M.: 2017. - 792 p. M.: 2008. - 383 p.
Written on the basis of domestic and foreign literature. Contains all the main topics of the course, defined in the State Educational Standard, approved by the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation. The textbook differs from previously published books in that it presents in an accessible form the most complex theoretical problems of a market economy, coupled with Russian reality.
The key problems of economic theory are stated according to the principle: "maximum knowledge - minimum time". The emphasis is on revealing the essence and role of economic theories and economic laws in the practice of a market economy.
For students, graduate students studying in economic specialties, teachers, as well as for those who study economic theory in the framework of natural sciences and the humanities.
Format: pdf (20 17, 7 92s.)
The size: 12.6 MB
Download: drive.google ; Rghost
Format: doc (2008 , 383 p.)
The size: 3.4Mb
Download: drive.google ; Rghost
CONTENT
SECTION I. INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMIC THEORY
CHAPTER 1. ECONOMIC THEORY: SUBJECT AND METHODS
1.1. THE SUBJECT OF ECONOMIC THEORY
1.2. FOUNDERS OF ECONOMIC THEORY
1.3. ECONOMIC LAWS
1.4. METHODS OF ECONOMIC THEORY
1.5. LEVELS OF ECONOMIC ANALYSIS: MACRO-, MEDIUM- AND MICROANALYSIS
1.6. ECONOMIC POLICY AND ECONOMIC GOALS
1.7. RUSSIAN ECONOMIC POLICY AT THE BEGINNING OF THE III MILLENNIUM
CHAPTER 2. RESOURCES AND NEEDS? THE BASIS OF ANY ECONOMY
2.1. RESOURCES AND THEIR RARITY
2.2. UNLIMITED NEEDS
2.3. ECONOMIC ACTIVITIES OF PEOPLE: PRODUCTION, DISTRIBUTION, EXCHANGE, CONSUMPTION
2.4. ECONOMY AND EFFICIENCY
2.5. THE NEED TO CHOICE. TABLE AND POSSIBILITY CURVE
2.6. THE LAW OF INCREASING OPPORTUNITY COSTS
CHAPTER 3 THE FREE MARKET ECONOMY: THE LIMITED ROLE OF GOVERNMENT
3.1. FREE MARKET ECONOMY: MAIN FEATURES
3.2. OWN. PRIVATE PROPERTY AS THE BASIS OF A MARKET ECONOMY
3.3. FREEDOM OF BUSINESS AND CHOICE
3.4. PRIORITY OF PERSONAL INTEREST IN DECISION MAKING
3.5. COMPETITION, THE SYSTEM OF MARKETS AND PRICES
3.6. MARKET ECONOMY? OPEN ECONOMY
3.7. NON-INTERVENTION OF THE GOVERNMENT IN THE ECONOMY
CHAPTER 4. THE LAW OF DEMAND
4.1. WHAT IS A MARKET? TYPES OF MARKETS. MARKET INFRASTRUCTURE
4.2. THE CONCEPT OF DEMAND. THE LAW OF DEMAND. DEMAND CURVE
4.3. WHAT DEPENDS ON THE CHANGE OF DEMAND?
4.4. ELASTICITY OF DEMAND AND ITS SIGNIFICANCE FOR CONSUMERS
CHAPTER 5. THE LAW OF SUPPLY
5.1. THE CONCEPT OF THE OFFER. LAW OF SUPPLY. SUPPLY CURVE
5.2. WHAT DEPENDS ON CHANGING THE OFFER?
5.3. ELASTICITY OF SUPPLY AND ITS SIGNIFICANCE FOR MANUFACTURERS
CHAPTER 6. THE LAW OF SUPPLY AND DEMAND
6.1. THE CONCEPT OF THE EQUILIBRIUM QUANTITY OF GOODS AND THE EQUILIBRIUM PRICE
6.2. MECHANISM FOR FORMATION OF MARKET EQUILIBRIUM
6.3. STATE PRICES
CHAPTER 7. THREE FUNDAMENTAL PROBLEMS OF THE MARKET ECONOMY
7.1. INTRODUCTION TO THE PROBLEM
7.2. WHAT TO PRODUCE?
7.3. HOW TO PRODUCE?
7.4. FOR WHOM TO PRODUCE?
7.5. HOW ARE THREE FUNDAMENTAL QUESTIONS DECIDED IN DIFFERENT ECONOMIES?
CHAPTER 8. MONEY IN THE MARKET ECONOMY
8.1. WHAT IS MONEY?
8.2. FUNCTIONS OF MONEY
8.3. MONEY TYPES: COMMODITY, METAL, PAPER, BANKING
8.4. HOW BANK DEPOSITS (MONEY) ARE CREATED
8.5. MONEY SUPPLY IN CIRCULATION AND ITS AGGREGATES. THE CONCEPT OF THE MONETARY SYSTEM
8.6. THE QUANTITY OF PAPER MONEY REQUIRED IN CIRCULATION. MONEY TURNOVER
CHAPTER 9. THE MIXED MARKET ECONOMY: THE REALITIES OF MODERN CAPITALISM
9.1. MIXED ECONOMY: GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS
9.2. THE PRIVATE SECTOR AND ITS ECONOMIC AGENTS
9.3. CIRCULATION OF INCOME, RESOURCES, GOODS AND SERVICES IN THE PRIVATE SECTOR OF A CLOSED ECONOMY
9.4. PUBLIC SECTOR (GOVERNMENT PROCUREMENT AND TRANSFER PAYMENTS)
9.5. CIRCULATION OF INCOME AND EXPENSES IN A MIXED ECONOMY
CHAPTER 10. THE TRANSITION ECONOMY IN RUSSIA
10.1. WHAT IS A TRANSITION ECONOMY?
10.2. THE CONCEPT OF RUSSIA'S TRANSITION TO A MARKET ECONOMY
10.3. "ALPHABET" OF TRANSITION TO MARKET RELATIONS
10.4. PRINCIPLES FOR PROVIDING FINANCIAL AID TO RUSSIA BY THE WEST
10.5. WHAT IS THE SPECIFICITY OF THE TRANSITION TO A MARKET ECONOMY IN RUSSIA?
10.6. RESULTS OF THE TRANSITION ECONOMY IN RUSSIA
10.7. DEVELOPMENT STRATEGY OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION UNTIL 2010
SECTION II. MICROECONOMICS (ECONOMICS OF COMPANIES)
CHAPTER 11. THE THEORY OF CONSUMER BEHAVIOR
11.1. THEORY OF CONSUMER BEHAVIOR
11.2. TWO EXPLANATIONS OF THE LAW OF DEMAND
11.3. UTILITY MAXIMIZATION RULE. MARGINAL UTILITY AND THE DEMAND CURVE
11.4. CONSUMER CHOICE AND BUDGET CONTROL. INDIFFERENCE CURVE
11.5. THE ECONOMIC VALUE OF TIME
CHAPTER 12
12.1. WHAT IS ENTREPRENEURSHIP?
12.2. THE FIRM: ITS INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT
12.3. HOW AND WHY DO FIRMS EXPAND?
12.4. FIRMS AS ASSOCIATIONS OF DIFFERENT TYPES
CHAPTER 13. ORGANIZATIONAL AND LEGAL FORMS OF BUSINESS. JOINT-STOCK COMPANY
13.1. LEGAL FORMS OF BUSINESS: SOLE OWNERSHIP; PARTNERSHIP (PARTNERSHIP); CORPORATION
13.2. JOINT STOCK COMPANY (JSC). SHARES AND BONDS
CHAPTER 14. SMALL BUSINESS
14.1. ESSENCE AND MAIN FEATURES OF SMALL BUSINESS
14.2. DISTINCTIVE FEATURES OF A SMALL FIRM (MF)
14.3. SIGNIFICANCE OF SMALL BUSINESS (MB) IN THE ECONOMY
14.4. STATE SUPPORT FOR SMALL BUSINESS (WORLD PRACTICE)
14.5. SMALL BUSINESS DEVELOPMENT IN RUSSIA
14.6. MEASURES ON STATE SUPPORT OF SMALL BUSINESS IN RUSSIA
CHAPTER 15. THE COMPANY AND PRODUCTION COSTS
15.1. BASIC CONCEPTS: ADVANCED CAPITAL, PRODUCTION COSTS, SHORT AND LONG TERM
15.2. PRODUCTION COSTS IN THE SHORT PERIOD: FIXED, VARIABLES, GENERAL, AVERAGE
15.3. THE LAW OF DIMENSIONING RECOMMENDATIONS
15.4. PRODUCTION COSTS IN THE LONG PERIOD
15.5. WHAT IS THE MOST EFFICIENT ENTERPRISE SIZE?
CHAPTER 16. FIRM AND MARKETING
16.1. WHAT IS "MARKETING"?
16.2. PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING
16.3. MARKETING STRATEGY
16.4. PRICE POLICY AND ITS ROLE IN MARKETING
16.5. SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY AND ETHICS IN BUSINESS
CHAPTER 17. COMPANY AND TRADE (Wholesale and Retail)
17.1. STATEMENT OF A QUESTION
17.2. WHOLESALE
17.3. RETAIL
17.4. ADVERTISING? THE ENGINE OF TRADE IN THE MARKET ECONOMY
17.5. ADVERTISING AND PRICES
CHAPTER 18. FIRM AND MANAGEMENT
18.1. WHAT IS MANAGEMENT? HIS LEVELS
18.2. MANAGEMENT OF THE FIRM: BASIC PRINCIPLES
18.3. CLASSIFICATION OF MANAGEMENT STRUCTURES
18.4. MOTIVATION IN MANAGEMENT
18.5. ENSURING EFFICIENT ACTIVITIES OF THE ORGANIZATION
18.6. PROBLEMS OF RUSSIAN MANAGEMENT
CHAPTER 19. FIRM AND LABOR MARKET. DEMAND AND SUPPLY OF LABOR. WAGE
19.1. LABOR AND WORK FORCE. FEATURES OF WORK FORCE AS A COMMODITY
19.2. THE LAW OF DEMAND AND SUPPLY: THE MECHANISM OF ITS ACTION IN THE LABOR MARKET
19.3. WAGE AND ITS TYPES
19.4. EQUILIBRIUM PRICE OF LABOR (WAGE) AND EQUILIBRIUM LEVEL OF EMPLOYMENT
19.5. THE ECONOMIC EFFECT OF MINIMUM WAGES AND TRADE UNIONS
19.6. INEQUALITY IN THE DISTRIBUTION OF NATIONAL INCOME. LORENTZ CURVE. GINNY COEFFICIENT
19.7. INVESTING IN HUMAN CAPITAL
19.8. RUSSIAN INCOME POLICY AND SOCIAL SUPPORT OF THE POPULATION
CHAPTER 20. THE FIRM AND PROFIT
20.1. PROFIT: ECONOMIC AND NORMAL
20.2. FUNCTIONS AND SOURCES OF PROFIT
20.4. PROFIT GROWTH FACTORS
CHAPTER 21. FIRM AND MONEY CAPITAL MARKET. INTEREST RATE
21.1. THE NATURE OF LOAN CAPITAL
21.2. LOAN (BANK) INTEREST AND ITS RATE
21.3. THE ROLE OF THE INTEREST RATE IN ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT
CHAPTER 22. FIRM AND LAND MARKET. LAND RENT. RENT. LAND PRICE
22.1. LAND RENT: DEFINITION. RENT
22.2. TYPES OF LAND RENT
22.3. LAND PRICE
22.4. ALTERNATIVE LAND USE OPTIONS
CHAPTER 23
23.1. POSING THE QUESTION: MARKET MODELS
23.2. PURE OR PERFECT COMPETITION: CHARACTERISTICS
23.3. HOW DOES A FIRM DETERMINE THE VOLUME OF PRODUCTION THAT MAKES THE MAXIMUM PROFIT OR MINIMUM LOSS IN THE SHORT TERM: TWO APPROACHES
23.4. HOW DOES A COMPANY DETERMINE THE VOLUME OF PRODUCTION BRINGING THE MAXIMUM PROFIT OR THE MINIMUM LOSS IN THE LONG TERM?
23.5. FIRM EFFICIENCY UNDER PURE COMPETITION
CHAPTER 24
24.1. MONOPOLY (IMPERFECT) COMPETITION: CHARACTERISTIC FEATURES
24.2. MONOPOLY AS A FORM OF MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION
24.3. DETERMINATION OF PRICE, VOLUME OF PRODUCTION AND MAXIMIZATION OF PROFIT IN THE SHORT AND LONG TERM
24.4. COSTS OF MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION
24.5. NON-PRICE COMPETITION. ADVERTISING: SUPPORTERS AND CRITICS
CHAPTER 25
25.1. OLIGOPOLY: ESSENCE AND CHARACTERISTICS
25.2. DETERMINATION OF THE PRICE AND VOLUME OF PRODUCTION
25.3. THE ROLE OF NON-PRICE COMPETITION
25.4. EFFICIENCY OF OLIGOPOLY: TWO POINTS OF VIEW
CHAPTER 26
26.1. NATURAL (PURE) MONOPOLY: CHARACTERISTICS
26.2. NATURAL MONOPOLY AND COMPETITION
26.3. DETERMINATION OF PRODUCTION VOLUME, PRICE AND PROFIT MAXIMIZATION
26.4. THE VALUE OF A NATURAL MONOPOLY FROM THE POINT OF VIEW OF SOCIETY
26.5. THE ROLE OF NATURAL MONOPOLY IN A MARKET ECONOMY
26.6. REFORMING NATURAL MONOPOLIES IN RUSSIA
SECTION III. MACROECONOMICS
CHAPTER 27. GROSS NATIONAL PRODUCT
27.1. GROSS NATIONAL PRODUCT (GNP): DEFINITION
27.2. PRODUCTION AND REPRODUCTION OF GNP
27.3. CALCULATION OF GNP: BY PRODUCTION, INCOME AND EXPENDITURE
27.4. MACROECONOMIC INDICATORS DERIVATED FROM GNP
27.5. NOMINAL AND REAL GNP. NATIONAL WEALTH AND ITS DIFFERENCE FROM GNP
CHAPTER 28. Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply. RATCHET EFFECT
28.1. TOTAL VALUES (AGGREGATES) IN ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
28.2. TOTAL DEMAND. AGGREGATE DEMAND CURVE. NON-PRICE FACTORS
28.3. TOTAL OFFER. Aggregate Supply Curve. NON-PRICE FACTORS
28.4. EQUILIBRIUM: REAL OUTPUT AND THE PRICE LEVEL
28.5. RATCHET EFFECT
CHAPTER 29
29.1. WHAT IS THE ECONOMIC CYCLE? CYCLE PHASES
29.2. CAUSES OF ECONOMIC CYCLES
29.3. DURATION OF ECONOMIC CYCLES
CHAPTER 30
30.1. CONSUMPTION, SAVINGS, INVESTMENT: GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS
30.2. KEYNSIAN THEORY OF AGGREGATE DEMAND. MULTIPLIER MODEL
30.3. PRINCIPLE OF ACCELERATION
30.4. MODEL OF MULTIPLIER-ACCELERATOR INTERACTION
30.5. RUSSIAN ECONOMY: WAYS TO EXIT THE CRISIS
CHAPTER 31. INFLATION
31.1. INFLATION: DEFINITION. OPEN AND SUPPRESSED INFLATION
31.2. TYPES OF INFLATION
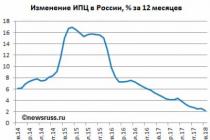
31.3. MEASURING INFLATION
31.4. ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL CONSEQUENCES OF INFLATION. HYPERINFLATION
31.5. ANTI-INFLATION POLICY
31.6. FEATURES OF RUSSIAN INFLATION AND WAYS TO OVERCOME IT
CHAPTER 32. UNEMPLOYMENT. THE PROBLEM OF EMPLOYMENT AND UNEMPLOYMENT IN RUSSIA
32.1. THE CONCEPT OF UNEMPLOYMENT AND THE REASONS FOR ITS APPEARANCE
32.2. MAIN TYPES OF UNEMPLOYMENT
32.3. UNEMPLOYMENT RATE. LEVEL OF GENERAL AND REGISTERED UNEMPLOYMENT IN RUSSIA
32.4. FULL EMPLOYMENT. NATURAL RATE OF UNEMPLOYMENT
32.5. ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL CONSEQUENCES OF UNEMPLOYMENT
32.6. THE PROBLEM OF EMPLOYMENT AND UNEMPLOYMENT IN RUSSIA
32.7. MAIN DIRECTIONS FOR SUPPORTING EMPLOYMENT OF THE POPULATION AND FIGHTING UNEMPLOYMENT IN MODERN RUSSIA
CHAPTER 33. PUBLIC FINANCES
33.1. WHAT IS PUBLIC FINANCE?
33.2. INCOME OF THE STATE. TAXES AND THEIR STRUCTURE: DIRECT AND INDIRECT TAXES. LAFFER CURVE
33.3. DISTRIBUTION OF THE TAX BURDEN
33.4. PUBLIC EXPENDITURES AND THEIR STRUCTURE
33.5. STATE LOANS AS A WAY TO COVER THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN GOVERNMENT EXPENDITURE AND INCOME
33.6. MAIN TASKS OF TAX REFORM IN RUSSIA AT THE BEGINNING OF THE III MILLENNIUM
CHAPTER 34. STATE BUDGET. STATE DEBT
34.1. STATE BUDGET: PROFIT AND DEFICIENCY
34.2. PUBLIC DEBT: DEFINITION AND ISSUES ASSOCIATED WITH IT
34.3. METHODS TO COMBAT THE BUDGET DEFICIT AND GROWTH OF PUBLIC DEBT
34.4. FEATURES OF THE PUBLIC DEBT POLICY IN RUSSIA
34.5. RUSSIA'S BUDGET POLICY
CHAPTER 35. STATE FISCAL POLICY AND ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT
35.1. STATE FISCAL POLICY: DEFINITION AND ITS TYPES
35.2. NEOCLASSICAL SYNTHESIS AS THE BASIS OF THE ECONOMIC POLICY OF THE STATE
35.3. KEYNESIANS AND MONETARISTS: THEIR IMPACT ON ECONOMIC POLICY
35.4. NET EXPORT EFFECT AND FISCAL POLICY ISSUES IN THE WORLD ECONOMY
CHAPTER 36. ECONOMIC GROWTH
36.1. WHAT IS ECONOMIC GROWTH? DEFINITION, MEASUREMENT, VALUE
36.2. FACTORS OF ECONOMIC GROWTH
36.3. FACTORS HOLDING ECONOMIC GROWTH
36.4. MODELS OF ECONOMIC GROWTH
36.5. STATE AND ECONOMIC GROWTH
36.6. SUPPORTERS AND CRITICICS OF THE THEORY OF ECONOMIC GROWTH
36.7. THE POLICY OF ECONOMIC GROWTH IN RUSSIA IN THE XXI CENTURY
CHAPTER 37. INFRASTRUCTURE AND ECONOMIC GROWTH
37.1. INFRASTRUCTURE: DEFINITION AND SPECIFIC FEATURES
37.2. IMPACT OF INFRASTRUCTURE ON ECONOMIC GROWTH
37.3. SYSTEM OF CONTROL OVER THE DEVELOPMENT OF INFRASTRUCTURE
37.4. PRIORITY TASKS IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF INFRASTRUCTURE IN RUSSIA
SECTION IV. WORLD ECONOMY (INTERNATIONAL TRADE AND INTERNATIONAL FINANCE)
CHAPTER 38. INTERNATIONAL ( FOREIGN) TRADE
38.1. INTERNATIONAL ( FOREIGN) TRADE: GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS
38.2. WHAT BRINGS INTERNATIONAL TRADE?
38.3. THE ROLE OF FOREIGN TRADE
38.4. CIRCULATION OF INCOME AND EXPENSES INCLUDING FOREIGN TRADE
CHAPTER 39. THEORIES OF INTERNATIONAL TRADE. THE THEORY OF GLOBALIZATION
39.1. THEORIES OF ABSOLUTE ADVANTAGE AND COMPARATIVE COST OF PRODUCTION
39.2. HECKSHER'S THEORY OF INTERNATIONAL TRADE? OLINA
39.3. "LEONTIEV'S PARADOX"
39.4. ALTERNATIVE THEORIES OF INTERNATIONAL TRADE
39.5. THE THEORY OF GLOBALIZATION
CHAPTER 40 FREE TRADE AND PROTECTIONISM
40.1. THE NATURE OF FREE TRADE
40.2. PROTECTIONISM: ECONOMIC REASONS IN ITS FAVOR
40.3. ECONOMIC REASONS AGAINST PROTECTIONISM
40.4. CUSTOMS UNION
CHAPTER 41. EFFICIENCY OF FOREIGN TRADE
41.1. BENEFITS FROM FOREIGN TRADE AND ITS DISTRIBUTION
41.2. TERMS OF TRADING
41.3. IMPACT OF FOREIGN TRADE ON CHANGES IN THE STRUCTURE OF SUPPLY AND DEMAND
41.4. FOREIGN TRADE MULTIPLIER
41.5. FOREIGN TRADE OF RUSSIA
CHAPTER 42. CURRENCY
42.1. WHAT IS CURRENCY? CURRENCY CONVERTIBILITY. DEVALUATION AND REVALUATION OF THE CURRENCY
42.2. EXCHANGE RATE. NOMINAL AND REAL EXCHANGE RATES
42.3. WORLD MONETARY SYSTEMS
CHAPTER 43. BALANCE OF PAYMENTS AND ITS STRUCTURE
43.1. WHAT IS THE BALANCE OF PAYMENTS?
43.2. BALANCE OF PAYMENT STRUCTURE
43.3. CAUSES OF CHRONIC BALANCE OF PAYMENT DEFICIENCY AND WAYS TO ELIMINATE IT
CHAPTER 44. FOREIGN ECONOMIC POLICY OF RUSSIA IN THE TRANSITION ECONOMY
44.1. LIBERALIZATION OF FOREIGN TRADE
44.2. NEW ROLE OF THE STATE IN FOREIGN TRADE
44.3. FOREIGN TRADE POLICY DEVELOPMENT STRATEGY
44.4. FOREIGN INVESTMENT IN RUSSIA
44.5. CREATING A FAVORABLE INVESTMENT CLIMATE IN THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION IN THE XXI CENTURY
44.6. CURRENCY MARKET OF RUSSIA
44.7. FOREIGN ECONOMIC POLICY OF RUSSIA AT THE BEGINNING OF THE III MILLENNIUM
SECTION V. ECONOMY AND SOCIAL POLICY IN RUSSIA UNTIL 2010
CHAPTER 45
45.1. SOCIO-ECONOMIC IMAGE OF RUSSIA IN THE LAST DECADE OF THE XX CENTURY
45.2. WAYS TO RECOVER THE DESTROYED RUSSIAN ECONOMY AND THE SOCIAL ENVIRONMENT OF RUSSIANS
45.3. DOMINANTS OF THE RUSSIAN CIVILIZATION IN THE BEGINNING OF THE III MILLENNIUM
CHAPTER 46
46.1. WHAT IS SOCIAL POLICY?
46.2. THE SOCIAL SITUATION IN THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION AT THE TURN OF THE XXI CENTURY AND ITS MAIN GOALS
46.3. FORMATION OF SOCIAL PARTNERSHIP POLICY AND MECHANISMS OF ITS DEVELOPMENT IN RUSSIA
46.4. THE NON-PROFIT SECTOR AND ITS CONTRIBUTION TO SOCIAL ISSUES
CHAPTER 47. INCOME POLICY AND THE SYSTEM OF SOCIAL PROTECTION IN RUSSIA
47.1. DYNAMICS OF LIVING STANDARDS AND PRINCIPLES OF INCOME DISTRIBUTION
47.2. FEATURES OF THE FORMATION OF NOMINAL AND REAL INCOMES OF THE POPULATION IN THE PERIOD OF TRANSITION TO A MARKET ECONOMY
47.3. MAIN TRENDS IN THE DYNAMICS OF REAL INCOME OF THE POPULATION DURING THE ECONOMIC REFORM
47.4. WAGE: DISADVANTAGES AND PROBLEMS OF ITS REGULATION
47.5. PRINCIPLES OF FORMING THE POLICY OF INCOME OF THE POPULATION
CHAPTER 48
48.1. SOCIAL PROTECTION OF THE POPULATION: ESSENCE, PRINCIPLES, DIRECTIONS
48.2. FORMS AND METHODS OF SOCIAL PROTECTION
48.3. WAYS OF DEVELOPMENT OF THE SYSTEM OF SOCIAL PROTECTION OF THE POPULATION
48.4. REFORMING THE SOCIAL INSURANCE SYSTEM
48.5. THREE OPTIONS FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE SYSTEM OF SOCIAL PROTECTION OF THE POPULATION FOR THE COMING DECADE
48.6. PROSPECTS, GOALS AND OBJECTIVES OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE SYSTEM OF SOCIAL PROTECTION OF THE POPULATION IN RUSSIA
CHAPTER 49
49.1. FOUNDERS OF ECONOMIC THEORY: FROM MERCANTILISM TO MARGINALISM
49.2. CLASSICAL POLITICAL ECONOMY
49.3. THE TEACHING OF ADAM SMITH
49.4. THE TEACHING OF DAVID RICARDO
49.5. ECONOMIC ROMANTISM
49.6. ECONOMIC THOUGHT OF THE 20-30-X. 19th century
49.7. ECONOMIC DOCTRINE OF K. MARX AND F. ENGELS
49.8. ECONOMIC THOUGHT OF THE SECOND HALF OF THE XIX CENTURY
ECONOMY
(BASICS OF ECONOMIC THEORY)
for execution abstract
for students of non-economic specialties
all forms of education
Sevastopol 2016
FORMING THE SUMMARY
Bibliographic list
1. TOPICS OF SUMMARY ON ECONOMIC THEORY 2016/17/ac. year
Economic theory as a universal economic science.
System economic categories and laws.
Economic needs and their relationship with production.
Socio-economic content of production factors.
Productive forces and production potential of society.
Social and economic efficiency production.
Essence, types and structure of industrial relations.
Economic systems and their evolution.
Ownership in the system of production relations.
Economic interests and needs.
Natural and commodity production.
money and money turnover.
Socio-economic content of production costs.
The market in the system of social reproduction.
Market demand and supply.
Competition, its place and role in economic progress.
The structure of the market and the functioning of its main elements.
18. Market infrastructure.
Banks and their role in the economic system.
The enterprise as a primary structural link social production.
Production assets (capital) of the enterprise.
Essence, types and organizational forms entrepreneurship
Essence, forms, types and systems wages.
Profit as a result of the enterprise.
Loan capital in the system of commodity relations.
agricultural relations.
Land rent.
State in a market economy.
The economic growth.
World economy.
FORMING THE SUMMARY
The topic of the abstract is selected in accordance with the number of the student in the list of the student group.
The work is carried out in accordance with the requirements of current regulations. All aspects of the design of text documents are contained in the following documents:
GOST 7.32-2001 “Research report. Structure and rules of registration.
GOST 2.105-95 " General requirements to text documents
GOST 7.1-2003 “Bibliographic record. Bibliographic description. General requirements and rules for drawing up "
GOST 7.80-2000. "Bibliographic record. Title. General requirements and rules for drafting”, etc.
GOST 7.82-2001 “Bibliographic record. Bibliographic description of electronic resources. General requirements and rules for drafting.
Basic design requirements:
1) Text is printed at 1.5 intervals, based on no more than 40 lines per page, Times New Roman font, font size - 12, without slanting and underlining, highlighting in bold or color, one and a half leading).
2) The text is printed in black, the same throughout the work. Text alignment.
3) Margin sizes: left - 30 mm, right - at least 10 mm, top - at least 15 mm, bottom - at least 20 mm.
4) All pages of the work must be numbered. The page number is placed in the upper right corner without a dot.
5) Paragraph indent should be the same throughout the text and be equal to 15-17 mm.
6) References are necessary when citing and borrowing provisions, formulas, tables, illustrations from the works of other authors. References are made in the form "", where the first digit is the source number, the second page is where the material was taken from.
7) The table should be located directly after the text in which it is mentioned for the first time, or on the next page. Above the upper left corner of the table, the inscription "Table" is placed indicating its number (numbering through, or within the section (for example, Table 1.2).
8) Figures should be placed immediately after the text in which they are mentioned for the first time, or on the next page. Figures should have a title that is placed below it in the center. The drawing is designated by the word "Drawing", which, together with the number and title, is placed after the explanatory data.
9) The headings of the structural elements of the work are placed in the middle of the line without a dot at the end and are printed in capital letters without underlining. Each structural element should start on a new page. Headings of paragraphs, paragraphs and subparagraphs should be printed with a paragraph indent from a capital letter without a dot at the end.
10) Formulas and equations should be separated from the text in separate line. Above and below each formula or equation must be left on a blank line. Numbering of formulas through, or within the section.
11) The list of sources used should contain information about all the sources used in writing control work. The grouping of material used in the list of sources used can be:
- alphabetical;
- chronological;
– in the order of mentioning or citing sources in the main text.
However, it is recommended to place legislative and regulatory documents in the first place in terms of importance.
Examples of bibliographic description various sources :
…Laws:
About insolvency (bankruptcy): the federal law dated October 26, 2002 (as amended on February 5, 2007) // Russian newspaper. - 2007. - February 9
…Resolution:
Decree: On Approval State Program"Ensuring the safety of victims, witnesses and other participants in criminal proceedings for 2006-2008" : Government Decree Russian Federation dated April 10, 2006 No. 200 // Collection of Legislation of the Russian Federation. - 2006. - No. 16. - St. 1739.
...books under the heading:
Books by four or more authors, collections: Introduction to literary criticism. Literary work: basic concepts and terms: textbook. allowance / L.V. Chernets, V.E. Khalizev, S.N. Broitman [and others]; ed. L.V. Chernets. - M .: Higher. school; Publishing Center "Academy", 2000. - 556 p.
...books titled:
Pharmaceutical chemistry: textbook. allowance for students. universities / L.N. Protasova, M.I. Ivanov, A.A. Sidorov; sub-ed. I.N. Sovenko. – M.: Rior, 2014. – 323 p.
... Chapters or sections from books:
Kuzmin O. Methods of management investment portfolio/ O. Kuzmin, S. Prince // Economic encyclopedia / editorial board: Gavrylyshyn B. D. [ta іn.]. - K., 2001. - T. 2. - S. 349.
... Articles from collections:
Grinyuk K. A. Indirect marketing technologies for promoting the total tourist product of Sevastopol / K. A. Grinyuk, A. A. Piskun, N. S. Sarieva // Vestn. SevGTU / Sevastop. state tech. un-t. - Sevastopol, 2004. - Issue. 53: Economics and finance. - S. 76-88.
...Newspaper articles:
Kushner, A. "Harmony is a mysterious power ...": On the 200th anniversary of the birth of Yevgeny Boratynsky / A. Kushner // Mosk. news. - 2000. - No. 15. - P. 5
... Articles from magazines:
Brusnitsyn, L. Ensuring the safety of participants in the process: opportunities and prospects for development / L. Brusnitsyn // Russian justice. - 2003. - No. 5. - S. 12-15.
… Electronic resources of remote access:
Overview of the grocery retail market [ Electronic resource]/MDNgroup. – Electron. Dan. – Kyiv: [b. i.], 2009. – Access mode: http://www.mdn-group.com/news/articles/180.
Akchurina A. M. Application of economic and mathematical methods in the management of the use of capital of enterprises of the petrochemical and chemical industry / A. M. Akchurina // Oil and gas business [Electronic resource] / Ufim. state oil tech. un-t. – Electron. magazine – [Ufa], cop. 2001-2008. – Access mode: http://www.ogbus.ru/authors/Akchurina/Akchurina_1.pdf. - Zagl. from the screen.
3. Examination questions in economic theory 2016 - 2017 academic year
1. The emergence and main stages in the development of political economy
2. Subject and functions of political economy
3. Classification of economic sciences. The place of political economy in the system of economic sciences
5. Methods of research in political economy
6. Main factors of social production
7.Production efficiency
8. Essence, classification and relationship with production economic needs
9. The Law of Elevation of Needs
10. Essence, functions and classification economic interests
11. Essence and structure of the economic system
12. Types and models of economic systems
13. The productive forces of society and production relations
14. Structure and types of economic (production) relations
15. Property as an economic and legal category
16. Types, types and forms of ownership
17. Forms of ownership in countries with market economy and the main trends in the change in property relations in present stage
18. Privatization: essence, necessity, principles
19.Objects, goals and methods of privatization
20. Essence, stages of development and main features of natural economy
21. Essence, causes and types of commodity production
22. Essence and properties of goods
23. Theories of value, cost and price.
24. Essence and functions of the law of value in commodity production
25. Theories of origin, essence and functions of money
26.Money circulation and its laws, definition money supply
27. Essence and types monetary system
28. Essence, causes, types and consequences of inflation
29. Essence, concepts and patterns transition economy
30.Theory and practice of the planned economy.
31. Essence and types of income. Nominal and real incomes.
32. Income distribution: Marxist and marginalist concepts
33. Theories, types, forms and systems of wages
34. Essence, functions of the objective basis of the market
35 Positive and negative features of the market
36. Signs of classification of markets and their types
37. Demand: essence, types and factors. Law of demand
38. Suggestion: essence, types and factors. Law of supply
39. Elasticity of supply and demand
40. Essence, functions and forms of competition
41. Reasons for the emergence, essence and main forms of monopoly
42. Antimonopoly policy of the state
43. The concept, functions, types and elements of the market infrastructure
44. Households as subjects of economic relations: main features and functions
45. Essence, main features and classification of enterprises
47.Capital of the enterprise, its circulation and turnover. Fixed and working capital
48. Depreciation of fixed capital, depreciation
49. Essence, conditions, types and functions of entrepreneurship
50. Essence and types of production costs
51. Essence, types and distribution of profit. The rate of return and its factors.
52. Agrarian relations and features of agricultural production, agro-industrial complex and its structure
53. Essence, types, causes and conditions for the emergence of land rent
54. Features of entrepreneurship in the agricultural sector
55. Market and price of land
56. Necessity and content state regulation economy, economic functions of the state
57.Economic theories of the role of the state in the economy
58.Methods and tools of state regulation of the economy
59. Essence and main directions economic policy
60. Essence, content and types of social reproduction
61. Theoretical models of social reproduction
62.Basic macroeconomic indicators
63. National wealth and its structure
65.Cyclic development and business cycle
66. Concepts and models of economic growth
67. Financial system of society
68. credit system societies
69. Objective basis and essence of the world economy
70.Structure of the world economy
71. International economic relations and their forms
72. World market of goods and services
74. Essence, causes and types of international labor migration
75. Essence, causes and levels of economic globalization
76. Essence, causes and classification global problems
78. Results of the socio-economic development of Russia in 2015.
Bibliographic list
1. Nosova S.S. Economic theory. - M.: KNORUS, 2016. - 336 p.
2. Sokolinsky and others. Economic theory. - M.: KNORUS, 2016. - 404 p.
3. Mamaeva L.N. Economic theory: textbook \ LN Mamaeva. – Rostov-on-Don; Phoenix, 2015. - 365.
4. Economics: a textbook for universities \ I.A. Maksimtsev, L.P. Kurakov, L.S. Tarasevich and others; under total ed. L.P. Kurakova. – M.: Publishing House of IAEP, 2015. – 512p.
5. Grodsky V.S. Economic theory: Tutorial. third generation standard. - St. Petersburg: Peter, 2015. - 208s.
6. Bordovsky V.P., Rudakova O.V., Samorodova E.M. Economic theory. - M .: Publishing House "Forum", INFRA, 2014. - 400 p.
7. Nikolaeva I.P. Economic theory: Textbook \ I.P. Nikolaeva. - M .: Publishing and Trade Corporation "Dashkov and K", 2013. - 328p.
8. Kurakov L.P. Economics: A textbook for universities \ L.P. Kurakov, G.E Yakovlev,
A.G. Kostromin, A.L. Kurakov. - M.: UniWesMedia, 2011. - 640s.
9. Big economic encyclopedic dictionary \ ed. comp.: I.A. Maksimtseva, L.P. Kurakov, L.S. Tarasevich and others. Ed. Kurakova L.P. - M.: UniVestMedia, 2011. - 1200s.
10. Anikin, A. V. Youth of science: life and ideas of thinkers-economists before Marx / A. V. Anikin. - 4th ed. - M.: Politizdat, 1985. - 366 p.
11. Balikov V.V. General economic theory: Textbook. – M.: Omega-L, 2007. – 732p.
12. Borodin E.T. Natural and social reproduction: Comprehension of Marxism and overcoming its contradictions / E.T. Borodin. - M.: Cognitive book Press, 2003. - 448 p.
13. Brevnov A.A. Fundamentals of economic theory: textbook. allowance for students. universities / A.A. Brevnov. - Kharkov: Odysseus, 2004. - 512 p.
14. Butuk A.I. Economic theory: Textbook / A.I. Butuk. - 2nd ed., revised. and additional .- K .: Vikar, 2003.- 668 p.
15. Gukasyan G.M. Economic theory: an introduction to economic theory, microeconomics, macroeconomics: study guide / G.M. Gukasyan, G.A. Makhovikova, V.V. Amosov. - 6th ed. - M. and others: Peter, 2008. - 240 p.
16. Kuzminov Ya.I. Well institutional economics: institutions, networks, transaction costs, contracts: textbook. for stud. universities / Ya. I. Kuzminov, K. A. Bendukidze, M. M. Yudkevich. - M.: GU VSHE, 2006. - 443 p.
17. The course of economics: textbook / Ed. B. A. Raizberg. - 4th ed., revised. and additional - M.: INFRA - M, 2003. - 672 p.
18. Course of economic theory: Textbook / Ed. Chepurina M.N., Kiseleva E.A. – 5th ed., corrected, supplemented, revised. - Kirov "Asa", 2005. - 832p.
19. Lortikyan, E. L. History economic reforms: world experience of the second half of the XIX-XX centuries: textbook. allowance for econom. universities and faculty. / E. L. Lortikyan. - Kharkov: Konsum, 1999. - 286 p.
20. Marshall A. Principles economics: in 3 volumes: per. from English / A. Marshall. - M.: Progress: Univers, T. 1. - 1993. - 415 p.
21. Simkina L.G. Economic theory: study guide / LG Simkina. - 2nd ed. - M. and others: Peter, 2008. - 384 p.
22. Modern economy: lecture course: multilevel textbook. allowance for students. universities / Ed. O.Yu. Mamedov. - Rostov n / a: Phoenix, 2000. - 544 p.
23. Sychev N.V. Political economy: a course of lectures / N.V. Sychev. - M.: EKMOS, 2002. - 383 p.
24. Timoshina, T. M. Economic history foreign countries: studies. allowance / T. M. Timoshina; Ed. M. N. Chepurina. - M.: Yustitsinform, 2000. - 496 p.
25. Tumakova, SV Fundamentals of economic theory. Political economy: textbook. allowance for universities / SV Tumakova. - K.: Vipol, 1999. - 597 p.
26. Filinkov A.M. Political economy / A.M. Filinkov.-Sevastopol.: SevNTU, 2006.- 149 p.
27. Economics: textbook. allowance / ed. E.A. Kuznetsov. - Ed. 4th, sr. - Kharkov: Odysseus, 2008. - 512 p.
28. Economic history of foreign countries: textbook. allowance for students. universities, education by economy special / Ed. V. I. Golubovich. - Minsk: Interpressservis: Ekoperspektiva, 2003. - 592 p.
29. Economic theory (political economy): textbook. for stud. universities, education by economy special / Ed. V.I. Vidyapin, G.P. Zhuravleva. - M.: INFRA - M, 1999. - 556 p.
30. Erhard, L. Welfare for all: per. from German / L. Erhard. - Donetsk: Nord - Press, 2002. - 319 p.
Sample design title page
Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation
FGBOU VO "Sevastopol State University»
Department of Enterprise Economics
abstract
discipline Economic theory
Option number 2
Completed by: student of the AKT-31z group
Ivanov E.V. __________________
Checked by: Ph.D., Associate Professor
Filinkov A.M. ___________________
"_____" _________________ 20__
Sevastopol 2016
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Economic theory: Textbook / Ed. Sokolinsky V.M.. - M.: KnoRus, 2015. - 352 p.
2. Economic theory: Textbook / Ed. I.P. Nikolaeva. - M.: Unity, 2015. - 495 p.
3. Economic theory: Textbook / Ed. Nikolaeva I.P. - M.: Unity, 2018. - 288 p.
4. Economic theory. Conceptual foundations and practice: Scientific publication. / Ed. V.F. Maksimova. - M.: Unity, 2015. - 751 p.
5. Institutional economic theory and its applications / Ed. O.S. Sukharev. - M.: Lenand, 2017. - 200 p.
6. Balashov, A.I. Economic theory. Textbook / A.I. Balashov and others - M.: Unity, 2015. - 192 p.
7. Balashov, A.I. Economic theory: Textbook / A.I. Balashov and others - M.: Unity, 2017. - 224 p.
8. Balashov, A.I. Economic theory: Textbook. / A.I. Balashov and others - M.: Unity, 2015. - 527 p.
9. Bardovsky, V.P. Economic theory: Textbook / V.P. Bardovsky, O.V. Rudakova, E.M. Samorodova. - M.: Forum, 2015. - 542 p.
10. Basovsky, L.E. Economic theory: Textbook / L.E. Basovsky, E.N. Basovskaya and others - M.: Infra-M, 2017. - 192 p.
11. Burganov, R.A. Economic theory: Textbook / R.A. Burganov. - M.: Infra-M, 2018. - 320 p.
12. Voitov, A.G. Economic theory: Textbook / A.G. Voitov. - M.: Dashkov i K, 2015. - 392 p.
13. Voitov, A.G. Economic theory: Textbook for bachelors / A.G. Voitov. - M.: Dashkov i K, 2015. - 392 p.
14. Gukasyan, G.M. Economic theory: key issues: Textbook / G.M. Ghukasyan. - M.: Infra-M, 2015. - 208 p.
15. Huseynov, R.M. Economic theory: textbook. / R.M. Huseynov, V.A. Semenikhin. - M.: Omega-L, 2018. - 157 p.
16. Danilenko, L.N. Economic theory: a course of lectures on micro- and macroeconomics: Textbook / L.N. Danilenko. - M.: Infra-M, 2018. - 592 p.
17. Zhuravleva, G.P. Economic theory. Microeconomics - 1, 2. Mesoeconomics: Textbook / G.P. Zhuravlev. - M.: Dashkov i K, 2016. - 934 p.
18. Zhuravleva, G.P. Economic theory. Macroeconomics -1, 2. Metaeconomics. Economics of transformations: Textbook / G.P. Zhuravlev. - M.: Dashkov i K, 2016. - 920 p.
19. Zhuravleva, G.P. Economic theory. Microeconomics: Uch. / G.P. Zhuravleva, N.A. Pozdnyakov, Yu.A. Pozdnyakov. - M.: Infra-M, 2019. - 160 p.
20. Kaznachevskaya, G.B. Economic theory: Textbook / G.B. Kaznacheva. - Rn / D: Phoenix, 2018. - 320 p.
21. Kaznachevskaya, G.B. Economic theory: Textbook / G.B. Kaznacheva. - Rn / D: Phoenix, 2018. - 252 p.
22. Kamaev, V.D. Economic theory. short course/ V.D. Kamaev, M.Z. Ilchikov, T.A. Borisovskaya. - M.: KnoRus, 2016. - 16 p.
23. Karpovich, O.G. Economic crime in Russia. Theory and practice of counteraction: Monograph. / O.G. Karpovich. - M.: Unity, 2015. - 199 p.
24. Karpovich, O.G. Economic crime in Russia. Theory and practice of counteraction: Monograph / O.G. Karpovich. - M.: Unity, 2017. - 352 p.
25. Korogodin, I.T. Economic theory of labor: Textbook "Higher education" / I.T. Korogodin. - M.: Economics, 2015. - 239 p.
26. Kochetkov, A.A. Economic theory: Textbook for bachelors / A.A. Kochetkov. - M.: Dashkov i K, 2016. - 696 p.
27. Larionov I.K. Economic theory: Textbook for bachelors / I.K. Larionov. - M.: Dashkov i K, 2015. - 408 p.
28. Larionov I.K. Economic theory. Economic systems: formation and development: Textbook / I.K. Larionov, S.N. Silvestrov. - M.: Dashkov i K, 2015. - 876 p.
29. Larionov I.K. Economic theory. Economic systems: formation and development: Textbook for masters / I.K. Larionov, S.N. Silvestrov. - M.: Dashkov i K, 2015. - 876 p.
30. Mamaeva, L.N. Economic theory: textbook / L.N. Mamaev. - R&D: Phoenix, 2015. - 365 p.
31. Mamaeva, L.N. Economic theory: Textbook / L.N. Mamaev. - Rn / D: Phoenix, 2017. - 352 p.
32. Makhovikova, G.A. Economic theory: Textbook and workshop / G.A. Makhovikov. - Lyubertsy: Yurayt, 2015. - 573 p.
33. Makhovikova, G.A. Economic theory: Textbook and workshop for academic bachelor's degree / G.A. Makhovikova, G.M. Gukasyan, V.V. Amosov. - Lyubertsy: Yurayt, 2016. - 443 p.
34. Nikolaeva, I.P. Economic theory: Textbook for bachelors / I.P. Nikolaev. - M.: Dashkov i K, 2015. - 328 p.
35. Nosova, S.S. Economic theory. elementary course / S.S. Nosov. - M.: KnoRus, 2015. - 352 p.
36. Nosova, S.S. Economic theory. Distance learning. Textbook / S.S. Nosov. - M.: KnoRus, 2019. - 350 p.
37. Nosova, S.S. Economic theory. teaching aid / S.S. Nosov. - M.: Rusajns, 2018. - 176 p.
38. Nosova, S.S. Economic theory (for bachelors) / S.S. Nosov. - M.: KnoRus, 2019. - 350 p.
39. Okeanova, Z.K. Economic theory: Textbook / Z.K. Oceanova. - M.: Dashkov i K, 2015. - 652 p.
40. Okeanova, Z.K. Economic theory: Textbook / Z.K. Oceanova. - M.: Dashkov i K, 2015. - 650 p.
41. Pyastolov, S.M. Economic theory / S.M. Pyastolov. - M.: Academia, 2018. - 126 p.
42. Pyastolov, S.M. Economic theory. Workshop: Textbook / S.M. Pyastolov. - M.: Academia, 2017. - 448 p.
43. Pyastolov, S.M. Economic theory: Workshop: Textbook / S.M. Pyastolov. - M.: Academia, 2015. - 104 p.
44. Pyastolov, S.M. Economic theory: Textbook / S.M. Pyastolov. - M.: Academia, 2017. - 206 p.
45. Pyastolov, S.M. Economic theory: Textbook / S.M. Pyastolov. - M.: Academia, 2016. - 232 p.
46. Romanova, E.V. Economic theory. Course of lectures / E.V. Romanova. - M.: Ripol-classic, 2017. - 160 p.
47. Rudnev, V.D. Political economy (economic theory): Textbook / V.D. Rudnev. - M.: Dashkov i K, 2016. - 856 p.
48. Rudneva, A.O. Economic theory: Textbook / A.O. Rudnev. - M.: Infra-M, 2018. - 512 p.
49. Rudneva, A.O. Economic theory: Textbook / A.O. Rudnev. - M.: Infra-M, 2016. - 544 p.
50. Sazhina, M.A. Economic theory: Textbook / M.A. Sazhina, G.G. Chibrikov. - M.: Forum, 2016. - 288 p.
51. Salikhov, B.V. Economic theory: Textbook / B.V. Salikhov. - M.: Dashkov i K, 2016. - 724 p.
52. Slagoda, V.G. Economic theory: Textbook / V.G. Slagoda. - M.: Forum, 2016. - 320 p.
53. Slagoda, V.G. Economic theory: Slave. tetra. / V.G. Slagoda. - M.: Forum, 2016. - 320 p.
54. Sokolinsky, V.M. Economic theory (for colleges) / V.M. Sokolinsky. - M.: KnoRus, 2018. - 335 p.
55. Stankovskaya, I.K. Economic theory: Textbook / I.K. Stankovskaya. - Rn / D: Phoenix, 2016. - 528 p.
56. Stolyarov, V.I. Economic theory. / IN AND. Stolyarov. - M.: Academia, 2016. - 24 p.
57. Sukharev, O.S. Evolutionary economic theory of institutions and technologies (problems of modeling): Institutions and technologies. Economic changes. Institutional Modeling / O.S. Sukharev. - M.: Lenand, 2017. - 144 p.
58. Sukharev, O.S. Economic theory of the evolution of institutions and technologies (problems of modeling in evolutionary theory and management): Institutions and technologies. Institutional modeling, structural models. Technological development, investment in changing the structure of technology / O.S. Sukharev. - M.: Lenand, 2019. - 312 p.
59. Talnishnikh, T.G. Economic theory: Textbook / T.G. Talnishhnikh. - M.: Infra-M, 2015. - 448 p.
60. Khudokormov, A.G. Economic theory in history. development.: Monograph / A.G. Khudokormov, A. Lapidyus. - M.: Infra-M, 2018. - 190 p.
61. Chernetsova, N.S. Economic theory / N.S. Chernetsova, V.A. Skvortsova, I.E. Medushevsky. - M.: KnoRus, 2016. - 251 p.
62. Shuvalova, O.V. Economic theory. part 1 / O.V. Shuvalov. - M.: Rusajns, 2015. - 259 p.
63. Yanbarisov, R.G. Economic theory: Textbook / R.G. Yanbarisov. - M.: Forum, 2017. - 16 p.
The structure of the textbook contains sections that reveal the evolution economic thought, microeconomics, macroeconomics and theoretical basis foreign trade. The main stages of the development of economic theory are considered, the basic concepts of economic theory are outlined, the theory consumer behavior, the concept of the firm, its interpretation in various economic theories. A feature of the textbook is the inclusion of sections on the knowledge economy, the market of information and knowledge. For effective assimilation of the material, after each topic, key concepts and tasks for intermediate control are given: problem situations, questions and tasks.
Step 1. Choose books in the catalog and click the "Buy" button;
Step 2. Go to the "Basket" section;
Step 3. Specify the required quantity, fill in the data in the Recipient and Delivery blocks;
Step 4. Click the "Proceed to payment" button.
On the this moment It is possible to purchase printed books, electronic accesses or books as a gift to the library on the EBS website only with 100% advance payment. After payment, you will be given access to the full text of the textbook within the Digital Library or we will start preparing an order for you at the printing house.
Attention! Please do not change the payment method for orders. If you have already chosen a payment method and failed to complete the payment, you need to re-register the order and pay for it in another convenient way.
You can pay for your order using one of the following methods:
- Cashless method:
- bank card: All form fields must be completed. Some banks ask you to confirm the payment - for this, an SMS code will be sent to your phone number.
- Online banking: banks cooperating with the payment service will offer their own form to fill out. Please enter the correct data in all fields.
For example, for " class="text-primary">Sberbank Online number required mobile phone and email. For " class="text-primary">Alpha Bank you will need a login in the Alfa-Click service and email. - Online wallet: if you have a Yandex wallet or Qiwi Wallet, you can pay for the order through them. To do this, select the appropriate payment method and fill in the proposed fields, then the system will redirect you to the page to confirm the invoice.