Surely everyone who has ever taken a loan or become a bank depositor, first came across the concept of "bank interest rate":
Interest rate- this is the amount, expressed as a percentage, which is set by the bank for the use of the loan and paid for certain period year, quarter or month.
- If the money is deposited in a current bank account or deposit, the depositor is the bank's creditor and the bank itself is the borrower.
- If the client borrows money from the bank (takes a loan), then the bank is now the lender, and the client is the borrower.
Knowing these simple truths will save you from the complexes that banks inspire in the population, explaining to them many kilometers of formulas for calculating interest with Newton's binomials, factorials, complex roots, powers and other mathematical crap complexity.
The interest rate determines the price of money
In either of these two cases, the interest rate has a valuing monetary dimension: what will be the savings of the depositor or the bank in a month, a year or several years.
The interest rate on depositors' deposits is usually lower than the rate on bank loans. This is the main income of banking and financial institutions- to take money at a lower price and dispose of it by re-borrowing at a higher one.
For depositors, a deposit is mainly a way to save money, not earn money, so deposit rates are now low, and in some European banks they are even negative.
The base interest rate is the lowest loan interest available to large trusted companies and clients. The BPS is usually set by central banks.
Historical note on rates
The historical range of rates is impressive:
- In Germany, for example, the base interest rate fluctuated between 90% and 2% between 1920 and 2000.
- In the UK - 0.5 - 15% in 1989 - 2009.
- In the US, the US Federal Reserve rate in 1954 - 2008 varied between 19% and 0.25%.
- In Zimbabwe, during the hyperinflationary period of 2007, the lending rate reached 800%.
Types of bets
Fixed and floating rates
Interest rates are:
- Fixed - unchanged for a certain period of time.
- Floating - changeable and periodically reviewed by the bank, depending on some indicators.
So, the classic indicator is LIBOR - the average rate of the London Interbank Credit Exchange.
Many banks determine the floating rate by the formula: LIBOR + n, where n is the fixed rate of a particular bank.
Russian banks can rely on an independent indicative rate, such as the MosPrime Rate.
Borrower in a growing market lending rates It is more profitable to take a loan at a fixed interest rate.

By the time of payment, bets are:
- decursive - paid at the end along with the repayment of the loan;
- antisipative - paid in advance when granting a loan.
Decursive rates are beneficial for borrowers, and antisipative rates are beneficial for lenders, but banks usually act in their own interests:
- interest on deposits is calculated decursively,
- credit - antisipative: when issuing a loan, the total interest is immediately determined, which is then divided by the number of periods (usually months).
decursive and antisipative methods are used in calculating simple and compound interest, when the initial amount of capital changes in each reporting period.
- The decursive method is convenient to use with floating rates.
- The antisipative method is convenient during periods of instability as a guarantor of the payment of compound interest.
The decursive rate is also called the loan interest, since it determines the ratio of the income received (interest) to the initial amount of money.
How to calculate the loan interest and the amount of buildup

The formula for determining the loan interest:
i = I/P (1), where:
- i (income) - loan interest;
- I - the sum of all accrued for reporting period percent;
- P - initial sum of money(present value).
The amount of growth F (future value) is determined by the formula:
F = P + i*n*P = P*(1 + i*n). (2)
Here n is the number of billing periods.
The ratio F/P is the growth factor k n .
k n = 1 + i*n. (3)
Calculation of the amount of extensionF is called compounding.
Compounding on the calculation example
- Let's make compounding bank loan in the amount of 1 million rubles, issued at 12% per annum (simple rate), for a period of 10 years according to formula (2)
F \u003d 1,000,000 * (1 + 0.12 * 10) \u003d 2,200,000 rubles.
The initial amount of money issued by the bank on a long-term ten-year loan, often used in mortgages, increased by 1,200,000 rubles, that is, more than doubled.
- You can also calculate the amount of growth for a short period (less than a year). In this case, the definition formula F (2) is transformed:
F = P * (1 + i * d/K). (four)
- d - quantity calendar days for which the loan was taken;
- K is the number of days in a year, i.e. 365 or 366.
Calculate the accrued amount of a loan in the amount of 50,000 rubles issued by an MFI for the annual period specified in the agreement simple bet at 15% for a period of 91 days.
Inserting the values into formula (4), we obtain:
F \u003d 50,000 * (1 + 0.15 * 91/365) \u003d 51,870 rubles.
Often, banks and MFIs require the return of amounts greater than the calculated ones - this means that additional hidden interest was calculated in the form of various commissions. Before concluding an agreement, you should carefully read all its clauses in search of illegal ways to increase capital.

Discounting
The reverse operation - the calculation of the initial amount P by the accrued F - is called discounting.
Discounting is calculated according to the formula:
P = F/ (1 + i*n). (5)
Let's calculate according to the formula (5):
P \u003d 100,000 / (1 + 0.1 * 3) \u003d 76,923 rubles.
Floating rate settlements
If the rate is floating, then the accumulated amount is calculated by summing the rates for each period of their change, and the formula is converted into some kind of abstract formula:
F = P *(1 + ∑(1…N) n*i) (6), where:
- n is a period from one to N;
- i - variable rate;
- ∑(1…N) is the sum of products n*i for all calculation periods.
It looks scary at first glance, but how this happens is very easy to understand by the example:
We use formula (6) for calculation:
F = 500,000 *(1 + 0.11 + 0.5 (0.125 + 0.14 + 0.155 + 0.17)) = 500,000 * 1.405 = 702,500 rubles.
Pay attention to the fact that the growth factor k, calculated at a fixed percentage by formula (3), at a floating percentage is determined by the expression in brackets of formula (6):
K = 1 + ∑(1…N) n*i. (7)
AT this example its value is 1.405.
Compound interest calculations
This calculation method is banking is used when accruing interest on long-term deposits, when interest is accrued on the amount accrued by previous interest.
The formula for calculating compound interest is shown in the figure below.
Rate and inflation
The interest rate can be nominal and real:
- Nominal - set by the bank.
- Real - adjusted for inflation.
The real rate i real is less than the nominal rate i nom by the inflation rate π.
i real \u003d i nom - π.
This formula is usually used when inflation is low. With a large inflation level, calculations are made using the more complex Fisher formula:
i real \u003d (i nom - π) / (1 + π).
The real value of money
To determine the real value of money, taking into account inflation over time, use the formula:
R= N/(1+i)ª.
R is the real value of money;
N is the nominal value;
i - inflation rate;
a is the number of periods (years, months, etc.).
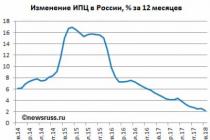
Banks usually increase the interest rate during periods of high inflation, laying its growth in the nominal rate. Such a step, in addition to fighting the fall in the price of money, gives them the opportunity to raise the interest rate on deposits so as not to lose depositors.

Financial illiteracy of the population is beneficial to bankers
Sometimes lending rates, especially fast loans, are contrary to common sense and are a veiled scam. Therefore, understanding what bank interest and how to calculate the amount of the increase should be for everyone who wants to take a loan.
Taking advantage of the financial illiteracy of the population, banks today offer such intricate and complex calculation formulas that an engineer or programmer's calculator requires. Meanwhile, it is quite simple to calculate the total amount of loan payments (aka the amount of the increase), as can be seen from the examples, on a regular calculator and even on a piece of paper. It can be calculated according to different formulas for payments on the body of the loan and on interest, but the deviations between your final calculations and bank ones should still not be too large. Moreover, here are the formulas for calculating simple rather than compound interest, which does not contradict the principles of annuity payments used today in lending.
Banks today practically do not use a differentiated method of repaying a loan, in which the remaining amount of the debt, and not the initial one, is taken into account when calculating interest. This is allegedly motivated by “concern for customers”: why, they say, should they strain their brains and make complex calculations every month? Thus, it turns out that our lending is one of the most unprofitable in the world.
Interest rates represent amounts indicated as a percentage of loans, which are paid by the recipients of credit funds for their use in a certain time period (quarter, month, year, etc.). If we consider interest rates from the position of money, then their value is a store of value.
Interest rates - what are they and how do they work?
Interest rates are based on transactions with other credit institutions. Thanks to their discount rates, Central Banks are able to influence the interest rates that are set in commercial banks, the exchange rate of national currencies, as well as the state inflation rate.
If interest rates fall, then business activity, as well as the inflation rate, rises.
Conversely, during an increase in interest rates, business activity decreases, which leads to depreciation and appreciation national currency.
The interest rate policy is perhaps one of the most important and at the same time rather complex regulatory instruments of activity. banking system. The main principles for constructing a scale of such rates are based on the demand/supply of credit resources, the amount of deposits, storage periods, inflation rates, etc.
What is the structure of interest rates in the general sense?
Interest rates are that part of the profit that borrowers pay to creditors for loans (otherwise a loan) cash, defined as some "irrational form of prices" borrowed money(loan capital).
Loan funds, in turn, are a set of monetary capital that are provided on the terms of repayment for temporary use for a certain amount of payment, expressed as a percentage. The form of movement of loan capital.
There is such a thing as the sources of interest rates, in the role of which is the surplus value formed during the process of productive use of loan funds.
The division of the profit that is obtained during the use of loans into the interest already assigned by the loan funds, and the actual profit itself, represents the entrepreneurial income received by the borrowers and arising under the loan market.
Thus, directly% - you express the relationship between the lenders and borrowers themselves and act as certain interest rates.
Interest rates are determined according to the specific conditions for the use of credit funds and are the subject of credit and monetary regulation from the Central Banks.
We note right away that the value of such rates can contribute to either OUTFLOW money capital from domestic government money markets or, conversely, INFLOWS. For this reason, in such markets, the mobility of funds is very high, and their direct movement between different state markets money capital is displayed in interest rates.
Thus, interest arbitrage is a technical tool that helps to equalize different national interest rates. But we note that in 2015 the movement of money capital is influenced not so much by this technical means how much fluctuation (jumps) in the exchange rate. Now let's look at the main types of interest rates.
Interest rates on loans. What is important to know?
Interest rates on loans are the payment of a loan taken from banks. In other words, this is a payment to your credit institution for the use of its funds during a certain time, i.e. credit resources. As a result, interest rates on loans here are the price of a loan (the price of borrowed money), i.e. the amount of funds that borrowers undertake to pay to creditors for the use of their capital for their needs.
The rate of interest, interest money, interest rate, interest rate, interest per annum, per annum, all these concepts are essentially the same phenomenon - an indicator of the loan price, which reflects the ratio "interest amount / loan amount", i.e. interest on loans. This percentage, in turn, is the amount of income from the provision of funds on credit.
All these concepts are closely related to the periods of accrual of interest on a loan, which are the period of time during which interest is accrued for the use of credit funds. As a rule, this is the period from the moment of issuing credit funds until its full repayment.
Interest rates depend on the types of loans, their amount, designated purpose, term of use, adequacy of ensuring the fulfillment of obligations under the Lending and Liquidity Agreements, the reputation of borrowers and their credit history, discount rates of National banks, inflation rate and other factors.
The main types of interest rates on loans are:
- simple,
- complex (floating),
- short-term
- and long term.
Let's take a closer look. Simple interest rates on loans have a clearly fixed value specified in the contract, for example, in 2015, the size of such rates varies from 10.5% to 14.5% per annum.
We note right away that banks have the right to charge loan interest, only for the period of time during which borrowers actually used credit funds. In other words, the interest on the loan should accrue as it is repaid only on the remaining, outstanding amount.
Borrowers pay interest on the loan along with a certain part (according to the payment schedule determined by the loan agreement) of the main debts. At the same time, loan interest is part of full size loan.
Among other things, interest rates on loans indirectly depend on the terms of the loan itself. So, for example, short-term loans, unlike long-term, as a rule, are issued in banks at a higher interest rate. What explains such a “discrepancy” in the percentage level? It's simple - the desire of lenders to maximize profits with minimal risk and minimal costs.
About interest rates on deposits
First, let's look at the basic concepts. What is bank deposits?
It is necessary to draw your attention to the fact that at excessively high interest rates on deposits, some banking institutions trying to hide their problems.
In other words, they are trying to raise funds at high rates in order to urgently close the "gap" in their balance sheet. If a bank offers you to open a deposit, where interest rates are several times higher than the average market value, then think carefully whether you should trust your savings to it?
How do interest rates affect the Forex market?
As mentioned above, an increase in lending rates leads to an inflow of foreign investors, thereby causing an increase in the exchange rate of the national currency and its rise in price. Reducing the discount rates makes it possible to make loans measured in the national currency cheaper, but at the same time, the amount of money in circulation grows and increases. For this reason, lowering the discount rate can lead to the fact that the exchange rate of the national currency will begin to fall.
If a decrease in discount rates is followed by a slight fall in the exchange rate of the national currency, then, most likely, in the very near future it is necessary to expect its long-term growth, and this without fail must be taken into account by those traders who open long-term deals on Forex.
In addition, interest rates affect those whose trading is not limited only. This moment due to the use leverage provided by brokers.
In other words, is the same loan with minimum term use equal days. For example, you open an order for the EUR/USD pair in the amount of one lot. It turns out that you have EUR available, and you borrow USD to make a purchase.
If, for example, the discount rate for EUR is 1%, and for American currency 2.5%, then you will place your Euros at 1% per annum, and dollars, respectively, at 2.5%. For the transfer of the position in the final result, the commission will be 1.5% per annum or in terms of days - 0.0041% per day.
Interest rates and the impact of inflation on them
Russian
Cash card, Russian Card for receiving cash from the machine.
Money supply, Russian The total money supply that determines the national economy and is in circulation.
Monetary system, Russian
Russian Assets and liabilities that are expressed in a fixed monetary value, for example: balance bank account, trade debtors, loans and trade creditors.
Money and clothing lottery, Russian , see lottery.
Monetary policy, Russian The set of measures in the field of money circulation and credit aimed at regulating economic growth, curbing inflation, providing employment and equalizing the balance of payments; serves as one of the most important methods of state intervention in the process of reproduction.
Monetary regulation, Russian One of the main means of state influence on economic processes. d.-k.r. economy of the Russian Federation is carried out by the Bank of Russia. he defines the rules required reserves, discount rates for loans, establishes economic standards for commercial banks, conducts transactions with securities. The Bank of Russia, in cooperation with the Government of the Russian Federation, develops and implements a unified state monetary policy aimed at protecting and ensuring the stability of the ruble.
Cash reward, Russian Reward in cash.
Money disaggio, Russian Exchange rate deviation valuable papers, stock values or banknotes downward in comparison with their face value. disaggio is usually expressed as a percentage of the face value.
Monetary allowance, Russian View material support military personnel established by the state. d.d. regulated by the federal law of the Russian Federation of May 27, 1998 No. 76-fz "on the status of military personnel" and others regulations. the circle of persons entitled to d.d. composition d.d. consists
Money dimension, Russian End-to-end measurement of results business transactions with the help of money, providing comparable results.
Cash security, Russian
Cash security, Russian A form of collateral for a loan that consists of maintaining a reserve fund from which payments can be made in case of losses and the presentation of relevant claims by investors.
Money circulation, Russian
Monetary obligation, Russian The obligation of one party to pay money to the other party on the basis of an agreement, as a result of causing harm and for other reasons. see also order of repayment of claims under the monetary obligation.
Cash cover, Russian The firm's degree of availability financial support required to make all payments on time.
Cash allowance, Russian
- cash benefits
Directly, Russian Directly, directly, first hand. arch. from the second (fifth, tenth) hands. , myself
Interest rate(interest rate) - the amount indicated as a percentage of the loan amount, which the recipient of the loan pays for using it for a certain period (month, quarter, year).
From the position of the theory of money, the interest rate is the price of money as.
Interest income is income from the provision of capital in debt in various forms ( , ), or it is income from investments in .
Interest rate is a fixed rate at which deadlines interest is paid. Typically, the interest rate characterizes the ratio annual amount percent ( interest income) to the principal amount. The interest rate is also used in the process of accruing value.
Interest rate is a fee charged by banks for loans. The interest rate is the basis of the cost accounting of banks. The interest rate depends on the size of the loan, its maturity, on the ratio of supply and demand for, as well as the degree of risk that a credit institution bears when lending a certain amount debtor.
History of interest rates
For the past two centuries, base interest rates have been set either by national governments or by central banks. For example, the US Federal Reserve Rate ranged from 0.25% to 19% between 1954 and 2008, while base rates ranged from 0.5% to 15% between 1989 and 2009, and the spread base rates in Germany was from close to 90% in the 1920s to around 2% in the 2000s. During an attempt to reverse the hyperinflationary spiral in 2007, the Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe raised interest rates on loans to 800%.
Central bank interest rates
Interest rate - the rate of the central bank on operations with other credit institutions. Through the central bank, it has the ability to influence the interest rates of commercial banks, in the country and.
When interest rates decrease, business activity rises and inflation rises. An increase in interest rates leads to a decrease business activity, reducing inflation and appreciation of the national currency.
The main interest rate in the United States: the Federal funds rate - the interest rate at which banks place available funds, located on accounts in the United States, to other banks on .
The rate in the Eurozone is the Refinancing tender rate - the interest rate that is the lowest possible for applications to raise funds in a tender.
Japan's main interest rate: The target interest rate on overnight loans is the level of interest that it wants to see as an average in the market for short-term deposits.
The interest rate, which is the main one in the UK, the so-called interest rate (Repo rate) is the rate at which the Bank of England issues short-term loans secured by securities.
The base rate for Canada: the target overnight rate (Overnight rate target) is the level of interest that the Bank of Canada wants to see as an average in the market for short-term deposits. To control the level of interest rates in the overnight market, the Bank of Canada establishes a so-called operating range with a width of 0.50%, the middle of which is always the target overnight interest rate.
Australia: interest rate Australian dollar overnight (Cash rate) - an interest rate determined as a result of supply and demand in the money market. Reserve Bank Australia sets the required level of this rate and maintains it by controlling .
Interest rates
Interest rates on loans can be greater than zero, equal to zero (" interest-free loan”) and less than zero (“negative” percentages). If interest rates reach a high value, this leads to usury.
Types of interest rates
There are several types of interest rates.
Fixed and floating rates
Depending on whether the rate changes over time, there are fixed and floating interest rates:
- - permanent, set to certain period and does not depend on any circumstances.
- subject to periodic review. The change in the rate is carried out on the basis of fluctuations of certain indicators. A classic example such indicators is (LIBOR, weighted average rate in London interbank market credit resources). Accordingly, the floating rate LIBOR + 5% will mean that the nominal value of the interest rate is 5% higher than the LIBOR rate.
Decursive and antisipative rates
Depending on the timing of interest payments, there are two types of interest rates:
- decursive rate- interest is paid at the end together with the principal amount of the loan;
- antisipative rate- the interest is paid at the time of the loan (in advance) and is determined on the basis of the final amount of the debt.
For the lender, the antisipative rate is more profitable, and for the borrower, the decursive rate. So, if the interest rate is 10%, then at a decursive rate on a loan of $1,000, the lender will receive $1,100 at the end of the term. At the antisipative rate, he will give the borrower $900 and at the end of the term he will receive $1000.
Real and nominal rates
Distinguish between nominal and real interest rates.
Real interest rate is the interest rate taking into account .
The relationship between the real, nominal rate and inflation is generally described by the following (approximate) formula:
I r = I n - I iwhere I r- real interest rate;
I n- nominal interest rate;
I i- the expected or planned level of inflation.
Irving Fisher proposed a more precise formula for the relationship between real, nominal rates and inflation, expressed by the Fisher formula named after him:
I r = (1 + I n)/(1 + I i) - 1 = (I n - I i)/(1 + I i)At I i = 0 and I i = I n both formulas give the same value. It is easy to see that for small values of the inflation rate I i the results differ little, but if inflation is high, then Fisher's formula should be applied.
According to Fisher, the real interest rate must be numerically equal to the marginal productivity of capital.
All actions of state regulatory bodies, and in particular, central banks, affecting finance and money turnover, are important factors for exchange rates. The price of a currency is determined primarily by the supply and demand associated with that currency on the international market. Therefore, the exchange rates of major currencies are created by the market, but central banks have a range of tools through which they can significantly affect exchange rates. These tools are used by central banks based on the goals of their financial policy(the main of which is the stability of the national currency) and the specific situation, which is determined by the state of the economy, the country's competitive position in the world market and political factors. Therefore, the markets are always very closely watching not only the economy, but also the financial statistics of the main trading countries, trying to predict the actions of central banks based on them.
Monetary Statistics Indicators
The amount of money in circulation (Money Supply) is one of the essential factors shaping exchange rate. An excess of one currency will create an increased supply of it internationally. foreign exchange market and cause its exchange rate to depreciate against other currencies. Accordingly, a shortage of currency in the presence of demand for it will lead to an increase in the exchange rate, characterizing the composition of money (the structure of the money supply). Monetary aggregates themselves are defined somewhat differently in various countries, but their general meaning is quite similar.
M1 - cash in circulation, located outside banks, traveler's checks, demand deposits, other checking deposits;
M2 - M1 + non-check savings deposits, term deposits in banks, overnight REPO operations, overnight US dollar deposits, funds on accounts mutual funds;
M3 - M2 + short-term government bonds, REPO transactions, Eurodollar deposits of US residents in foreign branches of US banks.
US monetary aggregate data is released weekly, usually on a Thursday.
The impact of data on monetary aggregates on currency cycles is assessed primarily through their relationship with the stages of economic cycles. The behavior of various monetary aggregates in business cycle quite similarly: they all show maximum growth rates before the start of the recession and growth minima at the end of the recession. For this reason, aggregate M2, for example, is included in the composite index of leading indicators. All aggregates experience the greatest growth during the recovery stage; M2, on average, has one growth rate in the recession stage and in the growth stage.
According to our estimates, as of September 16, 2019 the best brokers are:
For trade currencies– NPBFX ;
For trade binary options – Intrade.bar ;
For investment in PAMMs and other instruments - Alpari;
For trade shares– RoboForex.

Interest rates
None of the indicators of economics and finance is as important for tracking the dynamics of foreign exchange markets as interest rates. The Interest Rate Differential, that is, the difference in interest rates for two currencies, is the main factor that directly determines the relative attractiveness of a pair of currencies, and, consequently, the possible demand for each of them. There are many types of interest rates in the money market of each country: the rate at which commercial banks borrow money from the central bank (Official Interest Rate), rates at which banks borrow money from each other (Interbank Offered Rate), interest rates that determine the yield of government securities (Government Bonds Yields), interest rates at which banks issue loans to their customers (Lending Rates), interest rates at which commercial banks raise money in deposits (Deposit Rates) All these rates are closely related to each other and, ultimately, are determined by the official interest rate that sets central bank
Thanks to the transparency of the boundaries for financial capital, an investor today can choose the most profitable option for investing his money. Therefore, if a Japanese investor has funds in trillions of yen and can receive income on them in the form of interest on a deposit in a Japanese bank in the amount of, say, 0 1% per annum, then this investor, of course, will prefer a dollar deposit at 5.5% per annum in American bank, or he will buy American government bonds, which also pay high income, and guaranteed
The higher the interest rate for this currency compared to other currencies (large interest differential), the more foreign investors will be willing to buy this currency in order to deposit funds at a high interest rate. And since interest rates are always closely related, high stakes the banking market means both high rates on government bonds, as well as high yields on riskier bonds joint-stock companies. In a word, high interest rates make this currency attractive as an investment tool, which means that the demand for it in the international currency market is increasing, and the exchange rate of this currency is growing.
Central bank interest rates
Market interest rates on loans, deposits, etc. do not arise by themselves in the market element. In each country, credit conditions and interest rates in the money market are regulated by the central bank.
The discount rate characterizes the conditions under which the central bank (CB) provides funds to commercial banks. commercial Bank borrowed the amount S from the Central Bank with a discount rate d (%), this means that in fact the commercial bank received the amount (1 - d / 100) x S at its disposal, and it will return the amount S to the central bank. Usually the discount rate is set as a percentage per annum.
Interest rates (interest rate) of interbank borrowing in many countries are the main instrument of policy of central banks. They go by different names, but common sense one of them lies in the fact that at such interest rates commercial banks borrow funds from each other for a short time to regulate their balance sheets. The difference between the interest rate and the discount rate lies in the method of calculating the amounts. (1+r/100) x S
Officially regulated interbank borrowing rates are the determining day for all other rates money market, they determine the rates on government debt securities, the levels of return on all other financial instruments, interest on loans to bank customers
The main factor that directly and directly determines the exchange rate of one currency against another is the difference in interest rates acting on the two currencies (Interest Rate Differential).
For example, let a bank client have 1 million euros, which are released from the company's turnover for a period of 3 months and can be placed on deposit to generate income. In this case, suppose that the interest rates for the euro are 2.62 percent per annum, and higher rates apply for the dollar at 5 28 percent Then, by converting euros into dollars, you can get more income Let's say today's euro exchange rate is EUR = $1,0400. If you place the amount of 1 million euros in a deposit, then in 3 months the amount will be received.

If you convert 1 million euros into dollars but EUR exchange rate and place them in a dollar deposit, then the amount will be received:

If the euro exchange rate for these 3 months remained the same EUR = 1.0400$, then the result of the second option in euro would be 1.0132, and the difference between the amount received from converting the dollars received back into euro and the result obtained in the first option would be 1.0132 – 1.00655 = 0.00665 million = 6.650 euros, would be the benefit from converting euros to dollars and dollar deposit operation, received due to the difference in interest rates on the dollar and on the euro.
Business Optimism Index
AT developed countries widely published regularly published indexes of business optimism, calculated on the basis of a survey on the state of the economy of leading businessmen - heads of large corporations.
In the US, this is the NAPM (National Association of Purchasing Management) index, in the UK, the CVI (Corporation of British) index.
Recently, Russia has also been calculating and regularly publishing indices of business optimism of Russian entrepreneurs.
An increase in this index increases confidence in national economy and contributes to the growth of the exchange rate.
Business Activity Indices
Extremely popular in last years in economic statistics indicators based on the method of constructing the so-called diffusion indices. Indices of this kind, which by their nature are indicators of the business optimism of business participants, are regularly published (under the names PMI) in the USA, England and Germany, where they are created by the relevant business associations. They are used both to assess the direction of public opinion and to measure the dynamics of objective indicators. . In Japan, a similar TANKAN index was adopted by Central Bank Japan as a tool for analyzing the dynamics of economic processes for making decisions in the field of monetary policy.
Diffusion indices, unlike many other indicators of socio-economic statistics, are purely subjective indicators. They do not measure the volume of output, the number of orders, income, etc., but are only a reflection of how participants in economic processes perceive ongoing changes - for the better. they (in their opinion) or they lead to deterioration. Despite such subjectivity, or rather, precisely because of it, these indices have extremely strong predictive properties, they are leading indicators that are highly correlated with the main parameters of economic cycles.
a) trade negotiations
Trade negotiations are an important part of economic policy any country. In particular, the ratio of imports and exports gives such important indicator economic development like a trade deficit. For the US deficit trade balance has been a major issue over the past few years, playing a significant role in the fall of the US dollar against major currencies. The result of trade negotiations finds an immediate response in the market, sometimes more than significant.
b) meetings of central banks
The main task of central banks is to regulate the internal economic life of the country. In addition, the adjustment of the internal and external value of the currency is also included in his duties. Therefore, any meeting of the central bank (or rather, its working committee) attracts the close attention of foreign exchange market participants. One of the main means of stimulating or, conversely, slowing down economic growth, attracting foreign capital, attractiveness government bonds and, as a result, the value of the currency, is the regulation of interest rates.
The most important are the actions of the US Federal Reserve System, which have a significant impact on the US stock market and to the world financial markets in general, therefore, participants are closely watching changes in interest rates and FOMC (Federal Open Market Committee) operations in the government securities market and statements by Fed representatives, in particular, its head A. Greenspan.
Scheduled Fed meetings are held eight times a year (once every one and a half months) The meeting reviews the economic situation in the country and, based on the analysis, determines further monetary policy countries, policy documents are adopted and the level of the credit interest rate of the sale is determined federal funds(Federal Funds Rate) and the value of the discount interest rate (Discount Rate). The final minutes of the meeting (Minutes of the FOMC) are published a few days later.
c) meetings of the G8, economic and trade unions
One of the tasks of the G8 is to regulate the world economy and, in particular, the specific situation in the world currency market. There is a certain agreement between the members of the G8 on this matter - the SWAP Agreement. The result of the meeting of the G8 countries may be the decision to conduct joint intervention in the world currency market by several central banks or other measures to limit or, conversely, stimulate the growth in the value of a particular currency .
Meetings of trade unions governing trade relations between countries or determining the policy of a particular region, can also have a fairly strong impact on a particular currency. The appeal of the US and Japan to the WTO (the World Trade Organization, established in January 1994), after the unsuccessful end of the next round of trade negotiations, left the yen practically without movement for almost a whole week. of the world economy and distributing loans, do not have a direct impact on currencies, although they may cause a certain response in the market. Most likely, in the present situation, one can count on determining a long-term strategy for the development of the market as a whole, rather than an immediate reaction.
d) speeches by heads of government, heads of central banks, prominent economists on the situation on the market
This is one of the factors that in most cases finds an immediate response in the market Speech by the head of the Swiss National Bank Lumiere on Swiss disinterest in a strong native currency on September 29, 1995 led to a jump Swiss franc from 11400 to 11480 in a few minutes and then to 11580 in the next hour. catastrophic collapse of the yen in less than two days from 104.55 to 9715, nullifying a two-week effort Central Bank Japan and the US Federal Reserve. Quite often, especially under certain conditions, the speech of a person can not only greatly affect the behavior of the currency, but also radically change the situation on the market.
Conclusion
Fundamental factors usually always have the expected impact, however, a trader should be careful not to take any of these factors as a 100% guarantee of a corresponding change in the exchange rate.
Several important additional points affecting the exchange rate.