed and have a good income.
The idea came to me to have a close acquaintance with foreign freelance exchanges. I wonder if any of you have already studied their principles and structure? If not, we will start right now, and if so, I will share my own impressions with you.
The first thing I will mention is salaries. From beginners, you can hear talk about "paradise places", where specialists receive exorbitant amounts. In fact, in order to count on a decent salary, it is necessary to correctly assess the forces. Exchanges are international, and people from hundreds of corners of the Earth work on them. Fierce competition exists in every segment:
- programming,
- design,
- copywriting,
- 3D modeling,
- engineering, etc.
Especially knock down the prices of Indian, Chinese and Pakistani specialists. These "daredevils" are ready to make websites for 30-50 dollars and for the same price they will create an architectural project two-storey cottage. For Europeans, this “oriental color” makes their hair stand on end. Yes, and Internet guest workers from Russia will find such prices ridiculous.
But there is also good news. There are more offers on foreign sites. And if employers need really high-quality work, then they try not to turn to comrades from China or India, but are looking for experienced professionals, albeit for serious money. Next, we turn to specific examples.
One of the most famous English-speaking exchanges, owned by the Australian company Freelancer Limited. Positions itself as the first largest crowdsourcing site in the world. At the time of writing, the number of completed projects is about 11 million, and registered users - 22.500.000. Since its foundation, this colossus has absorbed several projects:
- vWorker (USA),
- LimeExchange (USA),
- Scriptlance (Canada),
- EUFreelance (Sweden),
- GetAFreelancer (Sweden),
- Freelancer.de Booking Center (Germany),
- Freelancer.co.uk (UK).
Among similar resources, the platform has the highest Alexa rank (an indirect assessment of site traffic). This means that it is "live" and is of interest to employers. Agree, the statistics are impressive.

The main areas of cooperation are as follows:
- web development,
- creation software,
- services of lawyers and legal consultants,
- Accounting,
- mobile games and apps
- text writing,
- marketing,
- engineering,
- content management.
The specialization is varied. There are projects like 15 at. e., and within 200-500 USD.
Large, young and ambitious resource. The company merged two popular freelance exchanges, oDesk and Elance, and entered the market in the spring of 2015. The unique feature of Upwork is that an agent can receive an order with an hourly rate or a fixed budget. In the first case, the system requires the performer to install a special program on the PC to enter screenshots into his diary, where the stages of the work being performed are visible. Therefore, to sit back and stretch the time will not work. Only hardcore.
Here is a lesson for those who understand:
- web design,
- mobile apps,
- programming,
- creating articles,
- accounting business,
- marketing,
- graphic design,
- management and sales.

On the exchange it is allowed to use useful tools:
- Jira: bug tracking system, serves to organize interaction between users;
- Google Drive ("Google Drive"): for storing and sharing information;
- GitHub: online service for hosting and collaborative development of IT projects.
Specialists can unite in groups, collaborate, demonstrate to the customer the statistics of successfully completed tasks, supplement the portfolio with a video presentation.
This resource has been around for ten years, but it caught my eye recently. What I noticed on this exchange really surprised me. I will say more, I began to respect the Western approach to business. So, let's move on to review.
The profile of this site is narrower than that of the previously considered ones. She specializes in creating and selling content. Therefore, the lion's share of orders - for those who write, that is, for copywriters. But not only. Other vacancies available for:
- SEO optimizers,
- webmasters,
- translators,
- photographers,
- text designers.

At first it seems that there are no differences from Russian text platforms. But then I noticed one thing. Can you imagine? They have three schemes for acquiring content:
- Usage: The article is only purchased for publication, but you do not own the article. The same text can be purchased by others.
- Unique: you get a guarantee that the project has not been published anywhere and by anyone before. But full copyright does not come, and the buyer is obliged to use the content in its original form.
- Full Right: The owner is given full control over the text and can do whatever they want with it.
The first type is the cheapest, the last is the most expensive. At the same time, the author independently decides under which license to put the product on sale. The price for an average article (3000-4000 characters) is 35-65 dollars. But there are pearls for 100-200 USD.
A copywriter abroad is not just a person who has a good command of the word. It requires knowledge of the accepted terminology, understanding of the mentality of the target audience, the ability to use metaphors and lexical units. With a school level of English, there is frankly no chance of success.
Another nuance of the site: the calculation is carried out not by characters, but by the number of words. In the early stages, this approach will be unusual. But then you get involved and start counting “other categories”.
Also on "Constant Content" there is a store of images, drawings and videos. A very well thought out business move. Why torment the Internet in search of media files, if everything is collected in one place? In this section there is a part-time job for photographers and videographers.
Summing up: what determines the earnings of a freelancer
Registering on a foreign exchange does not mean starting to earn good money. Fees depend on the following factors:
- qualification and ability to improve it;
- ability to focus;
- the time you are willing to devote to work;
- the ability to find customers and negotiate with them;
- experience, positive feedback;
- content portfolio.
The better you do with the above, the higher the potential opportunities. Good luck!
Evgeny Zapletin says
I am developing mobile applications and more than three years I have been working on the international freelance exchange Upwork. I also blog jff.name , in which I talk about the features of working with foreign clients and the specifics of foreign exchanges. Today I will share my opinion about the pros and cons of working on international freelance platforms.
Recently, many have decided to try their hand at the international market due to a decrease in the level wages Russian-speaking freelancers due to currency fluctuations.
As in the Russian-speaking environment, there are a large number of different international exchanges, but, in fact, only a few of them deserve attention:
- upwork. The exchange that appeared as a result of the merger of two giants of international freelancing Elance and oDesk. A huge number of orders in various areas are published on this site every day, however, there are also many freelancers here.
- TopTal. This site positions itself as an exchange of specialists high level. In order to register there, you must pass a preliminary interview via Skype with a representative of the exchange, which checks knowledge of the English language and technical skills. Here the employee does not look for the project himself, but the exchange managers select contractors for each client and monitor the quality of implementation. Hourly rates are high, but there is not as much freedom as with regular freelancing.
- Freelancer.com, freelance.com, guru.com - general purpose exchanges similar to Upwork but less popular among clients and freelancers.
- There are also specialized exchanges, for example, 99designs.com, where only graphics-related projects are published, but there are no popular exchanges only for programmers now.
You can also check out the tproger editors.
AT this moment I work for Upwork and I'm fine with it, so my experience is more relevant to this exchange, but my friends make good money on other exchanges as well.
Advantages of working on foreign exchanges:
- earnings in foreign currency, no influence of exchange rate fluctuations on payment;
- the decency of clients is on average higher than on local exchanges;
- international exchanges are more loyal to their users;
- high wages;
- a large selection of freelance projects;
- on international exchanges, they love Russian-speaking freelancers and consider them the most professional workers.
But, despite this, of course, there are a number of disadvantages when working on foreign exchanges:
- difference in mentality;
- the problem of time zones;
- the need for knowledge of English to communicate with the client and support the exchange;
- the need to understand the local characteristics of the client;
- the difficulty of withdrawing funds and their legalization;
- big competition.
And not everything is obvious here.
If everything is clear with the exchange rate, then, for example, decency is more associated with the mentality and severity of laws in the West. Exchanges carefully monitor fraud and, at the first suspicion, freeze the profile, and if guilt is proven, the profile will be blocked forever and there will be practically no opportunity to create a new one. And although there are still clients who are trying not to pay for the work, but such a minority, they are easy to identify even before the start of the stock exchange history project.
However, the difference in mentality and local features adds a number of problems: it is necessary to understand what exactly the client wants if the client does not accurately describe technical task. For example, when implementing address geocoding, you will not be able to operate with the “regions” you are used to, since other countries have a different structure, for example, “regions” and “provinces”, and you need to know this. Also, a surprise for you may be the disappearance of a client in the middle of the working week, and the reason will be just a national holiday that you did not know about.
Unlike popular Russian-language exchanges, there is no need to buy any “pro” accounts or other ways to promote on the exchange to start working. Platforms earn on commission and take it after the fact. Therefore, to start working and take your first order, you only need to spend your time.
While you do not have reviews on the stock exchange, it will certainly be difficult to get a job, but it is quite realistic. In my opinion, there are several criteria that should be considered when taking your first order:
- fill out the profile on the stock exchange in a quality and complete manner, this will show the client that you are serious about the matter;
- write as individual as possible, which take into account the characteristics of the client and his tasks (the letter that you attach to the application for the project), since Western clients very rarely pay attention to the standard text that you simply copied from a neighboring project;
- respond within 30 minutes after the publication of the order (or better, faster), this will increase the chance that the client will notice you, because if you unsubscribe later, there will already be many competitors.
Although commissions on international labor exchanges are high (about 10%), labor rates compensate for this shortcoming. Paying $30 an hour for popular languages like Java and C# is par for the course, and the average hourly rate is in the region of $10-25 an hour. Such labor rates are extremely rare in local markets, while for Western clients such a price is quite low.
because of a large number users on international exchanges there are many projects, and a freelancer can choose what interests him. So, for example, if you are fond of a highly specialized language or technology, you can find a project for yourself. However, it is almost impossible to compete in the low price category with freelancers from Asia. You have to choose a narrower niche for yourself and develop your skills.
Well, the last significant feature is the problem of withdrawal and legalization of funds. And although at the moment there are a number of companies that greatly simplify this process, you still have to understand the features of international law and financial relations to withdraw your funds.
Withdrawal options vary by location and personal preference. So, for example, for freelancers from some countries, a good opportunity is to withdraw money through PayPal (for example, in Ukraine PayPal does not work for withdrawing money), since due to the peculiarities of the legislation of the Russian Federation, the income received through this system can be registered as income from electronic money. However, this method is not suitable for everyone and you still have to consult a lawyer before using it.
The next option is direct withdrawal to the card in the local bank (simple SWIFT payment), the disadvantage of this approach is the complexity of the legalization procedure, since it will be necessary to register all income as an external economic activity.
The simplest and at the same time complex option is to use international payment systems such as Skrill and Payoneer. The simplicity lies in the fact that they are easy to start using, just order a debit card and start withdrawing funds using it at ATMs.
And the difficulty is associated with the legalization of these approaches, in most post-Soviet countries the activity of such companies is not regulated and therefore their legalization is difficult. Also, such systems have referral programs, so if you want to get an additional cash bonus to your account, then find a special link on the Internet from other users before registering.
The word "stock" comes from the German Boerse or Latin bursa, which means wallet. Exchange- this is a permanent wholesale institutionalized market of the same type of goods and services, where, with the help of numerous intermediaries, operations are carried out related to the sale and purchase of significant consignments of goods at a contractual cost; special kind wholesale trade in products for a wide range of purposes and applications.
International currency and stock exchanges(exchange) - an institutionalized regularly functioning market in which trade is carried out foreign exchange(currency) and securities (stock exchange). Approximately 5–10% of transactions for the real supply of an asset and 90–95% of forward (future) transactions are made on international currency and stock exchanges. Exchange rates (price levels) of currencies and securities are formed on the stock exchange. These courses are a sensitive barometer of any changes in the economic and political life of a country. Rates fall sharply in years of crises and unfavorable market conditions and, conversely, rise during periods of recovery and growth in production. A general drop in stock prices is called a stock market crash.
The organization of the exchange is diverse, but basically it comes down to two types: the exchange as an open market, free for access by all traders, under the supervision of the state (Austria, France, etc.), and the exchange as a closed corporation of traders, accessible only to its members and free from state interference (Great Britain, SSL). Access to the latter is due to a well-known property qualification, recommendations from several members of the exchange and a ballot. From among the exchange corporation, the governing body of the exchange is selected - the Exchange Committee (in the USA - the Board of Governors). Under it, there is a so-called admission commission, which decides on the admission of new securities. It takes measures to ensure that the securities of small and medium-sized joint-stock companies are not admitted to the official exchange. In many countries there are unofficial, sometimes called black, stock exchanges where any securities are quoted.
Thus, there are two types of exchanges: public and private. On public exchanges, transactions can be made not only by members of the exchange. The activities of public exchanges are regulated by government laws. Private exchanges are organized in the form of joint-stock companies and closed corporations. Only shareholders who are members of these exchanges can enter into transactions on such exchanges. Exchange members usually do not receive dividends on their invested capital. Their profit is generated from the rewards received from clients for transactions made for them, i.е. exchange members act as brokers. The Exchange keeps records of operations, determines exchange prices (quotes), facilitates settlements, develops standard contracts, and conducts arbitration of disputes. For this purpose, specialized committees are created in the structure of the exchange, which are led by directors who are members of the board of exchanges. The president is usually at the head of the council.
Currency exchange - this is an element of the infrastructure of the foreign exchange market, the activity of which is to provide services for the organization and implementation of trading, during which equity holders enter into transactions with foreign currency. The currency exchange organizes the work of the basic elements of the infrastructure of the foreign exchange market: the trading system (a mechanism for searching for a counterparty), clearing and settlement systems (a mechanism for executing a transaction). There are currency exchanges specializing in futures trading in currencies and financial assets - the London International Financial Futures Exchange, the European Options Exchange in Amsterdam (European Options Exchange), the German Derivatives Exchange in Frankfurt (Deutsche Terminboerse), the Singapore Exchange (Singapore International Monetary Exchange), Sydney Futures Exchange, Austrian Futures Exchange in Vienna (Oesterreichische Termin Optionsboerse).
A foreign exchange exchange is a place where the sale and purchase of foreign and national currencies, based on the exchange rate relationship between them (quotes), which is formed in the market under the influence of supply and demand. Stock prices depend on purchasing power exchanged currencies, which, in turn, is determined by the economic situation in the issuing countries. Operations on the currency exchange are based on the convertibility of the currencies exchanged on it. The main task of the exchange is not to obtain high profits, but to mobilize temporarily free foreign exchange resources, redistribute them market methods from one sector of the economy to another and in establishing a real market rate of national and foreign currencies in conditions of fair and legitimate trade.
The largest volume of exchange currency transactions falls on London - 32%, followed by New York - 18%, Tokyo - 8%, Singapore - 7%, Frankfurt - 5%, Hong Kong, Paris and Zurich - 4% each, other countries remain about 18%. Unlike the universal London Stock Exchange, currency exchanges in Japan, France and Germany are mainly engaged in fixing reference exchange rates, so they are less significant in the world currency market.
Operations in the foreign exchange markets are carried out around the clock. The financial day starts from Wellington (New Zealand), then - Sydney, Tokyo, Hong Kong, Singapore, Bahrain, Frankfurt am Main, London, New York, Los Angeles. In total, there are three geographical zones of activity currency transactions(times are GMT):
- East Asian, centered in Tokyo, 21:00–07:00;
- European, centered in London, 7:00–13:00;
- American, centered in New York, 13:00–21:00.
The work of the exchange is organized mainly by the brokerage chamber and the board. The competence of the brokerage chamber includes the quotation of currencies and the supervision of exchange brokers. Forex brokers sit at their desks various banks and communicate with each other using a computer and phone. The computer terminal shows the current quotes of all major currencies with the date of transactions. Each big bank sends out its currency quote, i.e. indicates at what rate he is ready to trade. Having found a suitable rate, the buyer's bank contacts the seller by phone and concludes a deal. It takes less than a minute to complete a transaction. If necessary, it is documented. The Board controls the course of official quotations, direct supervision is entrusted to the members of the currency trading committee.
For currency quotes and the formation of exchange rates on the stock exchange, various methods are used. For example, the "Frankfurt Fixing" is used on the Frankfurt Currency Exchange. The essence of this mechanism is as follows: before the start of trading traders - traders in the foreign exchange market - submit orders to the broker with the rates of buying and selling currencies; on the basis of applications, the broker announces the volume of supply and demand of the currency, as well as the minimum rate of its purchase and the maximum rate of sale; then collect additional applications within the announced interval exchange rate. If the volume of orders to sell exceeds orders to buy, the broker reduces the selling rate, if vice versa, it increases the buying rate. With the same order volumes, the buying and selling rates are adjusted in the same proportion. Then new bids are collected and new exchange rate limits are set. Additional bids are collected until the selling rate equals the buying rate and the exchange rate fixes. If the rates match, but the volumes do not, trading continues.
One of the main functions of the Moscow Interbank Currency Exchange is the creation and development of such a mechanism for foreign exchange trading, which allows maintaining stability in the Russian foreign exchange market. The mechanism of exchange trading in foreign currency is constantly being improved. Thus, in Russia since June 1997 the system of electronic lot trades (SELT) has been operating.
SELT removed the previously existing temporary restrictions on foreign currency trading, dramatically increased its efficiency and flexibility on the Russian exchange market. In the system of electronic lot trading, participants have the opportunity to place orders throughout business day directly from remote workplaces, the conclusion of transactions takes place automatically as mutually satisfying applications are entered into the system. Trading participants may enter into transactions in SELT or register off-system transactions within the limit of net transactions and (or) the amount of funds deposited on MICEX accounts. Net transaction limits for bidders are set on a quarterly basis based on their own funds, and cannot exceed $70 million. The contribution of a trading participant to the risk-covering fund is USD 20,000. All-Russian interregional stock exchange was created throughout Russia. currency market. The organization of trading in the purchase and sale of foreign currency is based on the following principles:
- 1) regional interbank currency exchanges (ICE) are merged into a single trading system(ETS) based on SELT MICEX;
- 2) MICEX acts as an administrator providing trading on the UTS, as well as the calculation of the final obligations and claims of interbank currency exchanges and trading participants in Russian rubles and in foreign currency;
- 3) for transactions in euros for Russian rubles trading participants ensure that funds are credited in the currency, the sale of which is planned on the UTS, in the amount of expected transactions;
- 4) on the UTS, trading participants carry out transactions for the purchase and sale of foreign currency for Russian rubles on their own behalf and at their own expense, as well as in accordance with the instructions of clients;
- 5) trading participants accessing trading on the UTS through MICEX make settlements in Russian rubles through the MICEX account in the MICEX Clearing House.
The existing national system of exchange trading covers the leading financial regions of Russia and provides the possibility of simultaneous participation in trading of commercial banks located in different regions and time zones. Now more than 1100 participants have access to the ETS ( credit organizations and their affiliates). As part of the ETS (or morning trading session) trading is carried out in US dollars, euros and the Russian ruble with delivery "today" and "tomorrow", the sale of a part of export earnings. Within the framework of the "day" session, swap transactions, off-system transactions and trading in other currencies are carried out. official rate the Russian ruble against the US dollar and the euro is set on the basis of trading on the UTS.
At a single trading session in SELT MICEX, trades are held for Russian rubles in US dollars, euros, Ukrainian hryvnias, Kazakhstani tenges and Belarusian rubles.
MICEX plans on the basis of modernization and introduction of new technologies:
- prepare a system for conducting electronic dealing transactions (SPREDO). The proposed system takes into account the prevailing realities and traditions interbank market and is focused on providing banks with services for the automated conclusion of bilateral conversion transactions;
- develop access to trading in foreign currencies through open communication channels (Internet) and attract to this new trading participants who are currently conducting transactions on the UTS from the trading floor and through the Reuters system;
- trade of a new instrument - a currency swap. It is necessary to meet the needs of banks in an additional liquidity management tool, as well as to carry forward currency positions to later settlement dates.
Stock Exchange (stock exchange) - an organized and regularly functioning market for the purchase and sale of chain papers. Main functions: mobilization of temporarily free funds through the sale of securities; establishing market value valuable papers; the flow of capital between companies, industries and areas. The stock exchange serves mainly the so-called secondary market securities, on which previously issued securities are traded (in the primary securities market, new securities are sold after they are emissions ). Stock exchanges have the organizational and legal form of private joint-stock companies (USA, Japan, Great Britain) or state institutions(Germany, France). The largest stock exchanges in terms of stock turnover are located in New York, Tokyo, London and Frankfurt. In accordance with their charter, exchanges are usually managed by an exchange committee, which is elected general meeting members of the exchange (they can be both individuals and legal entities). Members of the stock exchange are divided into brokers (brokers ) and dealers and receive a significant portion of their profits from the performance of intermediary operations on behalf of their clients. The purchase and sale of securities on the stock exchange is carried out on the basis of their exchange rate (i.e. their selling price on the exchange), which fluctuates depending on the ratio between supply and demand for them. Registered exchange rates (stock quotes) are published in exchange bulletins and reprinted by many leading economic newspapers and magazines in the world. The average stock price of leading companies (stock price index) is an important economic indicator.
exchange rate - exchange rate of securities. It is determined by the following factors:
- a) current and expected returns;
- b) the size of the banking interest rate (loan interest), the price of gold, certain goods and real estate, since investments in bank accounts, in gold, in goods and real estate are an alternative to the application of temporarily free funds;
- c) liquidity - the ability to turn purchased securities into money without loss;
- d) exchange speculation, i.e. purchase and sale of securities on the stock exchange in order to receive speculative profit from the difference between exchange rates at the time of the conclusion and execution of the transaction.
Under Russian law, a stock exchange can be a non-profit partnership and a joint-stock company. The stock exchange as a non-profit partnership is not commercial organization, created by its members for the purpose of organizing trading in securities according to the rules established by this organization. Its purpose as an organization is not to make a profit, but to create favorable conditions for its members to profit from trading in securities. Initially, stock exchanges existed only as non-commercial, i.e. non-profit organizations. Accordingly, they themselves were not taxed by the state. The stock exchange as a joint-stock company is a commercial organization aimed at making a profit and increasing the market value of its shares. The emergence of commercial exchanges is associated with the process of computerization of the securities market. Development of computer forms of organizing trade in the securities market - a special type commercial activities. The owner of a computer exchange sells access to his computer market, which brings him a constant profit. The organization of exchange trading is turning into an independent type of commercial activity, isolated from commerce in the securities market itself.
Traditional stock exchanges, as non-profit organizations, are beginning to lack the financial resources to improve their trading systems. The only way to solve this problem is to turn them into joint-stock companies, obtain the necessary capital for further development, but at the same time assume obligations to receive profit and pay dividends on their shares.
By law, one shareholder (member) of the exchange cannot own 20% or more of its shares (or votes at a meeting in case of membership). This restriction is not valid if the shareholder (member) of the exchange is another stock exchange.
stock exchange in the form non-profit partnership may be transformed into a joint-stock company by decision of its members.
Participants in the stock exchange differ depending on its organizational form. If the exchange is a non-commercial partnership, then only its members can be participants, i.e. the people who created it. If the exchange is a joint-stock company, then the process of dividing its members into shareholders and participants takes place, i.e. those who get the right to trade on this exchange. Any participant in the securities market can be a stock exchange shareholder. Only professional traders can participate in the stock exchange: brokers, dealers and managers. The procedure for admission to trading on the stock exchange of certain specific participants is established by the stock exchange.
All other participants in the securities market can perform their operations on the stock exchange exclusively through the participants of this exchange. Direct access of investors to the exchange market according to Russian legislation is not yet possible even in a computerized market.
The basic requirements for the activities of the stock exchange are identical to the requirements for all organizers of trade in the securities market. Let's call distinctive features these requirements.
- 1. The rules for admitting securities to trading are divided into two groups: the rules for listing/delisting securities and the rules for admitting securities without going through the listing procedure.
- 2. The stock exchange may approve the specifications of transactions, the fulfillment of obligations under which depends on changes in prices for securities or on changes in stock indices. Such transactions in world practice are called futures and option contracts (for more details, see the specialized literature).
- 3. The stock exchange must ensure the transparency and publicity of its trades: indicate the place and time of their conduct, report the quote of securities, the results of trades, etc. The special significance of this rule lies in the fact that it can be interpreted in two ways: either only a public form of organization of securities trading is assigned to the stock exchange, or the conclusion of transactions with securities in electronic form does not apply to trading.
The main types of income of the stock exchange are:
- contributions of its participants (if the exchange exists in the form of a non-commercial partnership);
- listing fee;
- payment for all kinds of exchange services, primarily exchange fees for concluded transactions; proceeds from the sale of exchange information; income from the rental of premises and equipment; income from the sale of exchange technologies, etc.; receipts for the use of stock indices of this exchange as market assets;
- fines, etc.
The leading expenditure items of the stock exchange, like any other market organization, are:
- operating costs - salaries of hired personnel, Administrative expenses and other operating costs;
- depreciation deductions;
- rent payments for premises and equipment;
- capital costs associated with the introduction of new trading systems: the purchase of equipment, the creation of software, the cost of communication systems, etc.
In the last 10-20 years, the development of the stock market has been in the direction of the development of electronic forms of trade organization. The traditional form of trading in securities is public trading, in which the price is the result of direct ("presence") interaction of market participants. Computerization made it possible to replace the physical interaction of securities traders with their interaction through electronic communications converging in a single computer center, in which the process of concluding transactions takes place according to certain market rules. New stock exchanges in all countries are created from the very beginning as electronic exchanges, in which professional traders interact through electronic networks connecting them.
Generally electronic forms trading in the securities market develop in two opposite directions:
- 1) the evolution of exchange market organizers from public exchanges to electronic exchanges;
- 2) the evolution of professional participants in the non-exchange market towards the creation of an organized electronic market.
The first direction is connected with the transformation of public exchanges into electronic ones. This is characterized by the following logical (and historical) stages:
- 1st stage - creation of an electronic exchange as a set of its members, which are interconnected by electronic networks, and with their customers - in in the usual way(in person, via telephone, fax, etc.);
- 2nd stage - members of an electronic exchange establish electronic communication systems with their customers. The latter, in the presence of computers and special programs, can transmit their orders to brokers for their execution on the exchange;
- 3rd stage - clients of exchange members get direct access to trading on the exchange, but while maintaining control over their actions by a member of the exchange.
Legally, on this kind of electronic exchange, the purchase and sale of securities is still carried out first between the participants of the exchange, followed by accounting for transactions on client accounts, however, in this case, the broker no longer duplicates the client’s order, which directly enters the trading system for execution, although in broker order form. Hence the appearance that the clients themselves are trading. In other words, clients' orders are executed on the exchange, but accounting for all transactions related to them is carried out only through the mediation of the exchange participant (for which the latter, of course, receives his reward). With such an organization of electronic trading, a member of the exchange receives income not from his own transactions with securities (ie not from speculative transactions), but exclusively from his clients, without selling or buying securities on his own. In this case, the physical customer service is replaced not just by their electronic service by a broker, but by e-customer self-service.
In Russia, the revival of exchange trading took place in 1992-1993. At that time, dozens of exchanges were registered and began their activity in almost all regional centers, although already at the end of 1993 exchange activity began to gradually subside, and at the beginning of 1995 only a few dozen exchanges remained. In 1998, after the crisis, in Russian Federation there were a number of currency and stock exchanges, which were concentrated mainly in large industrial centers (such as Moscow, St. Petersburg, Nizhny Novgorod, Samara, Yekaterinburg, Vladivostok, Novosibirsk).
Basic terms and concepts
Bank(bank) - 1) in a broad sense, a system that serves to accumulate (money, information, etc.); 2) a financial institution that accumulates funds and savings, provides loans, implementing cash settlements, release and accounting bills and other securities, issue of money, transactions with gold, foreign currency and other functions.
Broker– an intermediary in transactions with currency, securities, goods, real estate, insurance, as well as in the conclusion of various agreements; mediates between the buyer and the seller for a certain fee; can conclude a transaction on its own behalf, but at the expense of the client.
"Bull"(bull) - a speculator who, believing that prices will soon increase, buys up or retains previously purchased contracts. The term is also applicable to investors who believe that prices will soon increase. Derivative words are also used in commercial practice to describe the investor's point of view:" bullish means an optimistic forecast, bearish means a pessimistic forecast.
Dealer(financial) - 1) a company or individual which operates on the stock exchange (market) at its own expense as a principal; 2) a bank employee specializing in conversion, deposit and other operations in the financial markets.
"Bear" (bear) - a bear speculator, an investor who expects the stock or the entire market to fall. A bear market is a long period of decline in the value of shares, usually by 20% or more. The opposite concept - "bull".
Traders- merchants, "market makers", always ready to buy/sell financial assets on a more or less permanent base own funds or at the request of clients.
Another selection of foreign exchanges little known in Runet. Today there are a few more general ones, an exchange for copywriters and a platform for translators.
freelancermap.com
Marketplace for IT professionals. There are jobs for programmers, web developers, engineers, system administrators. There is no need to pay for registration, they do not take any commission.
Almost 114 thousand users are registered on the site, and the number of projects has reached 4.5 thousand.
On the main page, you can immediately see fresh projects that appear daily. Under the name of each, it is indicated whether an employee is required in the office or remotely.
On the right side of the main page, you can see the profiles of newly registered freelancers. A lot of comrades from Germany.
There are three types of accounts for freelancers on the exchange. : Basic (Free), Premium ($9.65 per month), Business ($38 per month). The publication of projects is free.
Quite a live exchange, a lot interesting projects.
 Exchange for developers of websites, mobile applications and games. Performers from more than 40 countries of the world work here. The site is available in six languages - English, Spanish (by the way, it opens by default), French, German, Portuguese and Italian. Information about projects is closed, completely confidential. Work with the customer - through the manager
, which for each project is selected by a specialist from registered freelancers. We have already seen a similar model of cooperation on many foreign exchanges.
Exchange for developers of websites, mobile applications and games. Performers from more than 40 countries of the world work here. The site is available in six languages - English, Spanish (by the way, it opens by default), French, German, Portuguese and Italian. Information about projects is closed, completely confidential. Work with the customer - through the manager
, which for each project is selected by a specialist from registered freelancers. We have already seen a similar model of cooperation on many foreign exchanges.
The exchange concludes an agreement with each client and contractor. The customer has the opportunity to communicate with a freelancer and manage the project through the exchange.
The site is very concerned about the safety of its users, all payments go through the service only, all stages of work are controlled.
What annoys you is that the manager of the exchange chooses you as the executor. Suddenly you seem to him not qualified enough?
 Programming, translation, consulting, graphic design - these are the specializations of freelancers on this site.
Programming, translation, consulting, graphic design - these are the specializations of freelancers on this site.
Projects that need to be answered are published here - a scheme known to all freelancers. New tasks appear every day, but the size of their budget leaves much to be desired. Registration on the exchange is free . There are two types of account – Basic (Free) and Premium ($10 per month). You can upload your portfolio.
The exchange provides a working area, it is possible to work on a Safe deal.
There are many freelancers from the USA, Canada, Britain, the Philippines, Australia and India.
 Exchange for copywriters. Most of the performers here are from North America and Europe. There is a lot of work and it pays well.
Exchange for copywriters. Most of the performers here are from North America and Europe. There is a lot of work and it pays well.
Requirements for performers quite high:
Minimum - Bachelor's degree (Academic level writers get access to more challenging assignments);
Excellent command of English;
High speed Internet access.
Registration is free. But after filling out the registration form, you need to upload a sample of your work to show your level.
On the exchange there are projects with full and part-time employment. Each work is checked by moderators, so it must be of high quality. For every non-compliance with high standards, you are charged with money. - the exchange has a whole system of punishments. The site has its own check for the uniqueness of the text. For plagiarism, by the way, you are charged 50% of the payment for the order.
Good performers are rewarded with bonuses.
The exchange takes a commission for its services.
 The exchange specializes in proofreading, graphic design, different types art, photography, accounting, programming, marketing, etc.
The exchange specializes in proofreading, graphic design, different types art, photography, accounting, programming, marketing, etc.
Paid for freelancers . Basic account costs $6.25 per month, Silver is $9, Gold is $12.
All projects are categorized for convenience. Recommended projects and recommended freelancers are immediately visible on the main page.
Many performers from USA and India. To be honest, there are not as many projects as we would like, and the pay leaves much to be desired. You can find much more work on the stock exchanges without contributions.
 Already from the name it is clear that this is an exchange for translators. There is a lot of work, and the most diverse translations are needed. Mostly from English to other languages: French, Norwegian, Swedish, Spanish.
Already from the name it is clear that this is an exchange for translators. There is a lot of work, and the most diverse translations are needed. Mostly from English to other languages: French, Norwegian, Swedish, Spanish.
Customers can publish projects or find a translator, indicating from which language to which they need to translate, and from which country the performer should be (optional). By the way, there are not so many of our countrymen who translate from English into Russian.
On the exchange you can see the tariffs for transfers. As you can see, the transfer is relatively inexpensive, with prices hovering around $0.10.
Each translator or translation agency it is possible to create your own website on the basis of the exchange, using a special constructor. The domain name is free, and the site can be made multilingual.
To be continued. There are still a lot of foreign sites for freelancers!